Detect network connectivity
Mobile devices use Wi-Fi and cellular technologies to connect to the internet. This dependency means that your users could lose their internet connection while using your application. If you don't add code to protect against this possibility, your app could stop responding and provide your users with a bad experience.
In this unit, you protect your application by detecting when your users lose their internet connection. This information becomes important when we begin to consume REST web services.
Why detect network connectivity on mobile applications?
Detecting if you have an Internet connection on a mobile application is important. Mobile devices can frequently lose their connection due to poor coverage by a network service provider. Or if you're in an environment with limited or no reception, such as a tunnel, deep valley, or high mountain. There are also different types of network connectivity. If you're located in an environment that provides WiFi connectivity, you typically have higher bandwidth than if you're dependent on cellular access. You might still be able to connect to the Internet, but some operations, such as streaming video content, might be slower (and expensive) over a cellular link compared to a WiFi connection.
Because mobile devices have these challenges, you must write code to protect against them. If you don't, and your application attempts to perform operations that use the internet, your application might stop responding.
You also want to provide a good user experience when your application can't connect to the Internet. If your application stops working because there's no Internet service, your users might be left confused. The best thing to do is to provide information to your users. Tell them that you don't have an Internet connection and that your application might not perform fully without it. The following image shows an example:
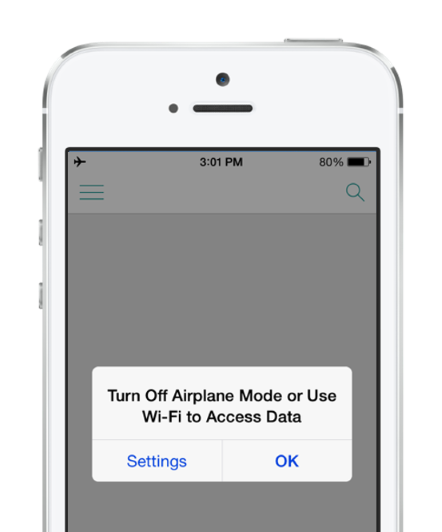
In this example, the application developer informs the user that they don't have an internet connection and they should attempt to connect to Wi-Fi.
Detect network connectivity
To check for network connectivity in a .NET Multi-platform App UI (MAUI) app, use the Connectivity class. This class exposes a property called NetworkAccess and an event named ConnectivityChanged. You can use these members to detect changes in the network.
You access the NetworkAccess property through another property called Current. The Connectivity class uses the Current property to access the platform-specific implementation.
The NetworkAccess property returns a value from the NetworkAccess enumeration. The enumeration has five values: ConstrainedInternet, Internet, Local, None, and Unknown. If the NetworkAccess property returns a value of NetworkAccess.None, then you know you don't have a connection to the Internet, and you shouldn't run networking code. This mechanism is portable across platforms. The following code shows an example:
if (Connectivity.Current.NetworkAccess == NetworkAccess.None)
{
...
}
The ConnectivityChanged event also allows you to determine if the device is connected to the Internet. The ConnectivityChanged event is triggered automatically when the network status changes. For example, if you start with an active network connection and eventually lose it, the ConnectivityChanged event is raised to inform you about the change. One of the parameters passed to the ConnectivityChanged event handler is a ConnectivityChangedEventArgs object. This object contains a property called IsConnected. You can use the IsConnected property to determine if you're connected to the internet. Here's an example:
Connectivity.Current.ConnectivityChanged += Connectivity_ConnectivityChanged;
...
void Connectivity_ConnectivityChanged(object sender, ConnectivityChangedEventArgs e)
{
bool stillConnected = e.IsConnected;
}
The ConnectivityChanged event allows you to write apps that can detect a change in network status and seamlessly adjust the functionality available according to the different environments.