Determine Azure Storage encryption
Azure Storage encryption for data at rest protects your data by ensuring your organizational security and compliance commitments are met. The encryption and decryption processes happen automatically. Because your data is secured by default, you don't need to modify your code or applications.
When you create a storage account, Azure generates two 512-bit storage account access keys for that account. These keys can be used to authorize access to data in your storage account via Shared Key authorization, or via SAS tokens that are signed with the shared key.
Microsoft recommends that you use Azure Key Vault to manage your access keys, and that you regularly rotate and regenerate your keys. Using Azure Key Vault makes it easy to rotate your keys without interruption to your applications. You can also manually rotate your keys.
Things to know about Azure Storage encryption
Examine the following characteristics of Azure Storage encryption.
Data is automatically encrypted before written to Azure storage.
Data is automatically decrypted when retrieved.
Azure Storage encryption, encryption at rest, decryption, and key management are transparent to users.
All data written to Azure Storage is encrypted through 256-bit advanced encryption standard (AES) encryption. AES is one of the strongest block ciphers available.
Azure Storage encryption is enabled for all new and existing storage accounts and can't be disabled.
Configure Azure Storage encryption
In the Azure portal, you configure Azure Storage encryption by specifying the encryption type. You can manage the keys yourself, or you can have the keys managed by Microsoft. Consider how you might implement Azure Storage encryption for your storage security.
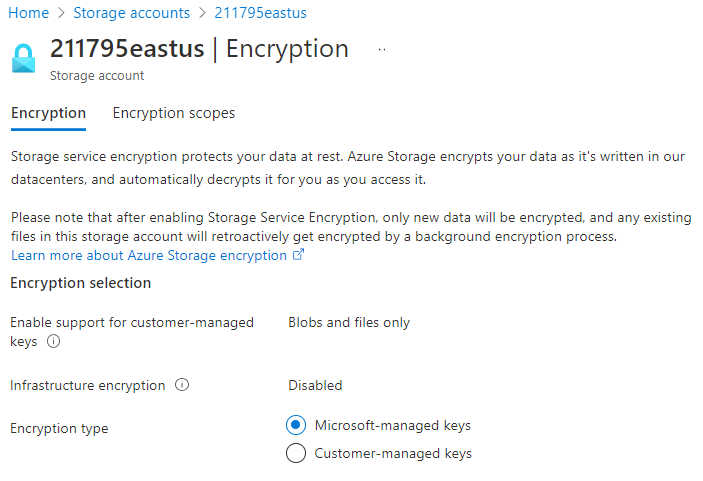
Infrastructure encryption. Infrastructure encryption can be enabled for the entire storage account, or for an encryption scope within an account. When infrastructure encryption is enabled for a storage account or an encryption scope, data is encrypted twice—once at the service level and once at the infrastructure level—with two different encryption algorithms and two different keys.
Platform-managed keys. Platform-managed keys (PMKs) are encryption keys generated, stored, and managed entirely by Azure. Customers don't interact with PMKs. The keys used for Azure Data Encryption-at-Rest, for instance, are PMKs by default.
Customer-managed keys. Customer managed keys (CMK), on the other hand, are keys read, created, deleted, updated, and/or administered by one or more customers. Keys stored in a customer-owned key vault or hardware security module (HSM) are CMKs. Bring Your Own Key (BYOK) is a CMK scenario in which a customer imports (brings) keys from an outside storage location.