Create shared access signatures
A shared access signature (SAS) is a uniform resource identifier (URI) that grants restricted access rights to Azure Storage resources. SAS is a secure way to share your storage resources without compromising your account keys.
You can provide a SAS to clients who shouldn't have access to your storage account key. By distributing a SAS URI to these clients, you grant them access to a resource for a specified period of time.
You'd typically use a SAS for a service where users read and write their data to your storage account. Accounts that store user data have two typical designs:
- Clients can upload and download data through a front-end proxy service, which performs authentication. This front-end proxy service has the advantage of allowing validation of business rules. if you handle large amounts of data or high-volume transactions, it can be difficult to scale this service
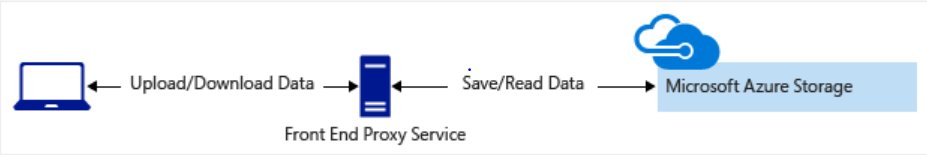
- A lightweight service authenticates the client, as needed. Next, it generates a SAS. Clients receiving the SAS can access storage account resources directly. The SAS defines the client's permissions and access interval. It reduces the need to route all data through the front-end proxy service.
Things to know about shared access signatures
Let's review some characteristics of a SAS.
A SAS gives you granular control over the type of access you grant to clients who have the SAS.
An account-level SAS can delegate access to multiple Azure Storage services, such as blobs, files, queues, and tables.
You can specify the time interval for which a SAS is valid, including the start time and the expiration time.
You specify the permissions granted by the SAS. A SAS for a blob might grant read and write permissions to that blob, but not delete permissions.
SAS provides account-level and service-level control.
Account-level. Use an account-level SAS to allow access to anything that a service-level SAS can allow, plus other resources and abilities. For example, you can use an account-level SAS to allow the ability to create file systems.
Service-level.You can use a service-level SAS to allow access to specific resources in a storage account. You'd use this type of SAS, for example, to allow an app to retrieve a list of files in a file system, or to download a file.
Note
A stored access policy can provide another level of control when you use a service-level SAS on the server side. You can group SASs and provide other restrictions by using a stored access policy.
There are optional SAS configuration settings:
IP addresses. You can identify an IP address or range of IP addresses from which Azure Storage accepts the SAS. Configure this option to specify a range of IP addresses that belong to your organization.
Protocols. You can specify the protocol over which Azure Storage accepts the SAS. Configure this option to restrict access to clients by using HTTPS.
Configure a shared access signature
In the Azure portal, you configure several settings to create a SAS. As you review these details, consider how you might implement shared access signatures in your storage security solution.
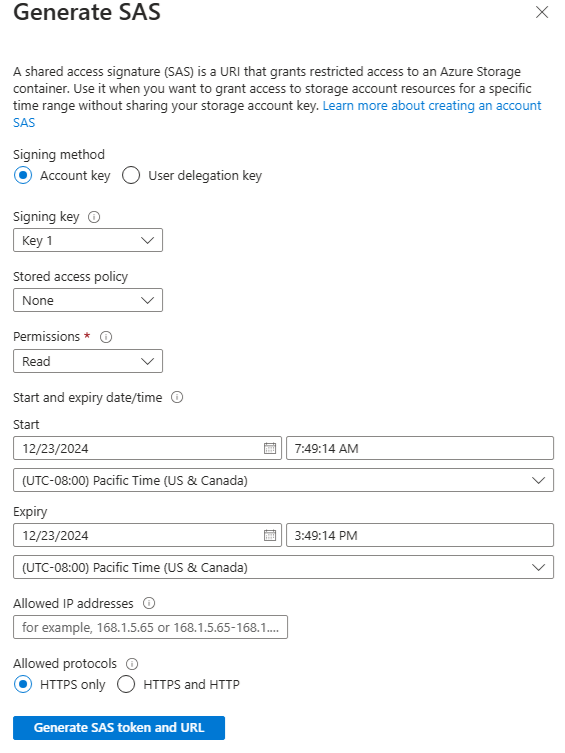
- Signing method: Choose the signing method: Account key or User delegation key.
- Signing key: Select the signing key from your list of keys.
- Permissions: Select the permissions granted by the SAS, such as read or write.
- Start and Expiry date/time: Specify the time interval for which the SAS is valid. Set the start time and the expiry time.
- Allowed IP addresses: (Optional) Identify an IP address or range of IP addresses from which Azure Storage accepts the SAS.
- Allowed protocols: (Optional) Select the protocol over which Azure Storage accepts the SAS.