Understand classification
You can use a machine learning classification technique to predict which category, or class, something belongs to. Classification machine learning models use a set of inputs, which we call features, to calculate a probability score for each possible class and predict a label that indicates the most likely class that an object belongs to.
For example, the features of a flower might include the measurements of its petals, stem, sepals, and other quantifiable characteristics. A machine learning model could be trained by applying an algorithm to these measurements that calculates the most likely species of the flower - its class.
Understand image classification
Image classification is a machine learning technique in which the object being classified is an image, such as a photograph.
To create an image classification model, you need data that consists of features and their labels. The existing data is a set of categorized images. Digital images are made up of an array of pixel values, and these are used as features to train the model based on the known image classes.
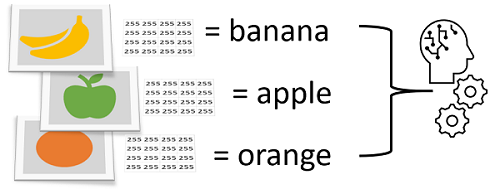
The model is trained to match the patterns in the pixel values to a set of class labels. After the model has been trained, you can use it with new sets of features to predict unknown label values.
Azure's Custom Vision service
Most modern image classification solutions are based on deep learning techniques that make use of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) to uncover patterns in the pixels that correspond to particular classes. Training an effective CNN is a complex task that requires considerable expertise in data science and machine learning.
Common techniques used to train image classification models have been encapsulated into the Azure AI Custom Vision service in Microsoft Azure; making it easy to train a model and publish it as a software service with minimal knowledge of deep learning techniques. You can use the Azure AI Custom Vision to train image classification models and deploy them as services for applications to use.