Retrieve application log files
Log files are a great resource for a Web developer, but only if you know how to find and use the logged information. Here, you look at the methods you can use to retrieve logged information for offline analysis.
Log file storage locations
The Azure infrastructure used to run Azure Web Apps in Windows isn't the same as for Linux apps, and log files aren't stored in the same locations.
Windows app log files
For Windows apps, file system log files are stored in a virtual drive that is associated with your Web App. This drive is addressable as D:\Home, and includes a LogFiles folder; within this folder are one or more subfolders:
- Application - Contains application-generated messages, if File System application logging is enabled.
- DetailedErrors - Contains detailed Web server error logs, if Detailed error messages are enabled.
- http - Contains IIS-level logs, if Web server logging is enabled.
- W3SVC<number> - Contains details of all failed http requests, if Failed request tracing is enabled.
Where storage to a Blob container is enabled, logs are stored in year, month, date, and hour folders, for example:
2019
01
10
08 - log entries for the period 08:00:00 to 08:59:59 on January 10th 2019
09 - log entries for the period 09:00:00 to 09:59:59 on January 10th 2019
Within the hour folder, there are one or more CSV files containing messages saved within that 60-minute period.
Linux app log files
For Linux Web Apps, the Azure tools currently support fewer logging options than for Windows apps. Redirections to STDERR and STDOUT are managed through the underlying Docker container that runs the app, and these messages are stored in Docker log files. To see messages logged by underlying processes, such as Apache, you need to open an SSH connection to the Docker container.
Methods for retrieving log files
How you retrieve log files depends on the type of log file, and on your preferred environment. For file system logs, you can use the Azure CLI or the Kudu console. Kudu is the engine behind many features in Azure App Service related to source control based deployment.
Azure CLI
To download file system log files using the Azure CLI, first copy the log files from the app's file system to Cloud Shell storage, and then run the following command.
az webapp log download --log-file \<_filename_\>.zip --resource-group \<_resource group name_\> --name \<_app name_\>
To download the zipped log files to your local computer, use the file download and upload tool in the Cloud Shell toolbar. Once downloaded, the files are ready for opening in Microsoft Excel, or other apps.
Note
The Azure CLI download includes all app logs, except for failed request traces.
Kudu
There's an associated Source Control Management (SCM) service site associated with all Azure Web Apps. This site runs the Kudu service, and other Site Extensions. It's Kudu that manages deployment and troubleshooting for Azure Web Apps, including options for viewing and downloading log files. The specific functionality available in Kudu, and how you download logs, depends on the type of Web App. For Windows apps, you can browse to the log file location, and then download the logs. For Linux apps, there might be a download link.
One way to access the Kudu console is to navigate to https://<app name>.scm.azurewebsites.net, and then sign in using deployment credentials.
You can also access Kudu from the Azure portal. On the App Service menu, under Development Tools, select Advanced Tools, and then on the Advanced Tools pane, select Go to open a new Kudu Services tab.
To download the log files from Windows apps:
Select Debug Console, and then select CMD.
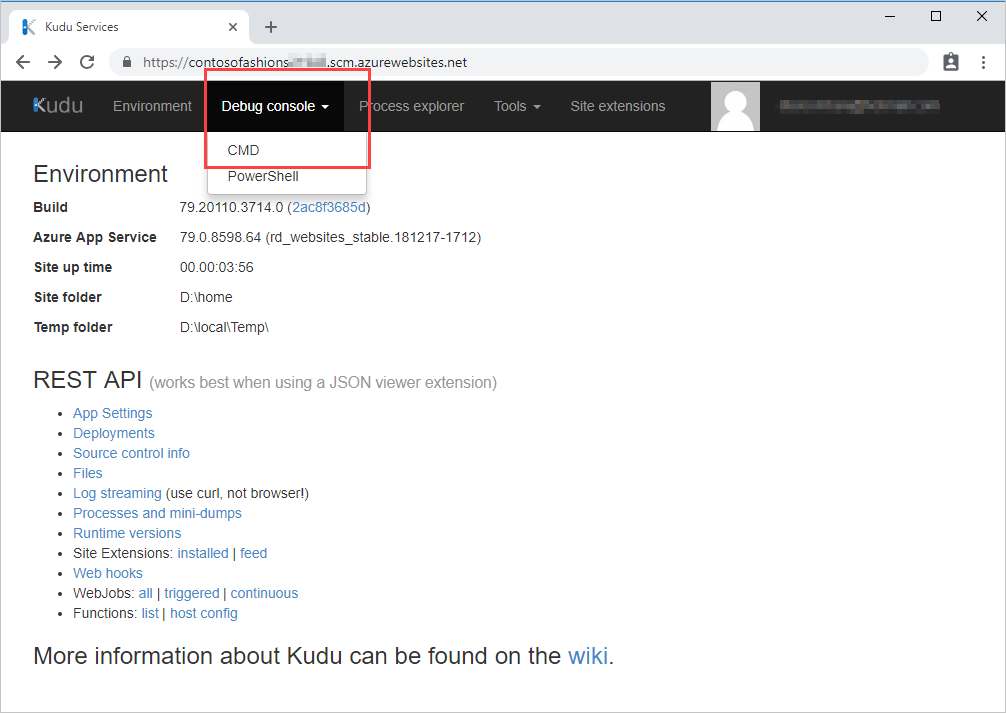
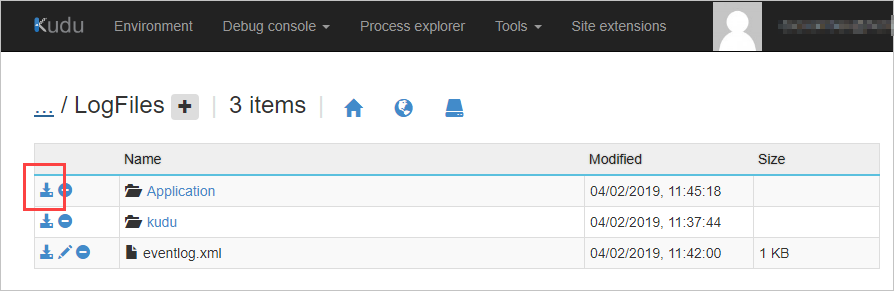
In the file explorer section, select LogFiles, and for the Application folder, select Download. The logs are downloaded to your computer as Application.zip.
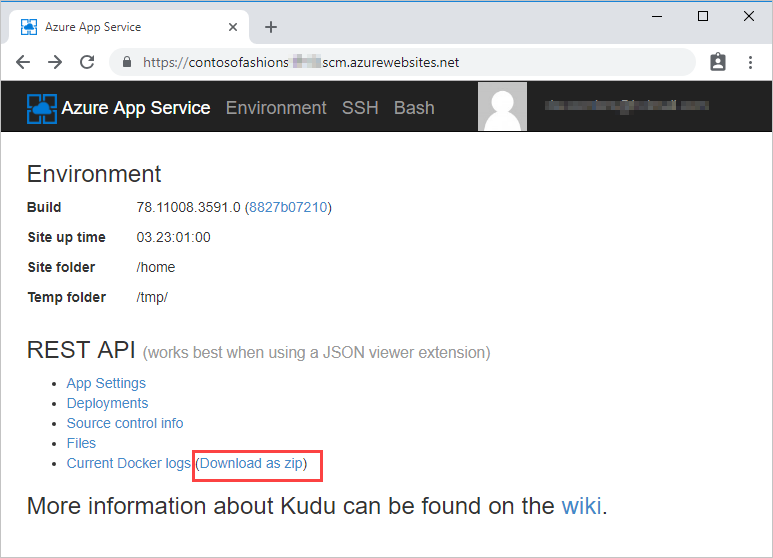
For Linux apps, select the download link on the Environment page.
Azure Storage browser
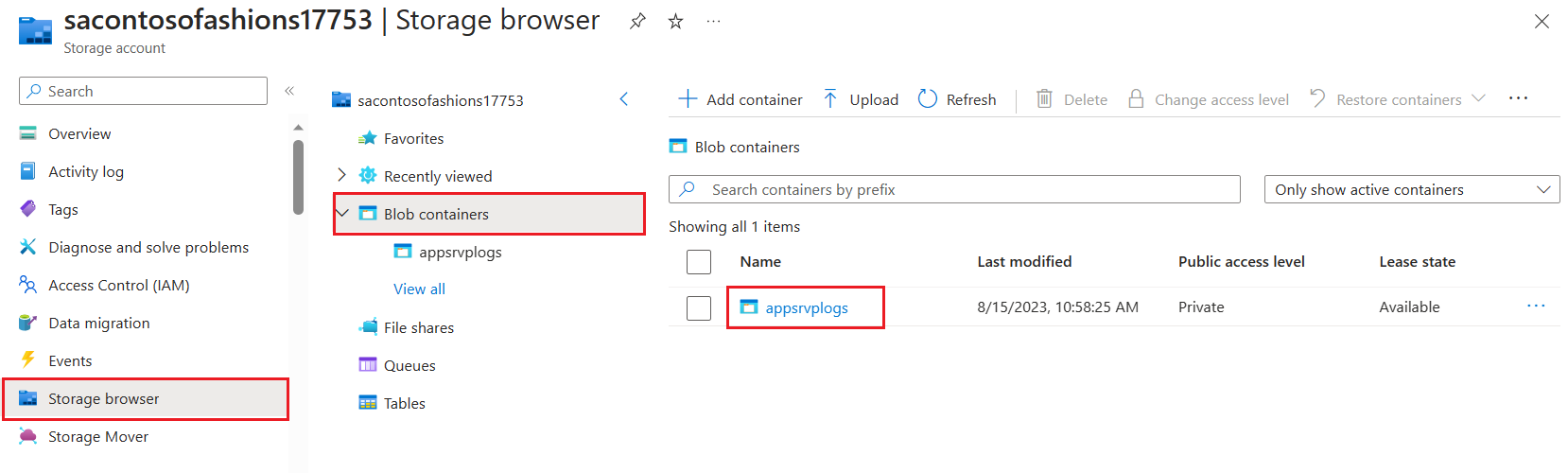
To access Windows logs saved to an Azure Blob Storage container, you can use the Azure portal. To view and download the contents of the log file container, select Storage accounts from the portal menu. Select your storage account and then select Storage browser. Open the type of storage container (for example, Blob containers), and select the name of the blob container that contains the log file. Inside the container, open the relevant year, month, date, and hour folder, then double-click a CSV file to download it to your computer.
If you have Microsoft Excel on your computer, the log file automatically opens as an Excel worksheet. Otherwise, you can open the file using a text editor, such as Notepad.