Configure Azure SQL Database and Azure SQL Managed Instance
You've verified that your deployment succeeded, and you know what resources are available. You might now want to configure your SQL managed instance, or SQL database.
Configure Azure SQL Managed Instance
Azure SQL Managed Instance is essentially a managed SQL Server instance. Many configurations available in SQL Server apply here. For example, you can configure using sp_configure and certain global trace flags. You also have options available around tempdb, model, and master. You have control over your network connectivity and configuration.
Database configuration
For databases in Azure SQL Managed Instance and Azure SQL Database, you have options available with the ALTER DATABASE command. There are SET options, and you can select the dbcompat value that you want. This value can help in migrations. You can also use the ALTER DATABASE command to change the edition or service tier.
In Azure SQL Database, you don't have access to the file configuration underneath. In Azure SQL Managed instance, you can perform file maintenance. Similar to SQL Managed Instance, you have options available for network connectivity, network configuration, and space management.
In Azure SQL Database specifically, stale page detection is enabled and the default server collation SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS is always used. Additionally, the following default options are set to ON:
SNAPSHOT_ISOLATION_STATEREAD_COMMITTED_SNAPSHOTFULL RECOVERYCHECKSUMQUERY_STORETDEACCELERATED_DATABASE_RECOVERY
Job management
SQL Server Agent provides a configuring and scheduling system for SQL Server users. You can achieve equivalent functionality in Azure SQL through the following options:
SQL Agent in SQL Managed Instance
SQL Agent is a fully supported service with Azure SQL Managed Instance. SQL Agent jobs are supported only for T-SQL and SQL Server Integration Services job steps. Command shell steps aren't supported. Although alerts aren't supported, email notifications are supported through database mail.
Elastic jobs for SQL Database
Azure SQL Database doesn't support SQL Server Agent. However, you can use the Elastic Job Agent service in Azure to create and schedule jobs. Jobs are T-SQL scripts that you can run against many databases, including parallel execution.
Azure Automation
You can use the Azure Automation service to orchestrate processes through a concept called a runbook. A runbook can consist of code like PowerShell or Python, and it can be directed to any Azure resource.
Restricted configuration choices
The Azure SQL Managed Instance and Azure SQL Database services restrict the following configurations. These restrictions might affect how you run some tasks.
- You can't stop or restart servers.
- You can't use:
- Instant file initialization.
- Locked pages in memory.
FILESTREAMand availability groups.- Server collation. In SQL Managed Instance, you can select server collation during deployment, but not change it.
- Startup parameters.
- Error reporting and customer feedback.
ALTER SERVER CONFIGURATION.ERRORLOGconfiguration.
- Mixed Mode security is forced.
- Logon audit is done through SQL audit.
- Server proxy account isn't applicable.
Azure SQL Managed Instance and SQL Database are platform as a service (PaaS) offerings. Restricting these choices shouldn't inhibit your ability to use a fully managed SQL Server service.
Storage management
For Azure SQL Managed Instance, there's a possible maximum storage size allowed for the instance based on your chosen SLO. You choose a maximum storage for the instance up to this possible maximum size. If you reach the maximum storage, you might get Message 1105 for a managed database or Message 1133 for the instance.
Just like SQL Server, any new database's size is based on the model database size. The model database is a 100-MB data file and an 8-MB log file. Also like SQL Server, the model size is configurable. You can alter the size and the number of files, but you don't have control over their physical location. Microsoft has commitments on I/O performance based on your deployment choice. Additionally, because remote storage is used in the General Purpose service tier, the data file and log file size can affect performance.
For Azure SQL Database, there's a possible maximum size of database files based on your chosen SLO. You choose a Data max size up to this possible maximum size. Maxsize for database files, as defined by the sys.database_files.max_size column, can grow to Data max size.
To understand this idea of Data max size versus Maxsize, consider an example where a 1 TB (Data max size) General Purpose database is deployed. When you do this deployment, your database requires only ~500 GB, not 1 TB. As your database grows and approaches Data max size, Maxsize for database files also grows up to the 1-TB level.
The transaction log is in addition to the data size and is included in what you pay for storage. It's truncated regularly due to automatic backups, and Accelerated Database Recovery is on by default. The log's maximum size is always 30 percent of Data max size. For example, if Data max size is 1 TB, then the maximum transaction log size is 0.3 TB, and the total of Data max size and log size is 1.3 TB.
The Azure SQL Database Hyperscale tier is different from the other service tiers. It creates a database that's initially 40 GB and grows automatically in size to the limit of 100 TB. The transaction log has a fixed size restriction of 1 TB.
Connectivity architecture and policy
Part of configuring your Azure SQL Database logical server or configuring Azure SQL Managed Instance involves determining the route of connection to your databases.
For Azure SQL Managed Instance, you can choose the connection type or policy during the deployment. In Azure SQL Database, you can choose the connection type after deployment.
You can keep the default of Proxy for connections from outside and Redirect for connections within Azure or configure something else. The following diagram shows how gateways are used for the proxy or redirect connection policy.
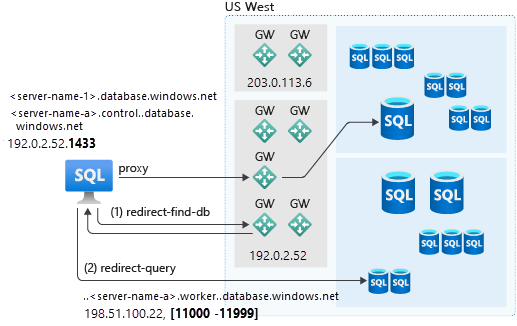
At the highest level, in Proxy mode, all connections are proxied through the gateway. In Redirect mode, after the connection is established and is using the gateway, the connection can connect directly to the database or managed instance. The gateway is redirect-find-db in the preceding figure.
The direct connection (redirect) allows for reduced latency and improved throughput. It also requires opening more ports to allow inbound and outbound communication in the range of 11000 to 11999.
In the next exercise, you see some commands for configuring Azure SQL with the Azure CLI. Then, you dive into evaluating the proxy and redirect connection policies.