Assess a database with Data Migration Assistant
Data Migration Assistant (DMA) is a standalone application that runs a set of tasks to help migrating or upgrading your SQL Server databases. DMA helps you to discover breaking changes, behavior changes, and deprecated features. If you're migrating to an on-premises SQL Server host, you can also run a feature parity assessment to find features in the target version that can enhance the performance of your database. For migrations to Azure SQL, DMA checks feature parity to uncover partially or unsupported features in Azure.
The duration of the DMA assessment depends on the size of the source database. To reduce assessment time for large databases, you can run compatibility and new feature recommendation assessments separately.
Note
While the Database Migration Assistant is a useful tool available, we recommend that you use the Azure Database Migration Service for large migrations and enhanced overall experience.
Install the Microsoft Data Migration Assistant
The Data Migration Assistant can be downloaded and installed on the machine from which you currently administer your databases. The DMA is isolated from any other software, and it has no dependencies other than the credentials for the SQL Server instance you want to upgrade. It's recommended not to install DMA on the same server as the SQL Server.
To install DMA, download the latest version of the tool from the Microsoft Download Center, and then run the DataMigrationAssistant.msi file.
After installing DMA, you'll need access to the SQL Server instances and the network infrastructure.
- When running an assessment, DMA requires access at the source database.
- When running an upgrade or migration, DMA requires access at the source and target databases. The account must have the CONTROL SERVER permission at the source, and admin permissions at the target.
It's recommended to run the DMA against the databases in your development or test environments prior to your production databases.
Discovering compatibility issues and feature parity
In our law firm scenario, you've identified the SQL Server instances within your organization that require upgrading. You want to check that the databases will continue to function after migration. Your CTO is creating a report detailing the return on investment (ROI) obtained by migrating the databases to the latest version of SQL Server. They want you to provide details of the features supported that provide benefits to the users. This information helps to demonstrate the benefits of the investment for users.
The Microsoft Data Migration Assistant (DMA) checks each database for compatibility issues and, because a few databases are moving to Azure SQL Database, it identifies features that won't be supported after migration. The DMA also recommends how to use new features in the target database.
Database compatibility
Discover issues that can affect an upgrade to an on-premises SQL Server. These are described as compatibility issues and are organized in the following categories:
- Breaking changes
- Behavior changes
- Deprecated features
Important
Migrating your database to a newer version of SQL Server doesn't guarantee improved performance. It's possible that without making any changes to the database during or after migration, the queries may not run optimally on the target due to changes in the query engine.
Feature parity
Data Migration Assistant creates a list of unsupported, and partially supported features if you run a feature parity assessment against a target Azure SQL Database, Azure SQL Managed Instance, or SQL Server for Linux.
DMA identifies unsupported features by comparing the components installed on your source instance with the target environment. For example, currently, Master Data Services (MDS), SQL Server Analysis Services (SSAS), and SQL Server Reporting Services (SSRS) aren't supported on Azure SQL Database or SQL Server for Linux. Any interaction with these services would require removal or redevelopment in order to ensure compatibility with the target environment.
Partially supported features in Azure SQL Database, or SQL Server for Linux, don't have the same depth of functionality as the on-premises Windows versions. The DMA automatically finds feature discrepancies so you can plan around any potential blockers.
Exercise: Run a feature parity assessment
- In DMA, select + New and provide the following information:
- Project type - Assessment
- Project name - <provide a name of your preference>
- Assessment type - Database Engine
- Source server type - SQL Server
- Target server type - Azure SQL Database. This is the target server you're assessing for compatibility.
- Select Create
- On the assessment page, select Check feature parity. Select Next.
Note
Depending on the SQL target version, Check feature parity assessment won't be available.
- On the Connect to a server sidebar, provide the connection details about your source server. Select Connect.
- On the Add sources sidebar, select the database for assessment. Select Add.
Note
Optionally, you can enter a folder path containing files with extended events for traces to be assessed.
- Select Start Assessment, and once the assessment is finished, you can view the results in the Review results tab.
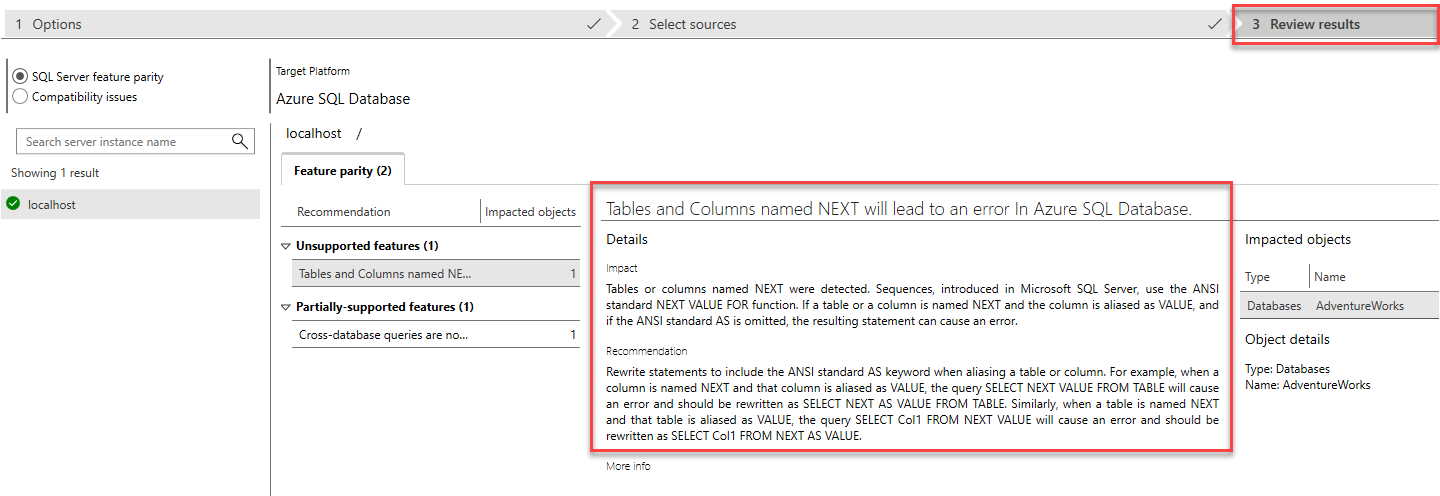
Compatibility assessment results
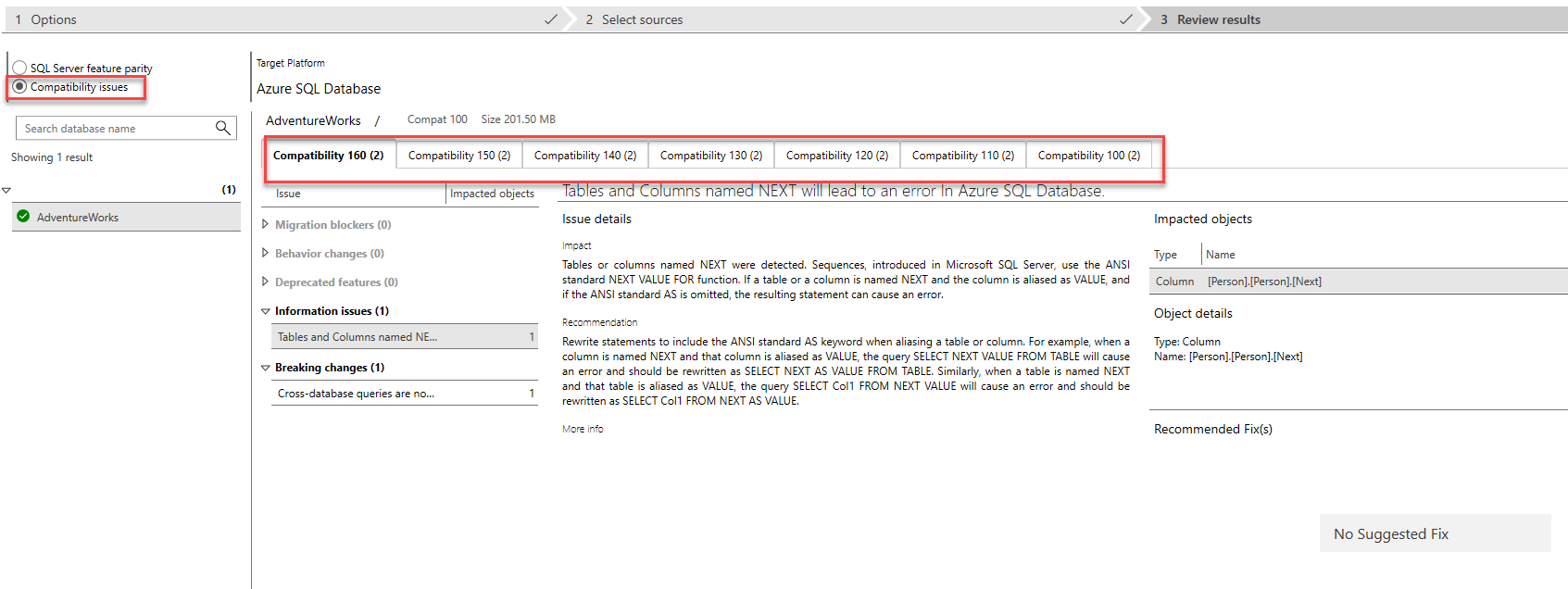
If you choose the Check compatibility issues option on the assessment page, the results are displayed in a slightly different format.
- There's a tab for each tested version. For each compatibility tab, there might be a Behavior changes note, listing issues for review.
- Depending on the issue, there might also be an Impacted objects section, with Recommended Fix(s) notes.
Optionally, you have the ability to save each assessment project and reopen it later to view the results. This allows you to revisit and re-evaluate the assessment if any changes have been made since the last check. You can also delete any assessments that are no longer need.