Exercise - Update and version a template spec
Your Azure Cosmos DB template spec is now used throughout your organization to provision lots of new Azure Cosmos DB accounts. Accordingly, all of them are configured to use continuous backup.
Your security team recently reviewed the Azure Cosmos DB security capabilities. It decided that new accounts should use Microsoft Entra authentication and Azure Cosmos DB role-based access control.
In this exercise, you update your template spec with a new version that includes the updated authentication configuration.
During the process, you'll:
- Update your template to reconfigure the backup policy.
- Publish a new version of your template spec.
- Verify that the template spec has been updated.
- Test the new version of your template spec by deploying another Azure Cosmos DB account.
Update the template
In Visual Studio Code, open the azuredeploy.json file.
Update the azuredeploy.json file to include the following changes:
{ "$schema": "https://schema.management.azure.com/schemas/2019-04-01/deploymentTemplate.json#", "contentVersion": "1.0.0.0", "parameters": { "location": { "type": "string", "defaultValue": "[resourceGroup().location]", "metadata": { "description": "The Azure region into which the Cosmos DB resources should be deployed." } }, "cosmosDBAccountName": { "type": "string", "defaultValue": "[concat('toy-', uniqueString(resourceGroup().id))]", "maxLength": 44, "minLength": 3, "metadata": { "description": "The name of the Cosmos DB account. This name must be globally unique, and it must only include lowercase letters, numbers, and hyphens." } }, "roleDefinitionFriendlyName": { "type": "string", "defaultValue": "Read and Write", "metadata": { "description": "A descriptive name for the role definition." } }, "roleDefinitionDataActions": { "type": "array", "defaultValue": [ "Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts/readMetadata", "Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts/sqlDatabases/containers/items/*" ], "metadata": { "description": "The list of actions that the role definition permits." } }, "roleAssignmentPrincipalId": { "type": "string", "metadata": { "description": "The object ID of the Azure AD principal that should be granted access using the role definition." } } }, "variables": { "roleDefinitionName": "[guid('sql-role-definition', resourceId('Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts', parameters('cosmosDBAccountName')))]", "roleAssignmentName": "[guid('sql-role-assignment', resourceId('Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts', parameters('cosmosDBAccountName')))]" }, "resources": [ { "type": "Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts", "apiVersion": "2021-04-15", "name": "[parameters('cosmosDBAccountName')]", "kind": "GlobalDocumentDB", "location": "[parameters('location')]", "properties": { "consistencyPolicy": { "defaultConsistencyLevel": "Session" }, "locations": [ { "locationName": "[parameters('location')]", "failoverPriority": 0, "isZoneRedundant": false } ], "databaseAccountOfferType": "Standard", "enableAutomaticFailover": false, "enableMultipleWriteLocations": false, "backupPolicy": { "type": "Continuous" } } }, { "type": "Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts/sqlRoleDefinitions", "apiVersion": "2021-04-15", "name": "[format('{0}/{1}', parameters('cosmosDBAccountName'), variables('roleDefinitionName'))]", "properties": { "roleName": "[parameters('roleDefinitionFriendlyName')]", "type": "CustomRole", "assignableScopes": [ "[resourceId('Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts', parameters('cosmosDBAccountName'))]" ], "permissions": [ { "dataActions": "[parameters('roleDefinitionDataActions')]" } ] }, "dependsOn": [ "[resourceId('Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts', parameters('cosmosDBAccountName'))]" ] }, { "type": "Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts/sqlRoleAssignments", "apiVersion": "2021-04-15", "name": "[format('{0}/{1}', parameters('cosmosDBAccountName'), variables('roleAssignmentName'))]", "properties": { "roleDefinitionId": "[resourceId('Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts/sqlRoleDefinitions', parameters('cosmosDBAccountName'), variables('roleDefinitionName'))]", "principalId": "[parameters('roleAssignmentPrincipalId')]", "scope": "[resourceId('Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts', parameters('cosmosDBAccountName'))]" }, "dependsOn": [ "[resourceId('Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts', parameters('cosmosDBAccountName'))]", "[resourceId('Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts/sqlRoleDefinitions', parameters('cosmosDBAccountName'), variables('roleDefinitionName'))]" ] } ] }Save the file.
In Visual Studio Code, open the main.bicep file.
Update the main.bicep file to include the following changes:
@description('The Azure region into which the Cosmos DB resources should be deployed.') param location string = resourceGroup().location @description('The name of the Cosmos DB account. This name must be globally unique, and it must only include lowercase letters, numbers, and hyphens.') @minLength(3) @maxLength(44) param cosmosDBAccountName string = 'toy-${uniqueString(resourceGroup().id)}' @description('A descriptive name for the role definition.') param roleDefinitionFriendlyName string = 'Read and Write' @description('The list of actions that the role definition permits.') param roleDefinitionDataActions array = [ 'Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts/readMetadata' 'Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts/sqlDatabases/containers/items/*' ] @description('The object ID of the Azure AD principal that should be granted access using the role definition.') param roleAssignmentPrincipalId string var roleDefinitionName = guid('sql-role-definition', cosmosDBAccount.id) var roleAssignmentName = guid('sql-role-assignment', cosmosDBAccount.id) resource cosmosDBAccount 'Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts@2021-04-15' = { name: cosmosDBAccountName kind: 'GlobalDocumentDB' location: location properties: { consistencyPolicy: { defaultConsistencyLevel: 'Session' } locations: [ { locationName: location failoverPriority: 0 isZoneRedundant: false } ] databaseAccountOfferType: 'Standard' enableAutomaticFailover: false enableMultipleWriteLocations: false } } resource roleDefinition 'Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts/sqlRoleDefinitions@2021-04-15' = { parent: cosmosDBAccount name: roleDefinitionName properties: { roleName: roleDefinitionFriendlyName type: 'CustomRole' assignableScopes: [ cosmosDBAccount.id ] permissions: [ { dataActions: roleDefinitionDataActions } ] } } resource roleAssignment 'Microsoft.DocumentDB/databaseAccounts/sqlRoleAssignments@2021-04-15' = { parent: cosmosDBAccount name: roleAssignmentName properties: { roleDefinitionId: roleDefinition.id principalId: roleAssignmentPrincipalId scope: cosmosDBAccount.id } }Save the file.
Publish a new version of the template spec
Publish the template spec by using this Azure PowerShell cmdlet in the Visual Studio Code terminal:
New-AzTemplateSpec `
-ResourceGroupName <rgn>[sandbox resource group name]</rgn> `
-Name ToyCosmosDBAccount `
-Version '2.0' `
-VersionDescription 'Adds Cosmos DB role-based access control.' `
-TemplateFile main.bicep
New-AzTemplateSpec `
-ResourceGroupName <rgn>[sandbox resource group name]</rgn> `
-Name ToyCosmosDBAccount `
-Version '2.0' `
-VersionDescription 'Adds Cosmos DB role-based access control.' `
-TemplateFile azuredeploy.json
Publish the template spec by using this Azure CLI command in the Visual Studio Code terminal:
az ts create \
--name ToyCosmosDBAccount \
--version 2.0 \
--version-description "Adds Cosmos DB role-based access control." \
--template-file main.bicep
az ts create \
--name ToyCosmosDBAccount \
--version 2.0 \
--version-description "Adds Cosmos DB role-based access control." \
--template-file azuredeploy.json
Verify the template spec
In your browser, go back to the Azure portal. Go to your resource group.
Select the template spec. Notice that the latest version is now listed as 2.0.
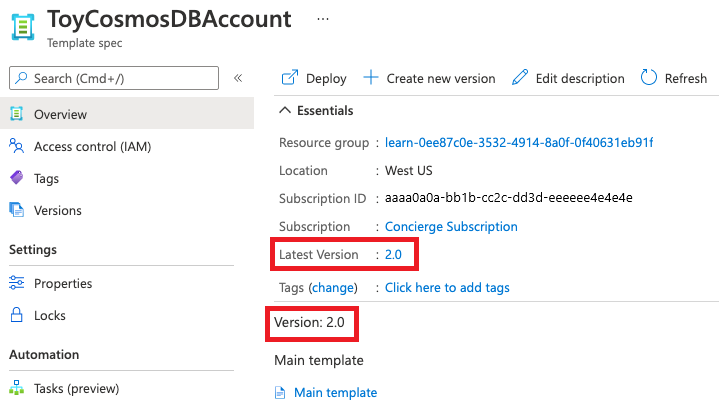
Select the Versions menu item. Notice that both versions are now listed.
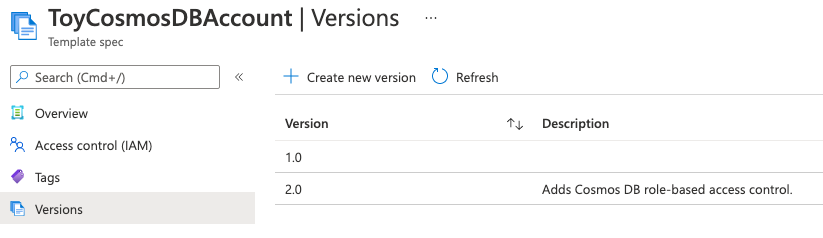
Template spec versions enable you to go back to previous versions of your template spec if you need to.
Deploy the new template spec version
Get the new template spec version's resource ID by running the following Azure PowerShell command:
$templateSpecVersionResourceId = ( ` Get-AzTemplateSpec ` -ResourceGroupName <rgn>[sandbox resource group name]</rgn> ` -Name ToyCosmosDBAccount ` -Version 2.0 ` ).Versions[0].IdNotice that you use the
Versionsproperty to get the template spec version's resource ID.Your new template spec version has a parameter for the user principal ID. Use the following commands to get your own user account's principal ID:
$token = (Get-AzAccessToken -ResourceUrl "https://graph.windows.net/").Token $userObjectId = (Invoke-RestMethod -Uri 'https://graph.windows.net/me?api-version=1.6' -Headers @{ 'Authorization' = "Bearer $token"}).objectIDThe commands use the Microsoft Graph API to query your own user profile.
Deploy the template spec by using this Azure PowerShell command in the Visual Studio Code terminal:
New-AzResourceGroupDeployment ` -TemplateSpecId $templateSpecVersionResourceId ` -roleAssignmentPrincipalId $userObjectId
Get the template spec version's resource ID by running the following Azure CLI command:
id=$(az ts show \ --name ToyCosmosDBAccount \ --resource-group "<rgn>[sandbox resource group name]</rgn>" \ --version "2.0" \ --query "id")Deploy the template spec by using this Azure CLI command in the Visual Studio Code terminal:
az deployment group create \ --template-spec $id \ --parameters roleAssignmentPrincipalId="d68d19b3-d7ef-4ae9-9ee4-90695a4e417d"
The deployment can take a minute or two to finish.
Verify the deployment
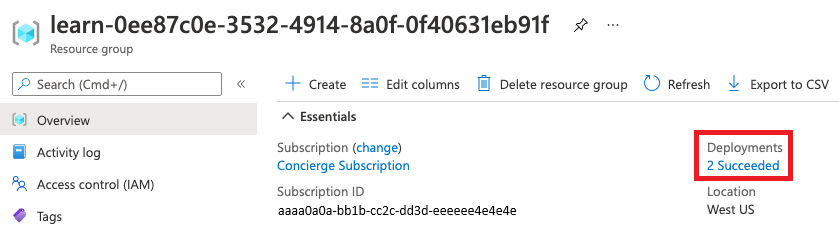
In your browser, go back to the Azure portal. Go to your resource group.
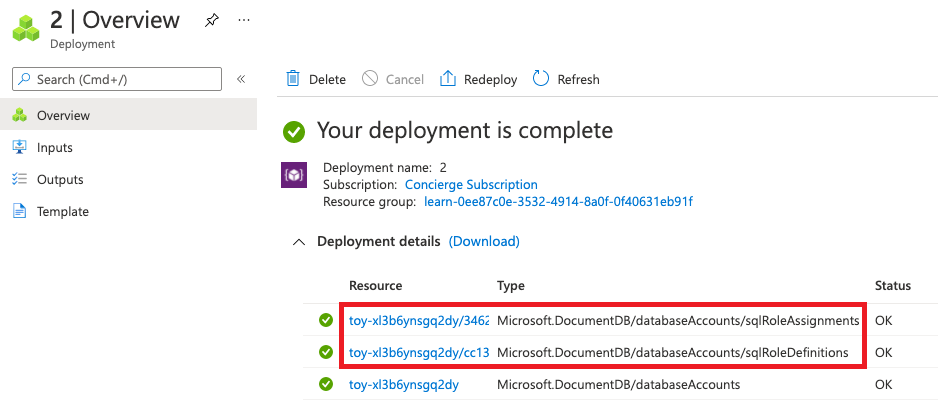
Next to Deployments, select 2 Succeeded.
Select the most recent deployment.
Select Deployment details to expand it. Confirm that the resources for Azure Cosmos DB role-based access control are deployed.