Install the first Report Server in SharePoint mode
Applies to:
SQL Server Reporting Services (2016) ❌ Power BI Report Server
SharePoint
The procedures in this topic guide you through a single server installation of Reporting Services in SharePoint mode. The steps include running the SQL Server installation wizard as well as configuration tasks that use SharePoint Central Administration. The topic can also be used for individual procedures for updating an existing installation, for example to create a Reporting Services service application.
Note
Reporting Services integration with SharePoint is no longer available after SQL Server 2016. Power View support is no longer available after SQL Server 2017.
For information on adding more Reporting Services servers to an existing farm, see the following:
A single server installation is useful for development and testing scenarios but it isn't recommended for production environments.
Example single-server deployment
A single-server installation is useful for development and testing scenarios but a single-server isn't recommended for a production environment. The single-server environment refers to a single computer that has SharePoint and Reporting Services components installed on the same computer. The topic does not cover scale-out with multiple Reporting Services servers.
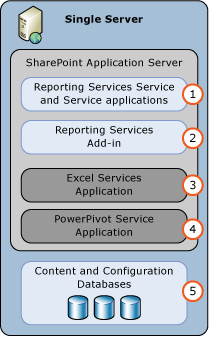
The following diagram illustrates the components that are part of a single server Reporting Services deployment.
Note
For SharePoint 2016, Excel Services has moved to the Office Online Server and cannot be used in a single server deployment. Office Online Server has to be deployed to a different server. For more information, see Office Online Server overview and Configure Excel Online administrative settings.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| (1) | SharePoint service installed from SQL Server installation. You can create one or more Reporting Services service applications. |
| (2) | Reporting Services add-in for SharePoint products provides the user interface components on the SharePoint Servers. |
| (3) | The Excel Service Application used by Power View and Power Pivot. This isn't available in a single server deployment for SharePoint 2016. An Office Online Server is required. |
| (4) | Power Pivot service application. |
Tip
For more complex deployment examples, see Deployment Topologies for SQL Server BI Features in SharePoint.
Setup accounts
This section describes the accounts and permissions used for the primary deployment steps of Reporting Services in SharePoint mode.
Installation and registering the Reporting Services Service:
- The current account during the installation (referred to as the 'setup' account) of Reporting Services in SharePoint mode needs to have administrative rights in the local computer. If you're installing Reporting Services after SharePoint is installed and the 'setup' account is also a member of the SharePoint farm administrators group, the Reporting Services installation will register the Reporting Services service for you. If you install Reporting Services before SharePoint is installed or the 'setup' account isn't a member of the farm administrators group, you register the service manually. See the section Step 2: Register and Start the Reporting Services SharePoint Service.
Creating Reporting Services Service Applications
Following installation and registering the Reporting Services service, create one or more Reporting Services service applications. The "SharePoint farm service account " needs to temporarily be a member of the local administrators group so the Reporting Services service application can be created. For more information on SharePoint 2013 account permissions, see Account permissions and security settings in SharePoint 2013 (https://technet.microsoft.com/library/cc678863.aspx) or for SharePoint 2016, see Account permissions and security settings in SharePoint 2016.
It is security best practice that SharePoint farm administrator accounts are not also local operating system administrator accounts. If you add a farm admin account to the local administrators group as part of your installation process, it is recommended you remove the account from the local administrators group after installation is complete.
Step 1: Install Reporting Services Report Server in SharePoint mode
This step installs a Reporting Services report server in SharePoint mode and the Reporting Services add-in for SharePoint products. Depending on what is already installed on your computer, you may not see some of the installation pages described in the following steps.
Important
For SharePoint 2016, the SharePoint server that Reporting Services will be installed on needs to have the Custom server role. The deployment of Reporting Services will succeed on a SharePoint server that isn't in the Custom role, but during the next SharePoint maintenance window, MinRole will stop the Reporting Services service because it detects that Reporting Services in SharePoint-integrated mode does not indicate support for any of the other SharePoint server roles. The Reporting Services service application only supports the Custom role.
Note
If you plan to install the Power Pivot service as well, on SharePoint 2016, install that prior to installing Reporting Services. The Power Pivot service can only be installed on a SharePoint server in the Custom role.
Apply the custom server role to a SharePoint 2016 server
Note
This does not apply to SharePoint 2013.
Log onto the SharePoint server that you plan to install Reporting Services.
Launch the SharePoint 2016 Management Shell as an administrator.
You can right-click on the SharePoint 2016 Management Shell and select Run as administrator.
From the PowerShell command prompt, run the following command.
Note
Make sure you specify the correct name of the SharePoint server.
Set-SPServer SERVERNAME -Role CustomYou should see a response that a timer job was scheduled. You'll need to wait for the job to execute.
Use the following command to verify the server's assigned role.
Get-SPServer SERVERNAMEThe Role should list Custom.
Install Reporting Services
Run the SQL Server Installation Wizard (Setup.exe).
Select Installation in the left side of the wizard and then select New SQL Server stand-alone installation or add features to an existing installation.
If you see the Product Key page, type your key or accept the default of the 'Enterprise Evaluation' edition.
Select Next.
If you see the License terms page, review and accept the license terms. Microsoft appreciates you agreeing to send feature usage data to help improve product features and support.
Select Next.
It is recommended that you select Use Microsoft Update to check for updates (recommended). This is optional.
Select Next.
On the Install Setup Files page, depending on what is already installed on your computer, you might see the following message:
"One or more affected files have operations pending. You must restart your computer after the setup process is completed."
Select Next.
If you see the Install Rules page. Review any warnings or blocking issues. Then select Next.
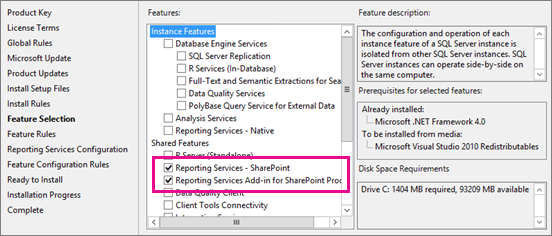
Select the following on the Feature Selection page:
Reporting Services - SharePoint
Reporting Services add-in for SharePoint Products.
You could optionally also select Database Engine Services for a complete environment, however you should have a SQL Server Database Engine instance that is hosting the SharePoint databases.
Select Next.
If you selected the Database Engine services, accept the default instance of MSSQLSERVER on the Instance Configuration page and click Next.
 The Reporting Services SharePoint service architecture isn't based on a SQL Server "instance" as was the previous Reporting Services architecture.
The Reporting Services SharePoint service architecture isn't based on a SQL Server "instance" as was the previous Reporting Services architecture.If you see the Server Configuration page type appropriate credentials. If you want to use the Reporting Services data alerting or subscription features, you need to change the Startup Type for SQL Server Agent to Automatic. You may not see the Server Configuration page, depending on what is already installed on the computer.
Select Next.
If you selected the Database Engine services, you'll see the Database Engine Configuration page, add appropriate accounts to the list of SQL Administrators and select Next.
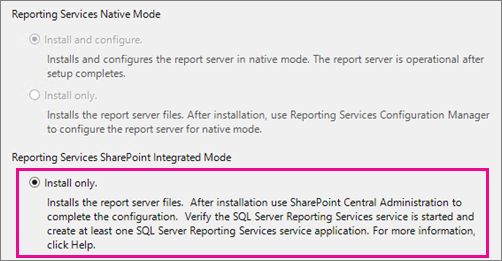
On the Reporting Services Configuration page you should see the Install only option is selected. This option installs the report server files, and does not configure the SharePoint environment for Reporting Services.
Note
When the SQL Server installation is complete, follow the other sections of this topic to configure the SharePoint environment. This includes installing the Reporting Services shared service and creating Reporting Services service applications.
Review any warnings and then select Next on the Feature Configuration Rules page if you stop on this page.
On the Ready to Install page, review the installation summary. The summary will include a Reporting Services SharePoint Mode child node that will show a value of SharePointFilesOnlyMode. Select Install.
The installation will take several minutes. You'll see the Complete page with the features listed and the status of each feature. You may see an information dialog indicating the computer needs to be restarted.
Step 2: Register and start the Reporting Services SharePoint Service
![]()
Note
If you're installing into an existing SharePoint farm, you do not need to complete the steps in this section. The Reporting Services SharePoint service is installed and started when you ran the SQL Server installation wizard as part of the previous section of this document.
The following are the common reasons why you need to manually register the Reporting Services service.
You installed Reporting Services SharePoint mode before SharePoint was installed.
The account used to install Reporting Services SharePoint mode wasn't a member of the SharePoint farm administrators group. For more information, see the section Setup accounts.
The necessary files were installed as part of the SQL Server installation wizard, but the services need to be registered into the SharePoint farm.
The following steps guide you through opening the SharePoint Management Shell and running PowerShell cmdlets:
Select the Start button
Select the Microsoft SharePoint 2016 Products or Microsoft SharePoint 2013 Products group.
Right-click SharePoint 2016 Management Shell, or SharePoint 2013 Management Shell, select Run as administrator.
Note
The SharePoint commands are not recognized in the standard Windows PowerShell window. Use the SharePoint Management Shell.
Run the following PowerShell command to install the Reporting Services SharePoint service. A successful completion of the command displays a new line in the management shell. No message is returned to the management shell when the command completes successfully:
Install-SPRSServiceRun the following PowerShell command to install the Reporting Services service proxy. A successful completion of the command displays a new line in the management shell. No message is returned to the management shell when the command completes successfully:
Install-SPRSServiceProxyRun the following PowerShell command to start the service or see the following notes for instructions on how to start the service from SharePoint Central administration:
get-spserviceinstance -all |where {$_.TypeName -like "SQL Server Reporting*"} | Start-SPServiceInstanceImportant
If you see an error message similar to the following:
> Install-SPRSService : The term 'Install-SPRSService' **isn't recognized** as the name of a cmdlet, function, script file, or operable program. Check the spelling of the name, or if a path was included, verify that the path is correct and try again.Either you're in the Windows PowerShell instead of the SharePoint Management Shell or Reporting Services SharePoint mode isn't installed. For more information on Reporting Services and PowerShell, see PowerShell cmdlets for Reporting Services SharePoint Mode.
You can also start the service from SharePoint central Administration rather than running the third PowerShell command. The following steps are also useful to verify that the service is running.
In SharePoint Central Administration, click Manage Services on Server in the System Settings group.
Find SQL Server Reporting Services Service and click Start in the Action column.
The status of the Reporting Services service will change from Stopped to Started. If the Reporting Services service isn't in the list, use PowerShell to install the service.
Note
If the Reporting Services service stays in the Starting status and does not change to Started, verify the 'SharePoint 2013 Administration' service is started in Windows Server Manager.
Step 3: Create a Reporting Services service application
This section provides the steps to create a service application and a description of the properties, if you're reviewing an existing service application.
In SharePoint Central Administration, in the Application Management group, select Manage Service Applications.
In the SharePoint ribbon, select the New button.
In the New menu, select SQL Server Reporting Services Service Application..
Important
If the Reporting Services option does not appear in the list, it is an indication that the Reporting Services shared service isn't installed. Review the previous section on how to use PowerShell cmdlts to install the Reporting Services service.
In the Create SQL Server Reporting Services Service Application page, enter a name for the application. If you're creating multiple Reporting Services service applications, a descriptive name or naming convention will help you organize your administration and management operations.
In Application Pool section, create a new application pool for the application (recommended). If you use the same name for both the application pool and the services application, it can make ongoing administration easier. This can also be affected by how many service applications you'll create and if you need to use several in a single application pool. See the SharePoint Server documentation on recommendations and best practices for application pool management.
Select or create a security account for the application pool. Be sure to specify a domain user account. A domain user account enables the use of the SharePoint managed account feature, which lets you update passwords and account information in one place. Domain accounts are also required if you plan to scale out the deployment to include additional service instances that run under the same identity.
In the Database Server, you can use the current server or choose a different SQL Server.
In Database Name the default value is
ReportingService_<guid>, which is a unique database name. If you type a new value, type a unique value. This is the new database to be created specifically for the services application.In Database Authentication, the default is Windows Authentication. If you choose SQL Authentication, refer to SharePoint documentation for best practices on how to use this authentication type in a SharePoint deployment.
In the Web Application Association section, select the Web Application to be provisioned for access by the current Reporting Services Service Application. You can associate one Reporting Services service application to one web application. If all of the current web applications are already associated with a Reporting Services service application, you see a warning message.
Select OK.
The process to create a service application could take several minutes to complete. When it is complete, you'll see a confirmation message and a link to a Provision Subscriptions and Alerts page. Complete the provision step if you want to use the Reporting Services subscriptions feature or the data alerts feature. For more information, see Provision Subscriptions and Alerts for SSRS Service Applications.
![]() For information on using PowerShell to create a Reporting Services service application, see:
For information on using PowerShell to create a Reporting Services service application, see:
See the following section Windows PowerShell script for Steps 1-4.
Topic To create a Reporting Services Service Application using PowerShell.
Step 4: Activate the Power View site collection feature.
Power View, a feature of SQL Server 2016 Reporting Services Add-in for Microsoft SharePoint Products, is a site collection feature. The feature is activated automatically for root site collections and site collections created after the Reporting Services add-in is installed. If you plan to use Power View, verify that the feature is activated.
If you install the Reporting Services add-in for SharePoint Products after the installation of the SharePoint Server, then the Report Server integration feature and the Power View integration feature will only be activated for root site collections. For other site collections, manually activate the features.
To activate or verify the Power View site collection feature
The following steps assume your SharePoint site is configured for the 2013 experience version, for SharePoint 2013.
Open your browser to the desired SharePoint site. For example https://<servername>/sites/bi
Select Settings
 .
.Select Site settings.
In the Site Collection Administration group select Site collection features.
Find Power View Integration Feature in the list.
Select Activate. The feature status will change to Active.
This procedure is completed per site collection. For more information, see Activate the Report Server and Power View Integration Features in SharePoint.
Windows PowerShell script for steps 1-4
The PowerShell script in this section is the equivalent of completing steps 1 to 4 in the previous sections. The script completes the following:
Installs Reporting Services service and service proxy, and starts the service.
Creates a service proxy named "Reporting Services".
Creates a Reporting Services service application named "Reporting Services Application".
Enables the Power View feature for a site collection.
Parameters
Update the -Account for the service proxy. The account needs to be a managed service account in the SharePoint farm. For more information, see the SharePoint topic Plan for administrative and service accounts in SharePoint 2013.
Update the -DatabaseServer parameter for the service application. This parameter is the database engine instance
Update the -url parameter of the site that you want the Power View feature enabled.
To use the script:
Open Windows PowerShell with administrative privileges.
Copy the following code into the script window.
Update the three parameters described in the previous section, and then run the script.
#This script Configures SQL Server Reporting Services SharePoint mode
$starttime=Get-Date
write-host -foregroundcolor DarkGray StartTime>> $starttime
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green "Import the SharePoint PowerShell snappin"
Add-PSSnapin Microsoft.Sharepoint.PowerShell -EA 0
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green "Install SSRS Service and Service Proxy, and start the service"
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green ">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>"
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green "Install the Reporting Services Shared Service"
Install-SPRSService
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green " Install the Reporting Services Service Proxy"
Install-SPRSServiceProxy
# Get the ID of the RS Service Instance and start the service
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green "Start the Reporting Services Service"
$RS = Get-SPServiceInstance | Where {$_.TypeName -eq "SQL Server Reporting Services Service"}
Start-SPServiceInstance -Identity $RS.Id.ToString()
# Wait for the Reporting Services Service to start...
$Status = Get-SPServiceInstance $RS.Id.ToString()
While ($Status.Status -ne "Online")
{
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green "SSRS Service Not Online...Current Status = " $Status.Status
Start-Sleep -Seconds 2
$Status = Get-SPServiceInstance $RS.Id.ToString()
}
$time=Get-Date
write-host -foregroundcolor DarkGray StartTime>> $starttime
write-host -foregroundcolor DarkGray $time
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green "Create a new application pool and Reporting Services service application"
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green ">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>"
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green "Create a new application pool"
#!!!! update "-Account" with an existing Managed Service Account
New-SPServiceApplicationPool -Name "Reporting Services" -Account "<domain>\User name>"
$appPool = Get-SPServiceApplicationPool "Reporting Services"
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green " Create the Reporting Services Service Application"
#!!!! Update "-DatabaseServer", an instance of the SQL Server database engine
$rsService = New-SPRSServiceApplication -Name "Reporting Services Application" -ApplicationPool $appPool -DatabaseName "Reporting_Services_Application" -DatabaseServer "<server name>"
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green "Create the Reporting Services Service Application Proxy"
$rsServiceProxy = New-SPRSServiceApplicationProxy -Name "Reporting Services Application Proxy" -ServiceApplication $rsService
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green "Associate service application proxy to default web site and grant web applications rights to SSRS application pool"
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green ">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>"
# Associate the Reporting Services Service Application Proxy to the default web site...
Get-SPServiceApplicationProxyGroup -default | Add-SPServiceApplicationProxyGroupMember -Member $rsServiceProxy
$time=Get-Date
write-host -foregroundcolor DarkGray StartTime>> $starttime
write-host -foregroundcolor DarkGray $time
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green "Enable the PowerView and reportserver site features"
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green ">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>"
#!!!! update "-url" of the site where you want the features enabled
Enable-SPfeature -identity "powerview" -Url https://server/sites/bi
Enable-SPfeature -identity "reportserver" -Url https://server/sites/bi
####To Verify, you can run the following:
#Get-SPRSServiceApplication
#Get-SPServiceApplicationPool | where {$_.name -like "reporting*"}
#Get-SPRSServiceApplicationProxy
Additional configuration
This section describes additional configuration steps that are important in most SharePoint deployments.
Configure Excel Services and Power Pivot
If you want to view Power View reports in an Excel 2016, or Excel 2013, workbook in SharePoint, Excel Services needs to be configured to use an Analysis Services Server in Power Pivot mode.
For SharePoint 2016, an Office Online Server needs to be configured in order to use Excel Services. For detailed information, refer to the following white papers.
Deploying SQL Server 2016 PowerPivot and Power View in SharePoint 2016
Deploying SQL Server 2016 PowerPivot and Power View in a Multi-Tier SharePoint 2016 Farm
For SharePoint 2016, you'll need to create, and configure, an Excel Services Application. For more information, see the following:
The section "Configure Excel Services for Analysis Services integration" in Install Analysis Services in Power Pivot Mode.
Manage Excel Services data model settings (SharePoint Server 2013).
Also, the application pool security account used by the Reporting Services service application, must be an administrator on the Analysis Services Server.
Provision subscriptions and alerts
The Reporting Services subscription and data alert features may require the configuration of SQL Server Agent permissions. If you see an error message that indicates SQL Server Agent is required and you have verified SQL Server Agent is running, update the permissions. You can click the link Provision Subscriptions and Alerts on the create service application success page to go to another page for provisioning SQL Server Agent. The provision step is needed if your deployment crosses computer boundaries, for example when the SQL Server database instance is on a different computer. For more information, see Provision Subscriptions and Alerts for SSRS Service Applications
Configure e-mail for SSRS service applications
The Reporting Services data alerts feature sends alerts in e-mail messages. To send e-mail you may need to configure your Reporting Services service application and you may need to modify the e-mail delivery extension for the service application. If you plan to use the e-mail delivery extension for the Reporting Services subscription feature, the e-mail settings are required. For more information, see Configure E-mail for a Reporting Services Service Application (SharePoint 2013 and SharePoint 2016).
Add Reporting Services content types to content libraries
Reporting Services provides predefined content types that are used to manage shared data source (.rsds) files, and Report Builder report definition (.rdl) files. Adding a Report Builder Report and Report Data Source content type to a library enables the New command so that you can create new documents of that type. For more information, see Add Reporting Services Content Types to a SharePoint Library.
Activate the Report Server File Sync Feature
If users will frequently upload published report items directly to SharePoint document libraries, the Report Server File Sync site level feature will be beneficial. The file sync feature will synchronize the report server catalog with items in document libraries on a more frequent basis. For more information, see Activate the Report Server File Sync Feature in SharePoint Central Administration.
Verify the installation
The following are suggested steps and procedures to verify the Reporting Services SharePoint mode deployment.
See the SharePoint section in the verification topic Verify a Reporting Services Installation.
In a SharePoint document library, create a basic Reporting Services report that only contains a text box, for example a title. The report does not contain any data sources or datasets. The goal is to verify you can open Report Builder, build a basic report, and preview the report.
Save the report to the document library and the run the report from the library. For more information on creating reports with Report Builder, see Start Report Builder (Report Builder).