Get started with log shipping on Linux
Applies to:
SQL Server - Linux
Log shipping is a SQL Server high availability (HA) configuration where a database from a primary server is replicated onto one or more secondary servers. Log shipping allows backup files from the source database to restore onto the secondary server. The primary server creates transaction log backups periodically, and the secondary servers restore them, updating the secondary copy of the database.
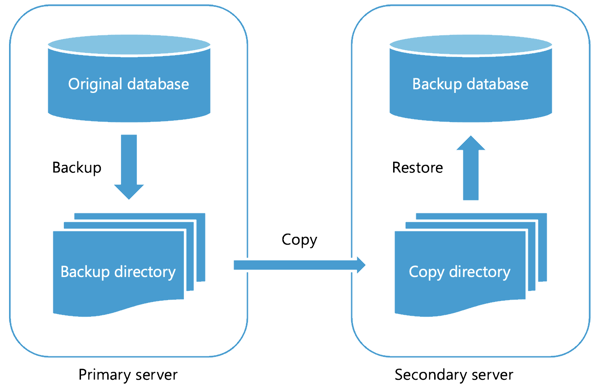
As described in the previous diagram, a log shipping session involves the following steps:
- Backing up the transaction log file on the primary SQL Server instance
- Copying the transaction log backup file across the network to one or more secondary SQL Server instances
- Restoring the transaction log backup file on the secondary SQL Server instances
Prerequisites
Set up a network share for log shipping using CIFS
Note
This tutorial uses CIFS + Samba to setup the network share.
Configure primary server
Install Samba with the following command:
For Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL):
sudo yum -y install sambaFor Ubuntu:
sudo apt-get install samba
Create a directory to store the logs for log shipping, and give the
mssqluser the required permissions:mkdir /var/opt/mssql/tlogs chown mssql:mssql /var/opt/mssql/tlogs chmod 0700 /var/opt/mssql/tlogsEdit the
/etc/samba/smb.conffile (you need root permissions), and add the following section:[tlogs] path=/var/opt/mssql/tlogs available=yes read only=yes browsable=yes public=yes writable=noCreate a
mssqluser for Samba:sudo smbpasswd -a mssqlRestart the Samba services:
sudo systemctl restart smbd.service nmbd.service
Configure secondary server
Install the CIFS client with the following command:
For RHEL:
sudo yum -y install cifs-utilsFor Ubuntu:
sudo apt-get install cifs-utils
Create a file to store your credentials. In this example, we use
/var/opt/mssql/.tlogcreds. Use the password you recently set for yourmssqlSamba account, and replace<domain>:username=mssql domain=<domain> password=<password>Run the following commands to create an empty directory for mounting and set permission and ownership correctly
mkdir /var/opt/mssql/tlogs sudo chown root:root /var/opt/mssql/tlogs sudo chmod 0550 /var/opt/mssql/tlogs sudo chown root:root /var/opt/mssql/.tlogcreds sudo chmod 0660 /var/opt/mssql/.tlogcredsAdd the line to
etc/fstabto persist the share. Replace<ip_address_of_primary_server>with the appropriate value://<ip_address_of_primary_server>/tlogs /var/opt/mssql/tlogs cifs credentials=/var/opt/mssql/.tlogcreds,ro,uid=mssql,gid=mssql 0 0Mount the shares:
sudo mount -a
Set up log shipping using Transact-SQL
Back up the database on the primary server:
BACKUP DATABASE SampleDB TO DISK = '/var/opt/mssql/tlogs/SampleDB.bak'; GOConfigure log shipping on the primary server:
DECLARE @LS_BackupJobId AS UNIQUEIDENTIFIER; DECLARE @LS_PrimaryId AS UNIQUEIDENTIFIER; DECLARE @SP_Add_RetCode AS INT; EXECUTE @SP_Add_RetCode = master.dbo.sp_add_log_shipping_primary_database @database = N'SampleDB', @backup_directory = N'/var/opt/mssql/tlogs', @backup_share = N'/var/opt/mssql/tlogs', @backup_job_name = N'LSBackup_SampleDB', @backup_retention_period = 4320, @backup_compression = 2, @backup_threshold = 60, @threshold_alert_enabled = 1, @history_retention_period = 5760, @backup_job_id = @LS_BackupJobId OUTPUT, @primary_id = @LS_PrimaryId OUTPUT, @overwrite = 1; IF (@@ERROR = 0 AND @SP_Add_RetCode = 0) BEGIN DECLARE @LS_BackUpScheduleUID AS UNIQUEIDENTIFIER; DECLARE @LS_BackUpScheduleID AS INT; EXECUTE msdb.dbo.sp_add_schedule @schedule_name = N'LSBackupSchedule', @enabled = 1, @freq_type = 4, @freq_interval = 1, @freq_subday_type = 4, @freq_subday_interval = 15, @freq_recurrence_factor = 0, @active_start_date = 20170418, @active_end_date = 99991231, @active_start_time = 0, @active_end_time = 235900, @schedule_uid = @LS_BackUpScheduleUID OUTPUT, @schedule_id = @LS_BackUpScheduleID OUTPUT; EXECUTE msdb.dbo.sp_attach_schedule @job_id = @LS_BackupJobId, @schedule_id = @LS_BackUpScheduleID; EXECUTE msdb.dbo.sp_update_job @job_id = @LS_BackupJobId, @enabled = 1; END EXECUTE master.dbo.sp_add_log_shipping_alert_job; EXECUTE master.dbo.sp_add_log_shipping_primary_secondary @primary_database = N'SampleDB', @secondary_server = N'<ip_address_of_secondary_server>', @secondary_database = N'SampleDB', @overwrite = 1;Restore the database on the secondary server:
RESTORE DATABASE SampleDB FROM DISK = '/var/opt/mssql/tlogs/SampleDB.bak' WITH NORECOVERY;Configure log shipping on the secondary server:
DECLARE @LS_Secondary__CopyJobId AS UNIQUEIDENTIFIER; DECLARE @LS_Secondary__RestoreJobId AS UNIQUEIDENTIFIER; DECLARE @LS_Secondary__SecondaryId AS UNIQUEIDENTIFIER; DECLARE @LS_Add_RetCode AS INT; EXECUTE @LS_Add_RetCode = master.dbo.sp_add_log_shipping_secondary_primary @primary_server = N'<ip_address_of_primary_server>', @primary_database = N'SampleDB', @backup_source_directory = N'/var/opt/mssql/tlogs/', @backup_destination_directory = N'/var/opt/mssql/tlogs/', @copy_job_name = N'LSCopy_SampleDB', @restore_job_name = N'LSRestore_SampleDB', @file_retention_period = 4320, @overwrite = 1, @copy_job_id = @LS_Secondary__CopyJobId OUTPUT, @restore_job_id = @LS_Secondary__RestoreJobId OUTPUT, @secondary_id = @LS_Secondary__SecondaryId OUTPUT; IF (@@ERROR = 0 AND @LS_Add_RetCode = 0) BEGIN DECLARE @LS_SecondaryCopyJobScheduleUID AS UNIQUEIDENTIFIER; DECLARE @LS_SecondaryCopyJobScheduleID AS INT; EXECUTE msdb.dbo.sp_add_schedule @schedule_name = N'DefaultCopyJobSchedule', @enabled = 1, @freq_type = 4, @freq_interval = 1, @freq_subday_type = 4, @freq_subday_interval = 15, @freq_recurrence_factor = 0, @active_start_date = 20170418, @active_end_date = 99991231, @active_start_time = 0, @active_end_time = 235900, @schedule_uid = @LS_SecondaryCopyJobScheduleUID OUTPUT, @schedule_id = @LS_SecondaryCopyJobScheduleID OUTPUT; EXECUTE msdb.dbo.sp_attach_schedule @job_id = @LS_Secondary__CopyJobId, @schedule_id = @LS_SecondaryCopyJobScheduleID; DECLARE @LS_SecondaryRestoreJobScheduleUID AS UNIQUEIDENTIFIER; DECLARE @LS_SecondaryRestoreJobScheduleID AS INT; EXECUTE msdb.dbo.sp_add_schedule @schedule_name = N'DefaultRestoreJobSchedule', @enabled = 1, @freq_type = 4, @freq_interval = 1, @freq_subday_type = 4, @freq_subday_interval = 15, @freq_recurrence_factor = 0, @active_start_date = 20170418, @active_end_date = 99991231, @active_start_time = 0, @active_end_time = 235900, @schedule_uid = @LS_SecondaryRestoreJobScheduleUID OUTPUT, @schedule_id = @LS_SecondaryRestoreJobScheduleID OUTPUT; EXECUTE msdb.dbo.sp_attach_schedule @job_id = @LS_Secondary__RestoreJobId, @schedule_id = @LS_SecondaryRestoreJobScheduleID; END DECLARE @LS_Add_RetCode2 AS INT; IF (@@ERROR = 0 AND @LS_Add_RetCode = 0) BEGIN EXECUTE @LS_Add_RetCode2 = master.dbo.sp_add_log_shipping_secondary_database @secondary_database = N'SampleDB', @primary_server = N'<ip_address_of_primary_server>', @primary_database = N'SampleDB', @restore_delay = 0, @restore_mode = 0, @disconnect_users = 0, @restore_threshold = 45, @threshold_alert_enabled = 1, @history_retention_period = 5760, @overwrite = 1; END IF (@@ERROR = 0 AND @LS_Add_RetCode = 0) BEGIN EXECUTE msdb.dbo.sp_update_job @job_id = @LS_Secondary__CopyJobId, @enabled = 1; EXECUTE msdb.dbo.sp_update_job @job_id = @LS_Secondary__RestoreJobId, @enabled = 1; END
Verify log shipping works
Verify that log shipping works by starting the following job on the primary server:
USE msdb; GO EXECUTE dbo.sp_start_job N'LSBackup_SampleDB'; GOVerify that log shipping works by starting the following job on the secondary server:
USE msdb; GO EXECUTE dbo.sp_start_job N'LSCopy_SampleDB'; GO EXECUTE dbo.sp_start_job N'LSRestore_SampleDB'; GOVerify that log shipping failover works by executing the following command:
Warning
This command will bring the secondary database online and break the log shipping configuration. You need to reconfigure log shipping after running this command.
RESTORE DATABASE SampleDB WITH RECOVERY;