Deploy SQL Server Big Data Cluster with high availability
Applies to:
SQL Server 2019 (15.x)
Important
The Microsoft SQL Server 2019 Big Data Clusters add-on will be retired. Support for SQL Server 2019 Big Data Clusters will end on February 28, 2025. All existing users of SQL Server 2019 with Software Assurance will be fully supported on the platform and the software will continue to be maintained through SQL Server cumulative updates until that time. For more information, see the announcement blog post and Big data options on the Microsoft SQL Server platform.
Because SQL Server Big Data Clusters is on Kubernetes as containerized applications, and uses features like stateful sets and persistent storage, this infrastructure has built-in health monitoring, failure detection, and failover mechanisms that cluster components leverage to maintain service health. For increased reliability, you can also configure SQL Server master instance and/or HDFS name node and Spark shared services to deploy with additional replicas in a high availability configuration. Monitoring, failure detection, and automatic failover are managed by the big data cluster management service, namely the control service. This service is provided without user intervention – all from availability group setup, configuring database mirroring endpoints, to adding databases to the availability group or failover and upgrade coordination.
The following image represents how an availability group is deployed in a SQL Server Big Data Cluster:
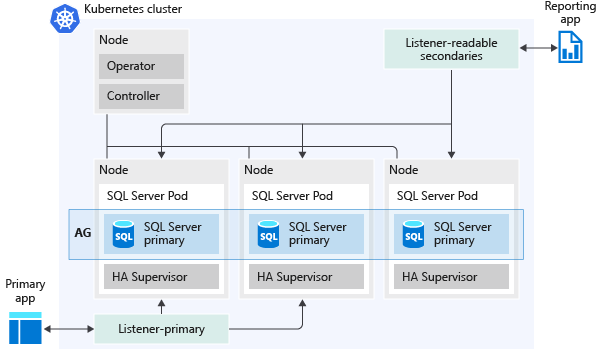
Here are some of the capabilities that availability groups enable:
If the high availability settings are specified in the deployment configuration file, a single availability group named
containedagis created. By default,containedaghas three replicas, including primary. All CRUD operations for the availability group are managed internally, including creating the availability group or joining replicas to the availability group created. Additional availability groups cannot be created in the SQL Server master instance in a big data cluster.All databases are automatically added to the availability group, including all user and system databases like
masterandmsdb. This capability provides a single-system view across the availability group replicas. Additional model databases -model_replicatedmasterandmodel_msdb- are used to seed the replicated portion of the system databases. In addition to these databases, you will seecontainedag_masterandcontainedag_msdbdatabases if you connect directly to the instance. Thecontainedagdatabases represent themasterandmsdbinside the availability group.Important
Databases that are created on the instance as a result of a workflow, like attach database, aren't automatically added to the availability group. SQL Server Big Data Clusters administrators will have to do this manually. To learn how to enable a temporary endpoint to the SQL Server instance master database, see Connect to SQL Server instance. Before the SQL Server 2019 CU2 release, databases that were created as a result of a restore statement had the same behavior, and databases had to be added manually to the contained availability group.
PolyBase configuration databases are not included in the availability group because they include instance level metadata specific to each replica.
An external endpoint is automatically provisioned for connecting to databases within the availability group. This endpoint
master-svc-externalplays the role of the availability group listener.A second external endpoint is provisioned for read-only connections to the secondary replicas to scale out the read workloads.
Deploy
To deploy SQL Server master in an availability group:
- Enable the
hadrfeature - Specify the number of replicas for the AG (minimum is 3)
- Configure the details of the second external endpoint created for connections to the read-only secondary replicas
You can use either the aks-dev-test-ha or the kubeadm-prod built-in configuration profiles to start customizing your big data cluster. These profiles include the settings required for resources you can configure additional high availability. For example, below is a section in the bdc.json configuration file that is relevant for enabling availability groups for SQL Server master instance.
{
...
"spec": {
"type": "Master",
"replicas": 3,
"endpoints": [
{
"name": "Master",
"serviceType": "LoadBalancer",
"port": 31433
},
{
"name": "MasterSecondary",
"serviceType": "LoadBalancer",
"port": 31436
}
],
"settings": {
"sql": {
"hadr.enabled": "true"
}
}
}
...
}
The following steps walk through an example on how to start from aks-dev-test-ha profile and customize your big data cluster deployment configuration. For a deployment on a kubeadm cluster, similar steps would apply, but make sure you are using NodePort for the serviceType in the endpoints section.
Clone your targeted profile
azdata bdc config init --source aks-dev-test-ha --target custom-aks-haOptionally make any edits to the custom profile as necessary.
Start cluster deployment using the cluster configuration profile created above
azdata bdc create --config-profile custom-aks-ha --accept-eula yes
Connect to SQL Server databases in the availability group
Depending on the type of workload you want to run against SQL Server master, you can connect either to the primary for read-write workloads or to the databases in the secondary replicas for read-only type of workloads. Here is an outline for each type of connection:
Connect to databases on the primary replica
For connections to the primary replica, use sql-server-master endpoint. This endpoint is also the listener for the AG. When using this endpoint, all connections are in the context of databases within the availability group. For example, a default connection using this endpoint will result in connecting to the master database within the availability group, not the SQL Server instance master database. Run this command to find the endpoint:
azdata bdc endpoint list -e sql-server-master -o table
Description Endpoint Name Protocol
------------------------------------ ------------------- ----------------- ----------
SQL Server Master Instance Front-End 11.11.111.111,11111 sql-server-master tds
Note
Failover events can occur during a distributed query execution that is accessing data from remote data sources like HDFS or data pool. As a best practice, applications should be designed to have connection retry logic in case of disconnects caused by failover.
Connect to databases on the secondary replicas
For read-only connections to databases in secondary replicas, use the sql-server-master-readonly endpoint. This endpoint acts like a load balancer across all the secondary replicas. When using this endpoint, all connections are in the context of databases within the availability group. For example, a default connection using this endpoint will result in connecting to the master database within the availability group, not the SQL Server instance master database.
azdata bdc endpoint list -e sql-server-master-readonly -o table
Description Endpoint Name Protocol
--------------------------------------------- ------------------ -------------------------- ----------
SQL Server Master Readable Secondary Replicas 11.11.111.11,11111 sql-server-master-readonly tds
Connect to SQL Server instance
For certain operations like setting server level configurations or manually adding a database to the availability group, you must connect to the SQL Server instance. Prior to SQL Server 2019 CU2, operations like sp_configure, RESTORE DATABASE or any availability groups DDL will require this type of connection. By default, big data cluster does not include an endpoint that enables instance connection and you must expose this endpoint manually.
Important
The endpoint exposed for SQL Server instance connections only supports SQL authentication, even in clusters where Active Directory is enabled. By default, during a big data cluster deployment, sa login is disabled and a new sysadmin login is provisioned based in the values provided at deployment time for AZDATA_USERNAME and AZDATA_PASSWORD environment variables.
Important
The contained availability group DDL is exclusively self managed in BDC. Any (external user) attempt to drop the contained availability or the database mirroring endpoint is not supported and can result in unrecoverable BDC state.
Here is an example that shows how to expose this endpoint and then add the database that was created with a restore workflow to the availability group. Similar instructions for setting up a connection to the SQL Server master instance apply when you want to change server configurations with sp_configure.
Note
Starting with SQL Server 2019 CU2, databases created as result of a restore workflow are added automatically to the contained availability group.
Determine the pod that hosts the primary replica by connecting to the
sql-server-masterendpoint and run:SELECT @@SERVERNAMEExpose the external endpoint by creating a new Kubernetes service
For a
kubeadmcluster run below command. ReplacepodNamewith the name of the server returned at previous step,serviceNamewith the preferred name for the Kubernetes service created andnamespaceName* with the name of your big data cluster.kubectl -n <namespaceName> expose pod <podName> --port=1533 --name=<serviceName> --type=NodePortFor an aks cluster run, run the same command, except that the type of the service created will be
LoadBalancer. For example:kubectl -n <namespaceName> expose pod <podName> --port=1533 --name=<serviceName> --type=LoadBalancerHere is an example of this command run against aks, where the pod hosting the primary is
master-0:kubectl -n mssql-cluster expose pod master-0 --port=1533 --name=master-sql-0 --type=LoadBalancerGet the IP of the Kubernetes service created:
kubectl get services -n <namespaceName>
Important
As a best practice, you should cleanup by deleting the Kubernetes service created above by running this command:
kubectl delete svc master-sql-0 -n mssql-cluster
Add the database to the availability group.
For the database to be added to the AG, it has to run in the full recovery model and a log backup has to be taken. Use the IP from the Kubernetes service created above and connect to the SQL Server instance then run the T-SQL statements as shown below.
ALTER DATABASE <databaseName> SET RECOVERY FULL; BACKUP DATABASE <databaseName> TO DISK='<filePath>' ALTER AVAILABILITY GROUP containedag ADD DATABASE <databaseName>The following example adds a database named
salesthat was restored on the instance:ALTER DATABASE sales SET RECOVERY FULL; BACKUP DATABASE sales TO DISK='/var/opt/mssql/data/sales.bak' ALTER AVAILABILITY GROUP containedag ADD DATABASE sales
Known limitations
These are known issues and limitations with contained availability groups for SQL Server master in big data cluster:
- The high availability configuration must be created when big data cluster is deployed. You cannot enable the high availability configuration with availability groups post deployment. At this time, only configuration enabled is for synchronous commit replicas.
Warning
Updating the synchronization mode to asynchronous commit for any of the replicas in the quorum commit, will result in an invalid configuration for high availability. Running in this configuration involves a data loss risk since in case of failure events affecting the primary replica, there is not an automatic failover triggered and the user must accept the risk for data loss when issuing manual failover.
- To successfully restore a TDE enabled database from a backup created on another server, you must ensure that that required certificates are restored on both SQL Server instance master as well as contained AG master. See here for an example on how to backup and restore the certificates.
- Certain operations like running server configuration settings with
sp_configurerequire a connection to the SQL Server instancemasterdatabase, not the availability groupmaster. You cannot use the corresponding primary endpoint. Follow the instructions to expose an endpoint and connect to the SQL Server instance and runsp_configure. You can only use SQL authentication when manually exposing the endpoint to connect to the SQL Server instancemasterdatabase. - While contained msdb database is included in the availability group and the SQL Agent jobs are replicated across, the jobs are only running per schedule on the primary replica.
- Replication feature is not supported for contained availability groups. SQL Server instances part of a contained AG can not function as a distributor or publisher, at either the instance level or contained AG level.
- Adding file groups while creating the database is not supported. As a workaround, you can first create the database and then issue an ALTER DATABASE statement to add any file groups.
- Prior to SQL Server 2019 CU2, databases created as result of workflows other than
CREATE DATABASEandRESTORE DATABASElikeCREATE DATABASE FROM SNAPSHOTare not automatically added to the availability group. Connect to the instance and add the database to the availability group manually. - Service Broker and Database Mail are not currently supported on Big Data Clusters deployed with high availability.
Next steps
- For more information about using configuration files in big data cluster deployments, see How to deploy SQL Server Big Data Clusters on Kubernetes.
- For more information about Availability Groups feature for SQL Server, see Overview of Always On Availability Groups (SQL Server).