Call an API from another API
How do you, as a developer, ensure Zero Trust when you have one API that needs to call another API? In this article, you learn how to securely develop your application when it's working on behalf of a user.
When a user drives an app's UI, the app might use a delegated permission so that the API knows which user on whose behalf the app is working. It would inspect the subject (sub) claim or object ID (oid) and tenant ID (tid) claims in the access token that the app provides when calling the API. The API wouldn't rely on the untrusted app, which is just a call coming from somewhere on the network. Instead, it would validate the token to ensure that the API only works on behalf of the app user that Microsoft Entra ID verified.
When one API (we refer to it as the Original API) calls another, it's vital that the API that we're calling (we refer to it as the Downstream API) follows the above-described validation process. The Downstream API can't rely on an untrusted network source. It must get the user identity from a properly validated access token.
If the Downstream API doesn't follow the proper validation process, the Downstream API must rely on the Original API to provide the identity of the user in another way. The Downstream API might incorrectly use an application permission to perform the operation. Then the Original API would become the sole authority over which users could achieve which results against the Downstream API. The Original API could intentionally (or unintentionally) allow a user to accomplish a task that the user couldn't otherwise accomplish. For example, one user could change the details of another user or read and update documents that the user doesn't have permission to access. Improper validation can cause serious security issues.
For better security, the Original API acquires a delegated permission access token to provide to the Downstream API when the Original API makes the call. Let's walk through how this works.
Client App acquires access token to call Original API
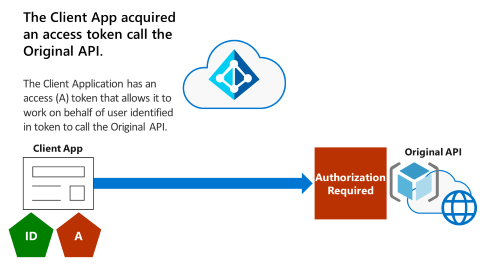
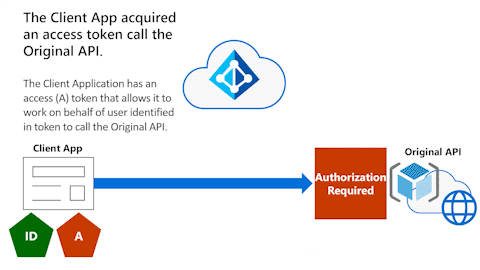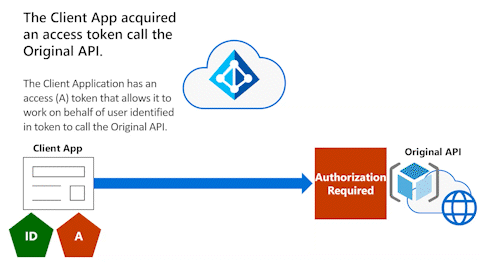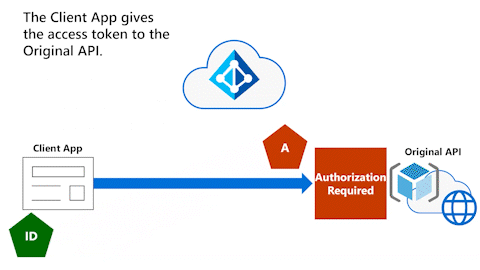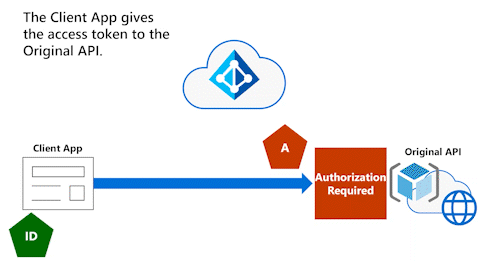
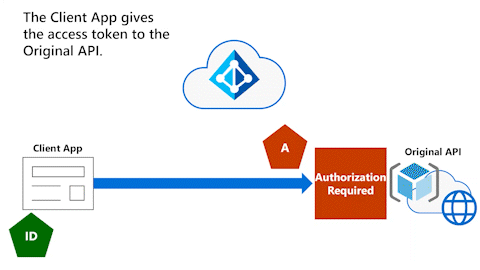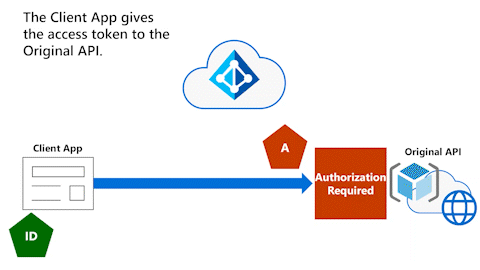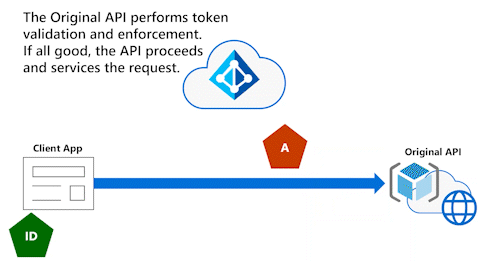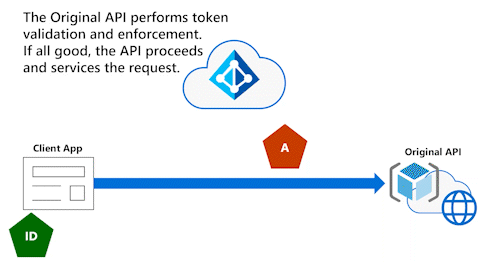
The following diagram shows the Client App and the Original API.
The Client Application acquired a delegated permission access token (indicated by the pentagon shape with the "A" label) to the Original API. The delegated permission access token allows it to work on behalf of the user to call the Original API that requires authorization.
Client App gives access token to Original API
The following animation shows the Client App giving the access token to the Original API. The Original API fully validates and inspects the access token to determine the identity of the Client App's user.
Original API performs token validation and enforcement
The next animation shows that, after the Client App gives the access token to the Original API, the Original API performs token validation and enforcement. If all is good, the API proceeds and services the request for the Client App.
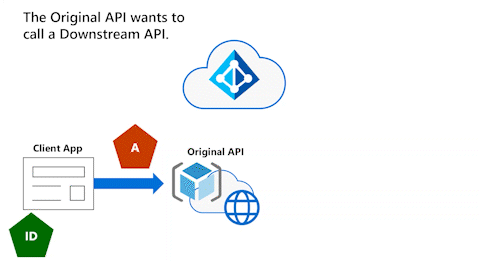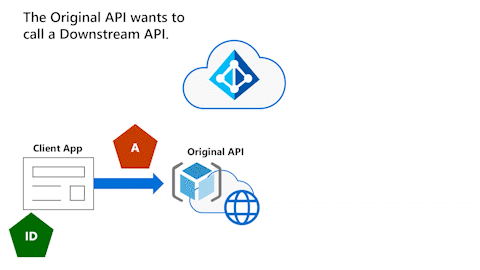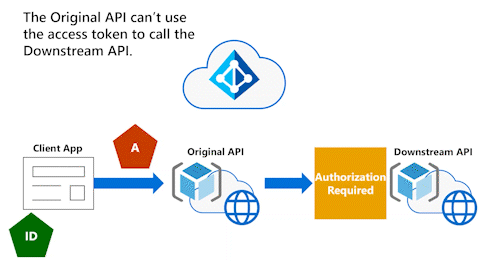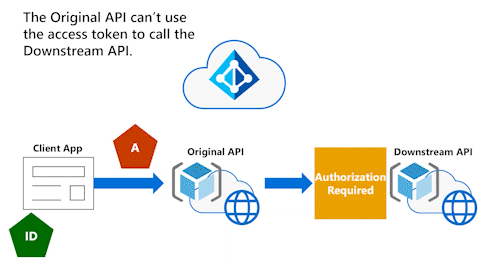
Original API can't use access token to call Downstream API
The following animation shows that the Original API now wants to call a Downstream API. However, the Original API can't use the access token to call the Downstream API.
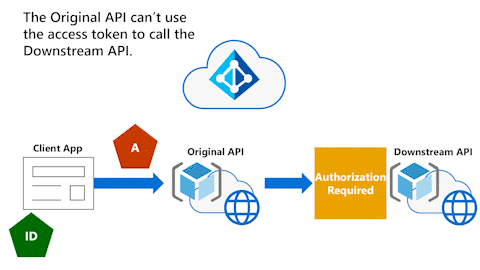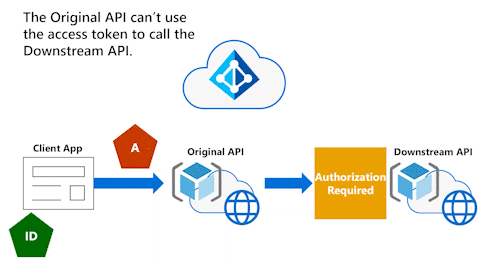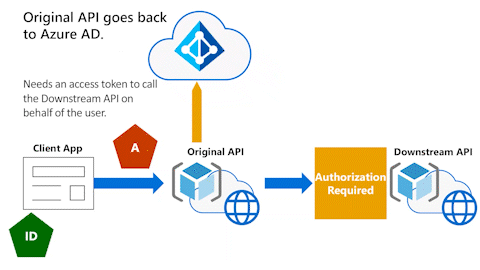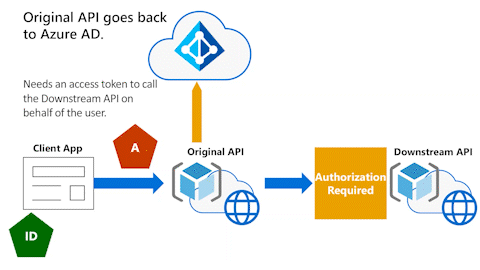
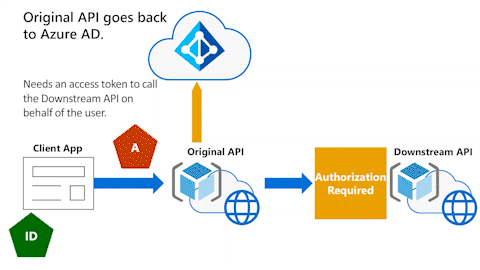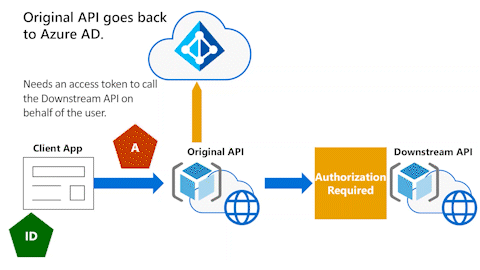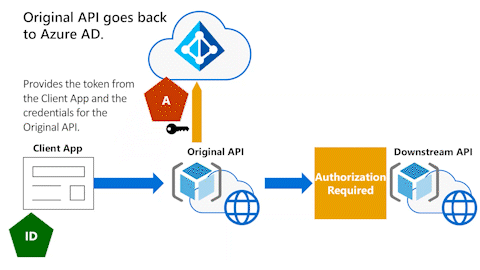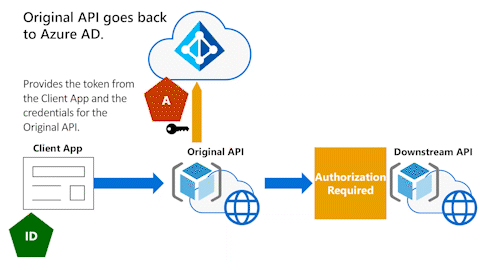
Original API goes back to Microsoft Entra ID
In the following animation, the Original API needs to go back to Microsoft Entra ID. It needs an access token to call the Downstream API on behalf of the user.
The next animation shows the Original API providing the token that the Original API received from the Client App and the Original API's client credentials.
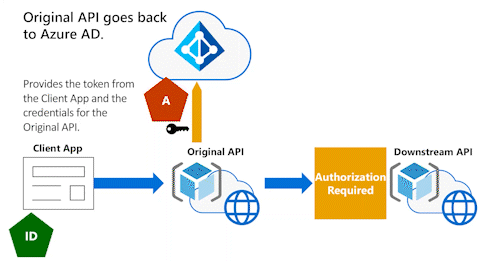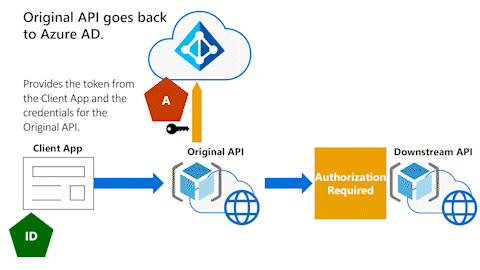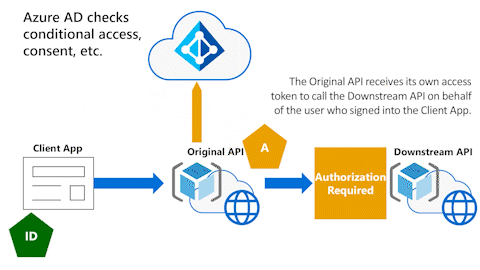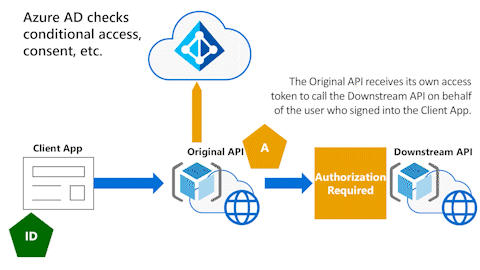
Microsoft Entra ID checks for things like consent or conditional access enforcement. You might have to go back to your calling client and provide a reason for not being able to get the token. You would typically use a claims challenge process to go back to the calling application with information regarding consent not being received (such as being related to conditional access policies).
Microsoft Entra ID performs checks
In the following animation, Microsoft Entra ID performs its checks. If everything is okay, Microsoft Entra ID issues an access token to the Original API to call the Downstream API on behalf of the user.
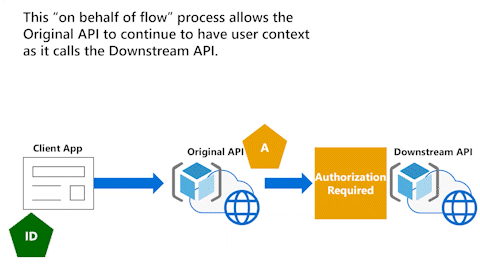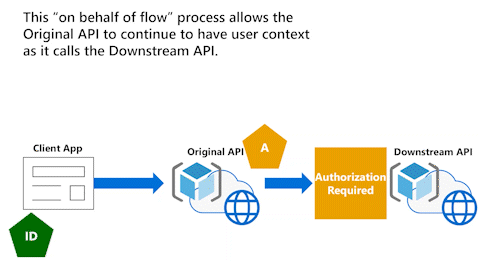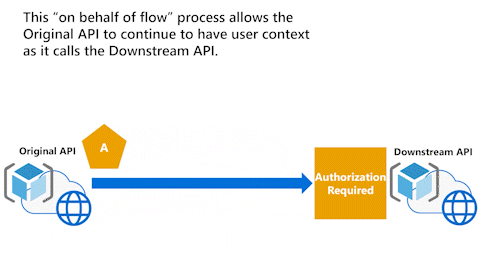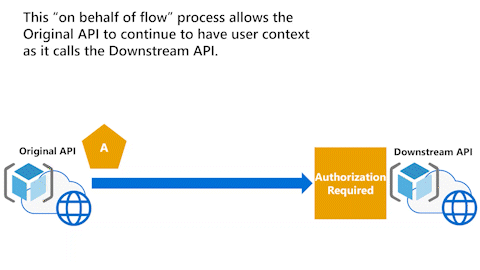
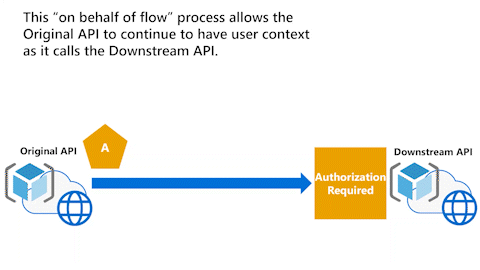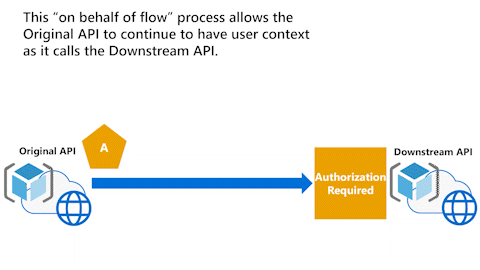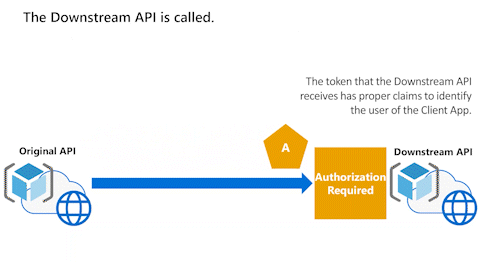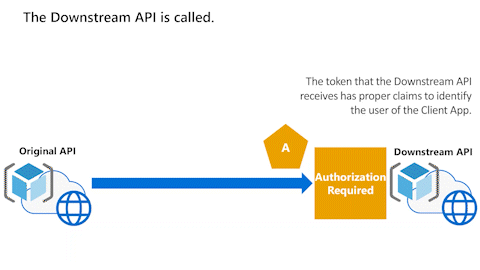
Original API has user context with On-Behalf-Of flow
The following animation illustrates the On-Behalf-Of flow (OBO) process that allows an API to continue to have the user context as it calls Downstream API.
Original API calls Downstream API
In the next animation, we call the Downstream API. The token that the Downstream API receives has the proper audience (aud) claim that indicates the Downstream API.
The token includes the scopes for granted consent and the original app user identity. The Downstream API can properly implement effective permissions to ensure that the identified user has permission to accomplish the requested task. You want to use the on behalf of flow to acquire tokens for an API to call another API to make sure that user context passes to all Downstream APIs.
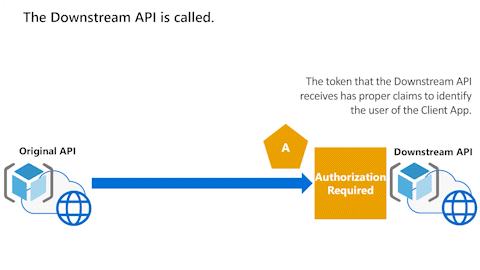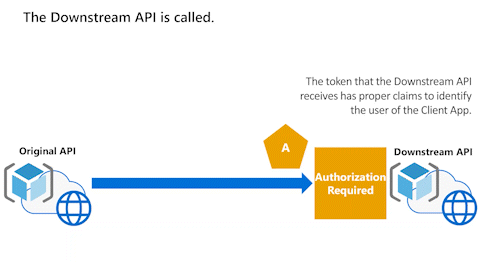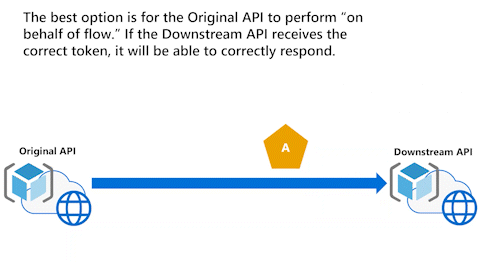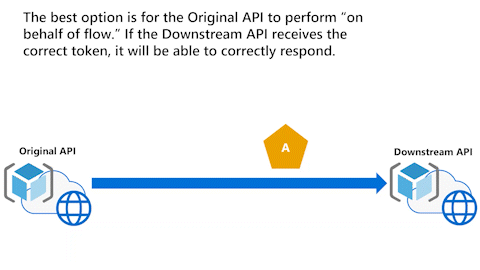
Best option: Original API performs On-Behalf-Of flow
This last animation shows that the best option is for the Original API to perform On-Behalf-Of flow (OBO). If the Downstream API receives the correct token, it can correctly respond.
When an API is acting on behalf of a user and needs to call another API, the API must use OBO to acquire a delegated permission access token to call the Downstream API on behalf of the user. APIs should never use application permissions to call Downstream APIs when the API is acting on behalf of a user.
Next steps
- Microsoft identity platform authentication flows & app scenarios describes authentication flows and the application scenarios in which they're used.
- API Protection describes best practices for protecting your API through registration, defining permissions and consent, and enforcing access to achieve your Zero Trust goals.
- Example of API protected by Microsoft identity consent framework helps you to design least privilege application permissions strategies for the best user experience.
- Customize tokens describes the information that you can receive in Microsoft Entra tokens. It explains how to customize tokens to improve flexibility and control while increasing application zero trust security with least privilege.
- The Secure custom APIs with Microsoft Identity Learn module explains how to secure a web API with Microsoft identity and how to call it from another application.
- Security best practices for application properties describes redirect URI, access tokens, certificates and secrets, application ID URI, and application ownership.
- Microsoft identity platform authentication libraries describes Microsoft Authentication Library support for various application types.