Store and Access Data in Azure Storage from Xamarin.Forms
Azure Storage is a scalable cloud storage solution that can be used to store unstructured, and structured data. This article demonstrates how to use Xamarin.Forms to store text and binary data in Azure Storage, and how to access the data.
Azure Storage provides four storage services:
- Blob Storage. A blob can be text or binary data, such as backups, virtual machines, media files, or documents.
- Table Storage is a NoSQL key-attribute store.
- Queue Storage is a messaging service for workflow processing and communication between cloud services.
- File Storage provides shared storage using the SMB protocol.
There are two types of storage accounts:
- A general-purpose storage accounts provides access to Azure Storage services from a single account.
- A Blob storage account is a specialized storage account for storing blobs. This account type is recommended when you only need to store blob data.
This article, and accompanying sample application, demonstrates uploading image and text files to blob storage, and downloading them. In addition, it also demonstrates retrieving a list of files from blob storage, and deleting files.
For more information about Azure Storage, see Introduction to Storage.
Note
If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a free account before you begin.
Introduction to Blob Storage
Blob storage consists of three components, which are shown in the following diagram:
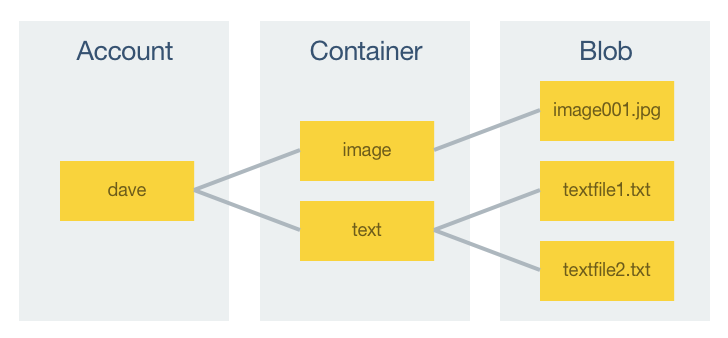
All access to Azure Storage is through a storage account. A storage account can contain an unlimited number of containers, and a container can store an unlimited number of blobs, up to the capacity limit of the storage account.
A blob is a file of any type and size. Azure Storage supports three different blob types:
- Block blobs are optimized for streaming and storing cloud objects, and are a good choice for storing backups, media files, documents etc. Block blobs can be up to 195Gb in size.
- Append blobs are similar to block blobs but are optimized for append operations, such as logging. Append blobs can be up to 195Gb in size.
- Page blobs are optimized for frequent read/write operations and are typically used for storing virtual machines, and their disks. Page blobs can be up to 1Tb in size.
Note
Note that blob storage accounts support block and append blobs, but not page blobs.
A blob is uploaded to Azure Storage, and downloaded from Azure Storage, as a stream of bytes. Therefore, files must be converted to a stream of bytes prior to upload, and converted back to their original representation after download.
Every object that's stored in Azure Storage has a unique URL address. The storage account name forms the subdomain of that address, and the combination of subdomain and domain name forms an endpoint for the storage account. For example, if your storage account is named mystorageaccount, the default blob endpoint for the storage account is https://mystorageaccount.blob.core.windows.net.
The URL for accessing an object in a storage account is built by appending the object's location in the storage account to the endpoint. For example, a blob address will have the format https://mystorageaccount.blob.core.windows.net/mycontainer/myblob.
Setup
The process for integrating an Azure Storage account into a Xamarin.Forms application is as follows:
- Create a storage account. For more information, see Create a storage account.
- Add the Azure Storage Client Library to the Xamarin.Forms application.
- Configure the storage connection string. For more information, see Connecting to Azure Storage.
- Add
usingdirectives for theMicrosoft.WindowsAzure.StorageandMicrosoft.WindowsAzure.Storage.Blobnamespaces to classes that will access Azure Storage.
Connecting to Azure Storage
Every request made against storage account resources must be authenticated. While blobs can be configured to support anonymous authentication, there are two main approaches an application can use to authenticate with a storage account:
- Shared Key. This approach uses the Azure Storage account name and account key to access storage services. A storage account is assigned two private keys on creation that can be used for shared key authentication.
- Shared Access Signature. This is a token that can be appended to a URL that enables delegated access to a storage resource, with the permissions it specifies, for the period of time that it's valid.
Connection strings can be specified that include the authentication information required to access Azure Storage resources from an application. In addition, a connection string can be configured to connect to the Azure storage emulator from Visual Studio.
Note
Azure Storage supports HTTP and HTTPS in a connection string. However, using HTTPS is recommended.
Connecting to the Azure Storage Emulator
The Azure storage emulator provides a local environment that emulates the Azure blob, queue, and table services for development purposes.
The following connection string should be used to connect to the Azure storage emulator:
UseDevelopmentStorage=true
For more information about the Azure storage emulator, see Use the Azure storage emulator for Development and testing.
Connecting to Azure Storage Using a Shared Key
The following connection string format should be used to connect to Azure Storage with a shared key:
DefaultEndpointsProtocol=[http|https];AccountName=myAccountName;AccountKey=myAccountKey
myAccountName should be replaced with the name of your storage account, and myAccountKey should be replaced with one of your two account access keys.
Note
When using shared key authentication, your account name and account key will be distributed to each person that uses your application, which will provide full read/write access to the storage account. Therefore, use shared key authentication for testing purposes only, and never distribute keys to other users.
Connecting to Azure Storage using a Shared Access Signature
The following connection string format should be used to connect to Azure Storage with an SAS:
BlobEndpoint=myBlobEndpoint;SharedAccessSignature=mySharedAccessSignature
myBlobEndpoint should be replaced with the URL of your blob endpoint, and mySharedAccessSignature should be replaced with your SAS. The SAS provides the protocol, the service endpoint, and the credentials to access the resource.
Note
SAS authentication is recommended for production applications. However, in a production application the SAS should be retrieved from a backend service on-demand, rather than being bundled with the application.
For more information about Shared Access Signatures, see Using Shared Access Signatures (SAS).
Creating a Container
The GetContainer method is used to retrieve a reference to a named container, which can then be used to retrieve blobs from the container or to add blobs to the container. The following code example shows the GetContainer method:
static CloudBlobContainer GetContainer(ContainerType containerType)
{
var account = CloudStorageAccount.Parse(Constants.StorageConnection);
var client = account.CreateCloudBlobClient();
return client.GetContainerReference(containerType.ToString().ToLower());
}
The CloudStorageAccount.Parse method parses a connection string and returns a CloudStorageAccount instance that represents the storage account. A CloudBlobClient instance, which is used to retrieve containers and blobs, is then created by the CreateCloudBlobClient method. The GetContainerReference method retrieves the specified container as a CloudBlobContainer instance, before it's returned to the calling method. In this example, the container name is the ContainerType enumeration value, converted to a lowercase string.
Note
Container names must be lowercase, and must start with a letter or number. In addition, they can only contain letters, numbers, and the dash character, and must be between 3 and 63 characters long.
The GetContainer method is invoked as follows:
var container = GetContainer(containerType);
The CloudBlobContainer instance can then be used to create a container if it doesn't already exist:
await container.CreateIfNotExistsAsync();
By default, a newly created container is private. This means that a storage access key must be specified to retrieve blobs from the container. For information about making blobs within a container public, see Create a container.
Uploading Data to a Container
The UploadFileAsync method is used to upload a stream of byte data to blob storage, and is shown in the following code example:
public static async Task<string> UploadFileAsync(ContainerType containerType, Stream stream)
{
var container = GetContainer(containerType);
await container.CreateIfNotExistsAsync();
var name = Guid.NewGuid().ToString();
var fileBlob = container.GetBlockBlobReference(name);
await fileBlob.UploadFromStreamAsync(stream);
return name;
}
After retrieving a container reference, the method creates the container if it doesn't already exist. A new Guid is then created to act as a unique blob name, and a blob block reference is retrieved as an CloudBlockBlob instance. The stream of data is then uploaded to the blob using the UploadFromStreamAsync method, which creates the blob if it doesn't already exist, or overwrites it if it does exist.
Before a file can be uploaded to blob storage using this method, it must first be converted to a byte stream. This is demonstrated in the following code example:
var byteData = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(text);
uploadedFilename = await AzureStorage.UploadFileAsync(ContainerType.Text, new MemoryStream(byteData));
The text data is converted to a byte array, which is then wrapped as a stream that's passed to the UploadFileAsync method.
Downloading Data from a Container
The GetFileAsync method is used to download blob data from Azure Storage, and is shown in the following code example:
public static async Task<byte[]> GetFileAsync(ContainerType containerType, string name)
{
var container = GetContainer(containerType);
var blob = container.GetBlobReference(name);
if (await blob.ExistsAsync())
{
await blob.FetchAttributesAsync();
byte[] blobBytes = new byte[blob.Properties.Length];
await blob.DownloadToByteArrayAsync(blobBytes, 0);
return blobBytes;
}
return null;
}
After retrieving a container reference, the method retrieves a blob reference for the stored data. If the blob exists, its properties are retrieved by the FetchAttributesAsync method. A byte array of the correct size is created, and the blob is downloaded as an array of bytes that gets returned to the calling method.
After downloading the blob byte data, it must be converted to its original representation. This is demonstrated in the following code example:
var byteData = await AzureStorage.GetFileAsync(ContainerType.Text, uploadedFilename);
string text = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(byteData);
The array of bytes is retrieved from Azure Storage by the GetFileAsync method, before it's converted back to a UTF8 encoded string.
Listing Data in a Container
The GetFilesListAsync method is used to retrieve a list of blobs stored in a container, and is shown in the following code example:
public static async Task<IList<string>> GetFilesListAsync(ContainerType containerType)
{
var container = GetContainer(containerType);
var allBlobsList = new List<string>();
BlobContinuationToken token = null;
do
{
var result = await container.ListBlobsSegmentedAsync(token);
if (result.Results.Count() > 0)
{
var blobs = result.Results.Cast<CloudBlockBlob>().Select(b => b.Name);
allBlobsList.AddRange(blobs);
}
token = result.ContinuationToken;
} while (token != null);
return allBlobsList;
}
After retrieving a container reference, the method uses the container's ListBlobsSegmentedAsync method to retrieve references to the blobs within the container. The results returned by the ListBlobsSegmentedAsync method are enumerated while the BlobContinuationToken instance is not null. Each blob is cast from the returned IListBlobItem to a CloudBlockBlob in order access the Name property of the blob, before it's value is added to the allBlobsList collection. Once the BlobContinuationToken instance is null, the last blob name has been returned, and execution exits the loop.
Deleting Data from a Container
The DeleteFileAsync method is used to delete a blob from a container, and is shown in the following code example:
public static async Task<bool> DeleteFileAsync(ContainerType containerType, string name)
{
var container = GetContainer(containerType);
var blob = container.GetBlobReference(name);
return await blob.DeleteIfExistsAsync();
}
After retrieving a container reference, the method retrieves a blob reference for the specified blob. The blob is then deleted with the DeleteIfExistsAsync method.