Reuse Xamarin.Forms pages in an iOS extension
iOS extensions enable you to customize existing system behavior by adding extra functionality to predefined by iOS and macOS Extension Points, such as custom context actions, password autofill, incoming calls filters, notification content modifiers, and more. Xamarin.iOS supports extensions and this guide will walk you through creating an iOS extension using Xamarin tools.
Extensions are distributed as part of a Container app and activated from a specific Extension Point in a Host app. The Container app is usually a simple iOS application, which provides a user with information about the Extension, how to activate, and use it. There are three main approaches to sharing code between an Extension and a Container app:
Common iOS project.
You can put all the shared code between the Container and the Extension into a shared iOS library and reference the library from both projects. Usually, the shared library contains native UIViewControllers and it has to be a Xamarin.iOS library.
File links.
In some cases, the Container app provides most of the functionality while the Extension needs to render a single
UIViewController. With few files to share, it's common to add a file link to the Extension app from the file located in the Container app.Common Xamarin.Forms project.
If app pages are already shared with another platform, such as Android, using the Xamarin.Forms framework, the common approach is to reimplement required pages natively in the Extension project, because the iOS Extension works with native UIViewControllers and not Xamarin.Forms pages. You have to perform additional steps to use Xamarin.Forms in the iOS extension, which are explained below.
Xamarin.Forms in an iOS Extension project
The ability to use Xamarin.Forms in a native project is provided via Native Forms. It allows ContentPage-derived pages to be added directly to native Xamarin.iOS projects. The CreateViewController extension method converts an instance of a Xamarin.Forms page to a native UIViewController, which could be used or modified as a regular controller. Because an iOS Extension is a special kind of a native iOS project, you can use Native Forms here as well.
Important
There are many known limitations for iOS Extensions. Although you can use Xamarin.Forms in an iOS Extension, you should do so very carefully, monitoring memory usage and startup time. Otherwise, the Extension could be terminated by iOS without any way to handle this gracefully.
Walkthrough
In this walkthrough, you are going to create a Xamarin.Forms application, a Xamarin.iOS Extension and reuse shared code in the Extension project:
Open Visual Studio for Mac, create a new Xamarin.Forms project using the Blank Forms App template, and name it FormsShareExtension:
In FormsShareExtension/MainPage.xaml, replace the content with the following layout:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?> <ContentPage x:Class="FormsShareExtension.MainPage" xmlns="http://xamarin.com/schemas/2014/forms" xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2009/xaml" xmlns:d="http://xamarin.com/schemas/2014/forms/design" xmlns:local="clr-namespace:FormsShareExtension" xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006" x:DataType="local:MainPageViewModel" BackgroundColor="Orange" mc:Ignorable="d"> <ContentPage.BindingContext> <local:MainPageViewModel Message="Hello from Xamarin.Forms!" /> </ContentPage.BindingContext> <StackLayout HorizontalOptions="Center" VerticalOptions="Center"> <Label Margin="20" Text="{Binding Message}" VerticalOptions="CenterAndExpand" /> <Button Command="{Binding DoCommand}" Text="Do the job!" /> </StackLayout> </ContentPage>Add a new class named MainPageViewMode to the FormsShareExtension project and replace the content of the class with the following code:
using System; using System.ComponentModel; using System.Windows.Input; using Xamarin.Forms; namespace FormsShareExtension { public class MainPageViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged { public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged; private string _message; public string Message { get { return _message; } set { if (_message != value) { _message = value; PropertyChanged?.Invoke(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(nameof(Message))); } } } private ICommand _doCommand; public ICommand DoCommand { get { return _doCommand; } set { if(_doCommand != value) { _doCommand = value; PropertyChanged?.Invoke(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(nameof(DoCommand))); } } } public MainPageViewModel() { DoCommand = new Command(OnDoCommandExecuted); } private void OnDoCommandExecuted(object state) { Message = $"Job {Environment.TickCount} has been completed!"; } } }The code is shared across all platforms and will also be used by an iOS Extension.
In solution pad, right click on the solution, select Add > New Project > iOS > Extension > Action Extension, name it MyAction and press Create:
To use Xamarin.Forms in the iOS Extension and the shared code, you need to add required references:
Right click on the iOS Extension, select References > Add Reference > Projects > FormsShareExtension and press OK.
Right click on the iOS Extension, select Packages > Manage NuGet Packages... > Xamarin.Forms and press Add Package.
Expand the Extension project and modify an entry point to initialize Xamarin.Forms and create pages. Per iOS requirements, an Extension must define the entry point in Info.plist as
NSExtensionMainStoryboardorNSExtensionPrincipalClass. Once the entry point is activated, in this case it is theActionViewController.ViewDidLoadmethod, you can create an instance of a Xamarin.Forms page and show it to a user. Therefore, open the entry point and replace theViewDidLoadmethod with the following implementation:public override void ViewDidLoad() { base.ViewDidLoad(); // Initialize Xamarin.Forms framework global::Xamarin.Forms.Forms.Init(); // Create an instance of XF page with associated View Model var xfPage = new MainPage(); var viewModel = (MainPageViewModel)xfPage.BindingContext; viewModel.Message = "Welcome to XF Page created from an iOS Extension"; // Override the behavior to complete the execution of the Extension when a user press the button viewModel.DoCommand = new Command(() => DoneClicked(this)); // Convert XF page to a native UIViewController which can be consumed by the iOS Extension var newController = xfPage.CreateViewController(); // Present new view controller as a regular view controller this.PresentModalViewController(newController, false); }The
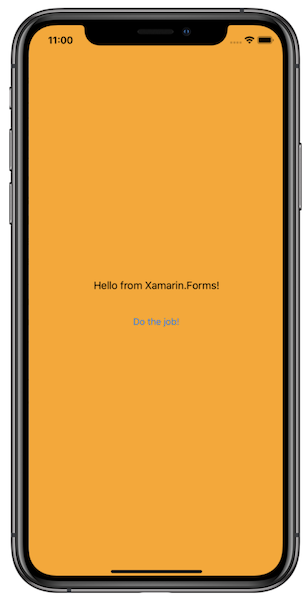
MainPageis instantiated using a standard constructor and before you can use it in the Extension, convert it to a nativeUIViewControllerby using theCreateViewControllerextension method.Build and run the application:
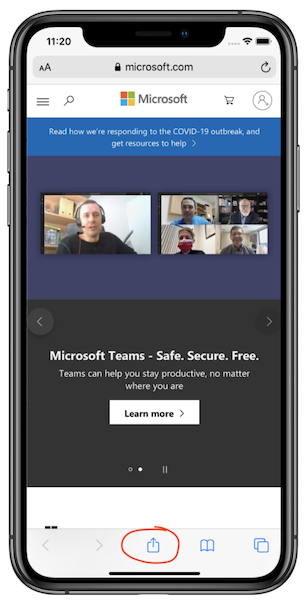
To activate the Extension, navigate to the Safari browser, type in any web address, e.g. microsoft.com, press navigate and then press the Share icon at the bottom of the page to see the available action extensions. From the list of available extensions select the MyAction Extension by tapping on it:
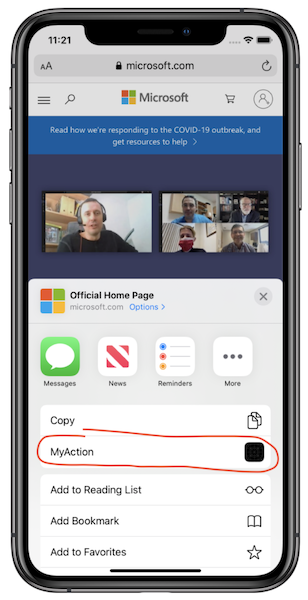
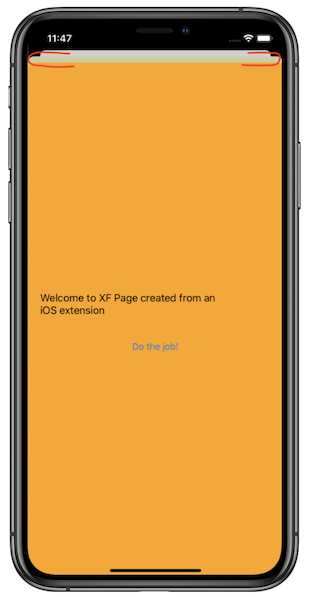
The Extension is activated and the Xamarin.Forms page is displayed to the user. All the bindings and commands work as in the Container app.
The original entry point view controller is visible because it is created and activated by iOS. To fix this, change the modal presentation style to
UIModalPresentationStyle.FullScreenfor the new controller by adding the following code right before thePresentModalViewControllercall:newController.ModalPresentationStyle = UIModalPresentationStyle.FullScreen;Build and run in the iOS simulator or a device:
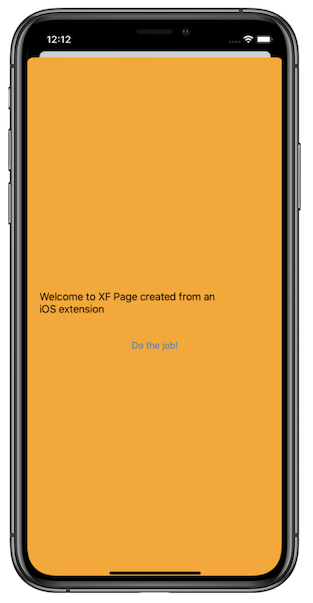
Important
For the device build make sure to use proper build settings and the Release configuration as described here.