Creating a Watch Face
This guide explains how to implement a custom watch face service for Android Wear 1.0. Step-by-step instructions are provided for building a stripped down digital watch face service, followed by more code to create an analog-style watch face.
Overview
In this walkthrough, a basic watch face service is created to illustrate the essentials of creating a custom Android Wear 1.0 watch face. The initial watch face service displays a simple digital watch that displays the current time in hours and minutes:
After this digital watch face is developed and tested, more code is added to upgrade it to a more sophisticated analog watch face with three hands:
Watch face services are bundled and installed as part of a Wear 1.0 app. In
the following examples, MainActivity contains nothing more than the
code from the Wear 1.0 app template so that the watch face service can be
packaged and deployed to the smart watch as part of the app. In effect,
this app will serve purely as a vehicle for getting the watch face
service loaded into the Wear 1.0 device (or emulator) for debugging and
testing.
Requirements
To implement a watch face service, the following is required:
Android 5.0 (API level 21) or higher on the Wear device or emulator.
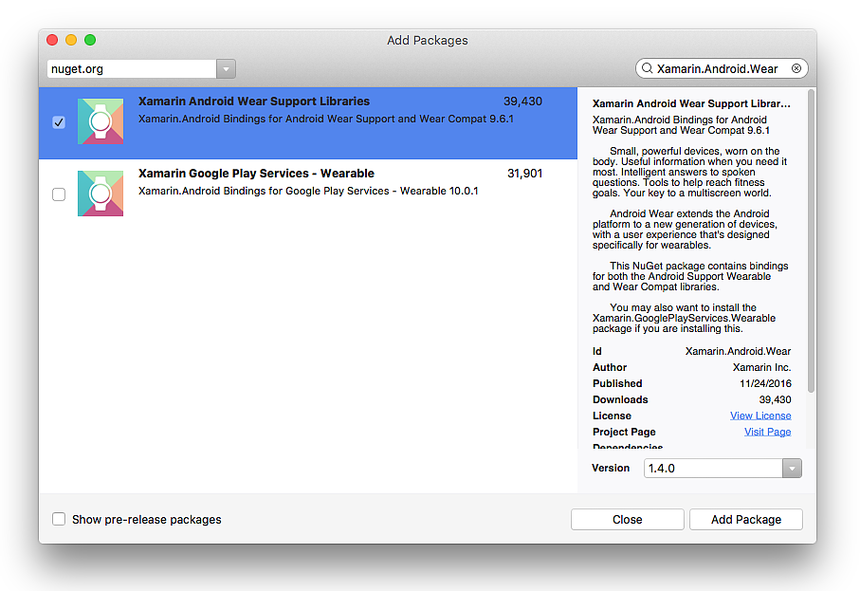
The Xamarin Android Wear Support Libraries must be added to the Xamarin.Android project.
Although Android 5.0 is the minimum API level for implementing a watch face service, Android 5.1 or later is recommended. Android Wear devices running Android 5.1 (API 22) or higher allow Wear apps to control what's displayed on the screen while the device is in low-power ambient mode. When the device leaves low-power ambient mode, it is in interactive mode. For more about these modes, see Keeping Your App Visible.
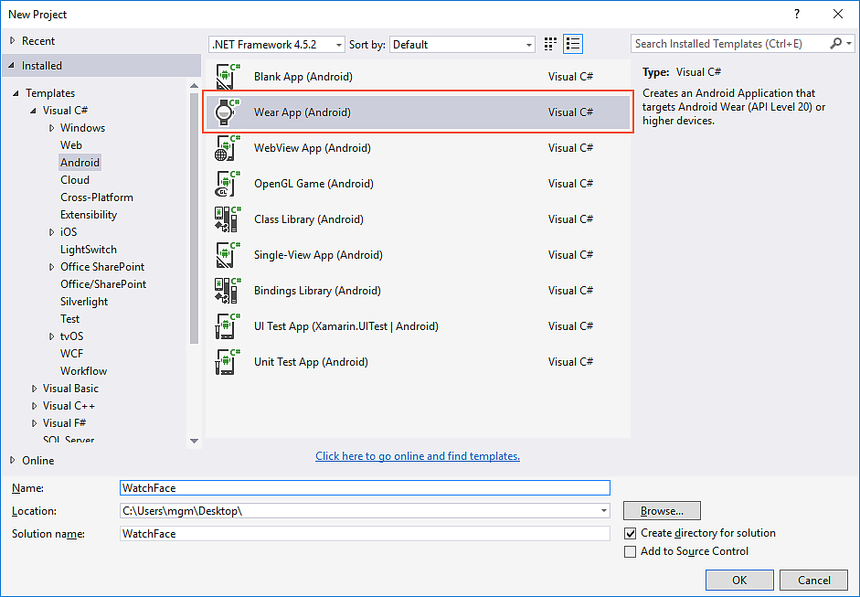
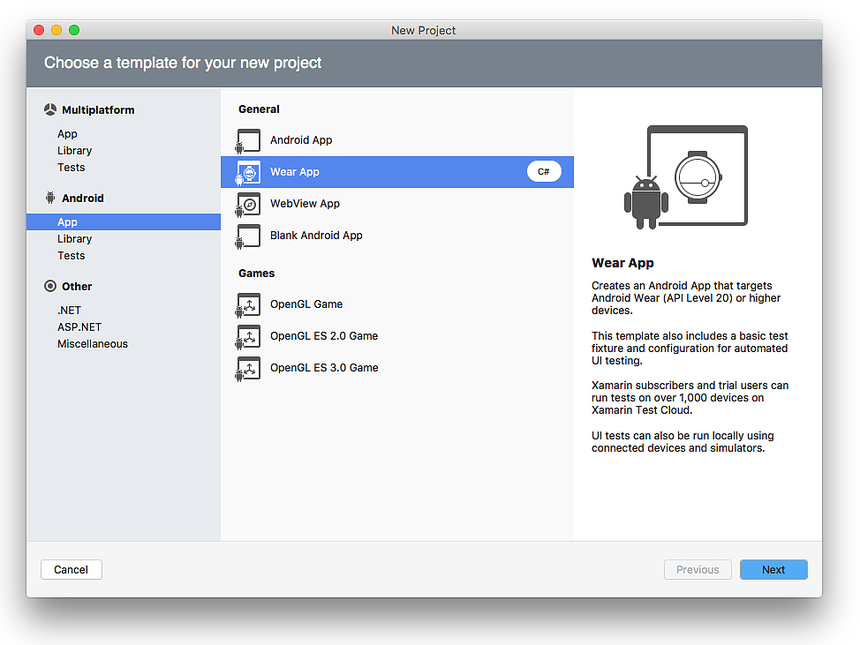
Start an App Project
Create a new Android Wear 1.0 project called WatchFace (for more information about creating new Xamarin.Android projects, see Hello, Android):
Set the package name to com.xamarin.watchface:
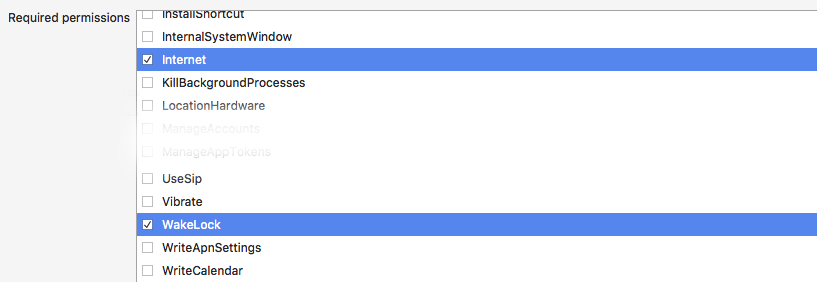
In addition, scroll down and enable the INTERNET and WAKE_LOCK permissions:
Next, download the following file, which will be added to the drawables folder later in this walkthrough:
 &ndash
&ndash
Add the Xamarin.Android Wear Package
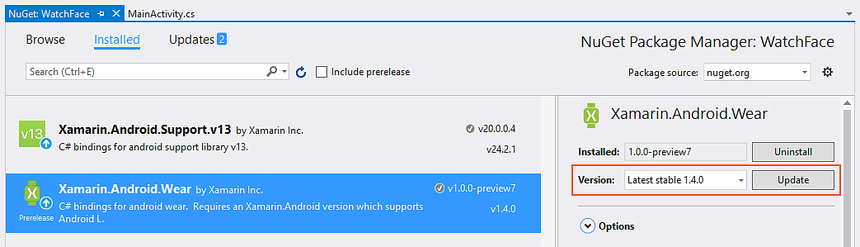
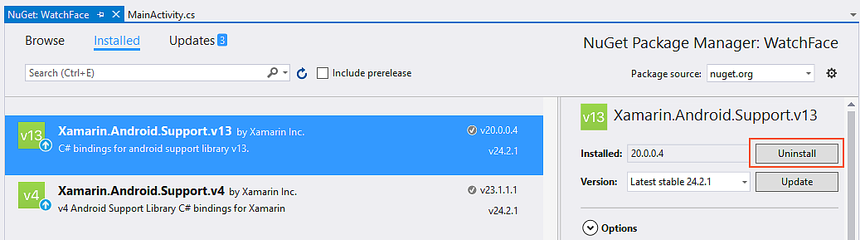
Start the NuGet Package Manager (in Visual Studio, right-click References in the Solution Explorer and select Manage NuGet Packages ...). Update the project to the latest stable version of Xamarin.Android.Wear:
Next, if Xamarin.Android.Support.v13 is installed, uninstall it:
Build and run the app on a Wear device or emulator (for more information about how to do this, see the Getting Started guide). You should see the following app screen on the Wear device:
At this point, the basic Wear app does not have watch face functionality because it does not yet provide a watch face service implementation. This service will be added next.
CanvasWatchFaceService
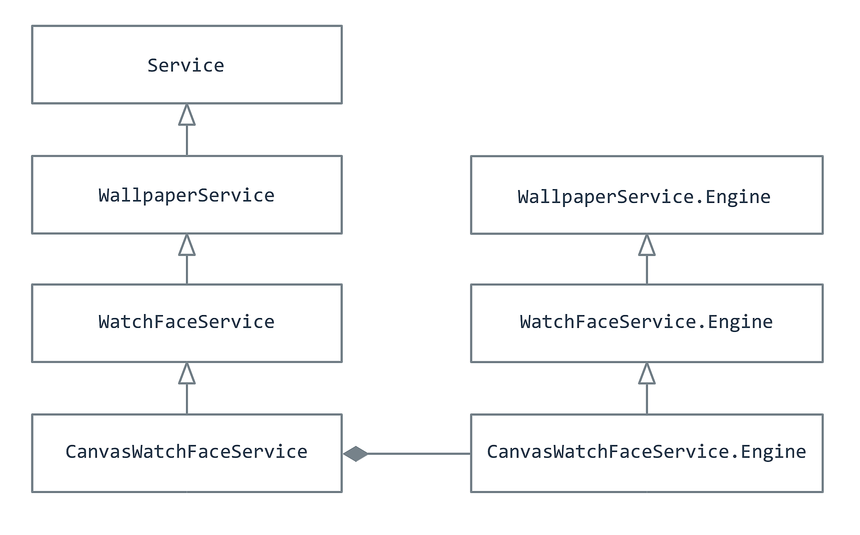
Android Wear implements watch faces via the CanvasWatchFaceService
class. CanvasWatchFaceService is derived from WatchFaceService,
which itself is derived from WallpaperService as shown in
the following diagram:
CanvasWatchFaceService includes a nested
CanvasWatchFaceService.Engine; it instantiates a
CanvasWatchFaceService.Engine object that does the actual work of
drawing the watch face. CanvasWatchFaceService.Engine is derived from
WallpaperService.Engine as shown in the above diagram.
Not shown in this diagram is a Canvas that CanvasWatchFaceService
uses for drawing the watch face – this Canvas is passed in via
the OnDraw method as described below.
In the following sections, a custom watch face service will be created by following these steps:
Define a class called
MyWatchFaceServicethat is derived fromCanvasWatchFaceService.Within
MyWatchFaceService, create a nested class calledMyWatchFaceEnginethat is derived fromCanvasWatchFaceService.Engine.In
MyWatchFaceService, implement aCreateEnginemethod that instantiatesMyWatchFaceEngineand returns it.In
MyWatchFaceEngine, implement theOnCreatemethod to create the watch face style and perform any other initialization tasks.Implement the
OnDrawmethod ofMyWatchFaceEngine. This method is called whenever the watch face needs to be redrawn (i.e. invalidated).OnDrawis the method that draws (and redraws) watch face elements such as hour, minute, and second hands.Implement the
OnTimeTickmethod ofMyWatchFaceEngine.OnTimeTickis called at least once per minute (in both ambient and interactive modes) or when the date/time has changed.
For more information about CanvasWatchFaceService, see
the Android
CanvasWatchFaceService API documentation.
Similarly,
CanvasWatchFaceService.Engine explains
the actual implementation of the watch face.
Add the CanvasWatchFaceService
Add a new file called MyWatchFaceService.cs (in Visual Studio, right-click WatchFace in the Solution Explorer, click Add > New Item..., and select Class).
Replace the contents of this file with the following code:
using System;
using Android.Views;
using Android.Support.Wearable.Watchface;
using Android.Service.Wallpaper;
using Android.Graphics;
namespace WatchFace
{
class MyWatchFaceService : CanvasWatchFaceService
{
public override WallpaperService.Engine OnCreateEngine()
{
return new MyWatchFaceEngine(this);
}
public class MyWatchFaceEngine : CanvasWatchFaceService.Engine
{
CanvasWatchFaceService owner;
public MyWatchFaceEngine (CanvasWatchFaceService owner) : base(owner)
{
this.owner = owner;
}
}
}
}
MyWatchFaceService (derived from CanvasWatchFaceService) is the
"main program" of the watch face. MyWatchFaceService implements only
one method, OnCreateEngine, which instantiates and returns a
MyWatchFaceEngine object (MyWatchFaceEngine is derived from
CanvasWatchFaceService.Engine). The instantiated MyWatchFaceEngine
object must be returned as a WallpaperService.Engine. The
encapsulating MyWatchFaceService object is passed into the
constructor.
MyWatchFaceEngine is the actual watch face implementation – it
contains the code that draws the watch face. It also handles system
events such as screen changes (ambient/interactive modes, screen
turning off, etc.).
Implement the Engine OnCreate method
The OnCreate method initializes the watch face. Add the following
field to MyWatchFaceEngine:
Paint hoursPaint;
This Paint object will be used to draw the current time on the watch
face. Next, add the following method to MyWatchFaceEngine:
public override void OnCreate(ISurfaceHolder holder)
{
base.OnCreate (holder);
SetWatchFaceStyle (new WatchFaceStyle.Builder(owner)
.SetCardPeekMode (WatchFaceStyle.PeekModeShort)
.SetBackgroundVisibility (WatchFaceStyle.BackgroundVisibilityInterruptive)
.SetShowSystemUiTime (false)
.Build ());
hoursPaint = new Paint();
hoursPaint.Color = Color.White;
hoursPaint.TextSize = 48f;
}
OnCreate is called shortly after MyWatchFaceEngine is started. It
sets up the WatchFaceStyle (which controls how the Wear device
interacts with the user) and instantiates the Paint object that will be
used to display the time.
The call to SetWatchFaceStyle does the following:
Sets peek mode to
PeekModeShort, which causes notifications to appear as small "peek" cards on the display.Sets the background visibility to
Interruptive, which causes the background of a peek card to be shown only briefly if it represents an interruptive notification.Disables the default system UI time from being drawn on the watch face so that the custom watch face can display the time instead.
For more information about these and other watch face style options, see the Android WatchFaceStyle.Builder API documentation.
After SetWatchFaceStyle completes, OnCreate instantiates the
Paint object (hoursPaint) and sets its color to white and its
text size to 48 pixels
(TextSize must be specified in pixels).
Implement the Engine OnDraw method
The OnDraw method is perhaps the most important
CanvasWatchFaceService.Engine method – it is the method that
actually draws watch face elements such as digits and clock face hands.
In the following example, it draws a time string on the watch face.
Add the following method to MyWatchFaceEngine:
public override void OnDraw (Canvas canvas, Rect frame)
{
var str = DateTime.Now.ToString ("h:mm tt");
canvas.DrawText (str,
(float)(frame.Left + 70),
(float)(frame.Top + 80), hoursPaint);
}
When Android calls OnDraw, it passes in a Canvas instance and the
bounds in which the face can be drawn. In the above code example,
DateTime is used to calculate the current time in hours and minutes
(in 12-hour format). The resulting time string is drawn on the canvas
by using the Canvas.DrawText method. The string will appear 70 pixels
over from the left edge and 80 pixels down from the top edge.
For more information about the OnDraw method, see the Android
onDraw API documentation.
Implement the Engine OnTimeTick method
Android periodically calls the OnTimeTick method to update the time
shown by the watch face. It is called at least once per minute (in both
ambient and interactive modes), or when the date/time or timezone have
changed. Add the following method to MyWatchFaceEngine:
public override void OnTimeTick()
{
Invalidate();
}
This implementation of OnTimeTick simply calls Invalidate. The
Invalidate method schedules OnDraw to redraw the watch face.
For more information about the OnTimeTick method, see the Android
onTimeTick
API documentation.
Register the CanvasWatchFaceService
MyWatchFaceService must be registered in the AndroidManifest.xml of
the associated Wear app. To do this, add the following XML to the
<application> section:
<service
android:name="watchface.MyWatchFaceService"
android:label="Xamarin Sample"
android:allowEmbedded="true"
android:taskAffinity=""
android:permission="android.permission.BIND_WALLPAPER">
<meta-data
android:name="android.service.wallpaper"
android:resource="@xml/watch_face" />
<meta-data
android:name="com.google.android.wearable.watchface.preview"
android:resource="@drawable/preview" />
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.service.wallpaper.WallpaperService" />
<category android:name="com.google.android.wearable.watchface.category.WATCH_FACE" />
</intent-filter>
</service>
This XML does the following:
Sets the
android.permission.BIND_WALLPAPERpermission. This permission gives the watch face service permission to change the system wallpaper on the device. Note that this permission must be set in the<service>section rather than in the outer<application>section.Defines a
watch_faceresource. This resource is a short XML file that declares awallpaperresource (this file will be created in the next section).Declares a drawable image called
previewthat will be displayed by the watch picker selection screen.Includes an
intent-filterto let Android know thatMyWatchFaceServicewill be displaying a watch face.
That completes the code for the basic WatchFace example. The next
step is to add the necessary resources.
Add resource files
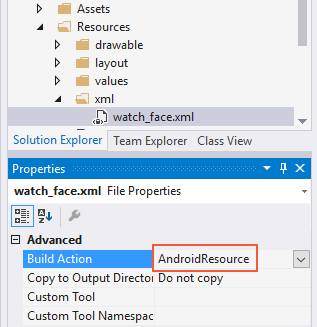
Before you can run the watch service, you must add the watch_face resource and the preview image. First, create a new XML file at Resources/xml/watch_face.xml and replace its contents with the following XML:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<wallpaper xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" />
Set this file's build action to AndroidResource:
This resource file defines a simple wallpaper element that will be
used for the watch face.
If you have not yet done so, download the following image:
 .
.
Install it at Resources/drawable/preview.png. Be sure to add this file
to the WatchFace project. This preview image is displayed to the user
in the watch face picker on the Wear device. To create a preview image for
your own watch face, you can take a screenshot of the watch face while
it is running. (For more about getting screenshots from
Wear devices, see Taking screenshots).
Try it!
Build and deploy the app to the Wear device. You should see the Wear app screen appear as before. Do the following to enable the new watch face:
Swipe to the right until you see the background of the watch screen.
Touch and hold anywhere on the background of the screen for two seconds.
Swipe from left to right to browse through the various watch faces.
Select the Xamarin Sample watch face (shown on the right):
Tap the Xamarin Sample watch face to select it.
This changes the watch face of the Wear device to use the custom watch face service implemented so far:
This is a relatively crude watch face because the app implementation is
so minimal (for example, it doesn't include a watch face background and
it doesn't call Paint anti-alias methods to improve the appearance).
However, it does implement the bare-bones functionality that is
required to create a custom watch face.
In the next section, this watch face will be upgraded to a more sophisticated implementation.
Upgrading the watch face
In the remainder of this walkthrough, MyWatchFaceService is upgraded
to display an analog-style watch face and it is extended to support
more features. The following capabilities will be added to create the
upgraded watch face:
Indicates the time with analog hour, minute, and second hands.
Reacts to changes in visibility.
Responds to changes between ambient mode and interactive mode.
Reads the properties of the underlying Wear device.
Automatically updates the time when a time zone change takes place.
Before implementing the code changes below, download
drawable.zip, unzip it, and move the unzipped
.png files to Resources/drawable (overwrite the previous
preview.png). Add the new .png files to the WatchFace project.
Update Engine features
The next step is upgrade MyWatchFaceService.cs to an implementation that draws an analog watch face and supports new features. Replace the contents of MyWatchFaceService.cs with the analog version of the watch face code in MyWatchFaceService.cs (you can cut and paste this source into the existing MyWatchFaceService.cs).
This version of MyWatchFaceService.cs adds more code to the existing methods and includes additional overridden methods to add more functionality. The following sections provide a guided tour of the source code.
OnCreate
The updated OnCreate method configures the watch face style as before, but it includes some additional steps:
Sets the background image to the xamarin_background resource that resides in Resources/drawable-hdpi/xamarin_background.png.
Initializes
Paintobjects for drawing the hour hand, minute hand, and second hand.Initializes a
Paintobject for drawing the hour ticks around the edge of the watch face.Creates a timer that calls the
Invalidate(redraw) method so that the second hand will be redrawn every second. Note that this timer is necessary becauseOnTimeTickcallsInvalidateonly once every minute.
This example includes only one xamarin_background.png image; however, you may want to create a different background image for each screen density that your custom watch face will support.
OnDraw
The updated OnDraw method draws an analog-style watch face using the following steps:
Gets the current time, which is now maintained in a
timeobject.Determines the bounds of the drawing surface and its center.
Draws the background, scaled to fit the device when the background is drawn.
Draws twelve ticks around the face of the clock (corresponding to the hours on the clock face).
Calculates the angle, rotation, and length for each watch hand.
Draws each hand on the watch surface. Note that the second hand is not drawn if the watch is in ambient mode.
OnPropertiesChanged
This method is called to inform MyWatchFaceEngine about the
properties of the Wear device (such as low-bit ambient mode and burn-in
protection). In MyWatchFaceEngine, this method only checks for
low bit ambient mode (in low bit ambient mode, the screen supports
fewer bits for each color).
For more information about this method, see the Android onPropertiesChanged API documentation.
OnAmbientModeChanged
This method is called when the Wear device enters or exits ambient
mode. In the MyWatchFaceEngine implementation, the watch face
disables anti-aliasing when it is in ambient mode.
For more information about this method, see the Android onAmbientModeChanged API documentation.
OnVisibilityChanged
This method is called whenever the watch becomes visible or hidden. In
MyWatchFaceEngine, this method registers/unregisters the time zone
receiver (described below) according to the visibility state.
For more information about this method, see the Android onVisibilityChanged API documentation.
Time zone feature
The new MyWatchFaceService.cs also includes functionality to update
the current time whenever the time zone changes (such as while
traveling across time zones). Near the end of MyWatchFaceService.cs,
a time zone change BroadcastReceiver is defined that handles
timezone-changed Intent objects:
public class TimeZoneReceiver: BroadcastReceiver
{
public Action<Intent> Receive { get; set; }
public override void OnReceive (Context context, Intent intent)
{
if (Receive != null)
Receive (intent);
}
}
The RegisterTimezoneReceiver and UnregisterTimezoneReceiver methods
are called by the OnVisibilityChanged method.
UnregisterTimezoneReceiver is called when the visibility state of the
watch face is changed to hidden. When the watch face is visible again,
RegisterTimezoneReceiver is called (see the OnVisibilityChanged
method).
The engine RegisterTimezoneReceiver method declares a handler for
this time zone receiver's Receive event; this handler updates the
time object with the new time whenever a time zone is crossed:
timeZoneReceiver = new TimeZoneReceiver ();
timeZoneReceiver.Receive = (intent) => {
time.Clear (intent.GetStringExtra ("time-zone"));
time.SetToNow ();
};
An intent filter is created and registered for the time zone receiver:
IntentFilter filter = new IntentFilter(Intent.ActionTimezoneChanged);
Application.Context.RegisterReceiver (timeZoneReceiver, filter);
The UnregisterTimezoneReceiver method unregisters the time zone
receiver:
Application.Context.UnregisterReceiver (timeZoneReceiver);
Run the improved watch face
Build and deploy the app to the Wear device again. Select the watch face from the watch face picker as before. The preview in the watch picker is shown on the left, and the new watch face is shown on the right:
In this screenshot, the second hand is moving once per second. When you run this code on a Wear device, the second hand disappears when the watch enters ambient mode.
Summary
In this walkthrough, a custom Android Wear 1.0 watchface was implemented
and tested. The CanvasWatchFaceService and
CanvasWatchFaceService.Engine classes were introduced, and the
essential methods of the engine class were implemented to create a
simple digital watch face. This implementation was updated with more
functionality to create an analog watch face, and additional methods
were implemented to handle changes in visibility, ambient mode, and
differences in device properties. Finally, a time zone broadcast
receiver was implemented so that the watch automatically updates the
time when a time zone is crossed.