Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Before you can start storing SQL Server data files in Azure Storage, you must first create an Azure Storage account and a blob container, and a shared access signature. Lesson 1 walks you through the steps of logging into the Azure Management Portal, creating a storage account, a blob container, and a shared access signature.
By default, only the owner of the storage account may access blobs, tables, and queues within that account. To be able to access these resources using this new SQL Server enhancement without sharing the storage account access key, you are required to do these:
Set the container's permissions to private.
Create a shared access signature. It enables you to delegate restricted access to a container, blob, table, or queue resource by specifying the interval for which the resources are available and the permissions that a client will have to it.
Use a stored access policy to manage shared access signatures for a container or its blobs. The stored access policy gives you an additional measure of control over your shared access signatures and also provides a straightforward means to revoke them.
For more information, see Manage Access to Azure Storage Resources.
Create Storage Account
To create a storage account on the Azure Management Portal, follow these steps:
Log in to the Azure Management Portal using your account. If you do not have an Azure account, visit Azure free trial.
Use the step by step instructions to create a storage account. Note that when creating a storage account to be used for the SQL Server Data Files in Azure feature, you should unselect or disable the geo-replication. This is because write order is not guaranteed for multiple blobs participating in geo-replication. If a storage account is geo-replicated and recovery is required, a corruption occurs.

Create a Blob container
In Azure, a container provides a grouping of a set of blobs. All blobs must be in a container. A storage account can contain an unlimited number of containers, but must have at least one container. A container can store an unlimited number of blobs. For most up-to-date information on storage size limits, see How to use the Azure Blob Storage Service in .NET.
To create a container in Azure, follow these steps:
Log in to the Azure Management Portal.
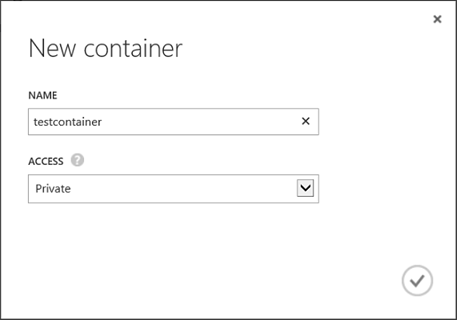
Select the storage account, click the CONTAINERS tab and click ADD CONTAINER at the bottom of the screen, which opens a new dialog box.
Enter a name for the container.
Select Private for Access Type. When you set the access to private, the container and blob data can be read by the Azure account owner only.
Note
To create a container programmatically, you can also use REST APIs. For more information, see Create Container and also Azure Storage Services REST API Reference.
Next Lesson:
Lesson 2. Create a policy on container and generate a Shared Access Signature (SAS) key