Transparent Data Encryption with Azure SQL Database
Azure SQL Database transparent data encryption (preview) helps protect against the threat of malicious activity by performing real-time encryption and decryption of the database, associated backups, and transaction log files at rest without requiring changes to the application.
TDE encrypts the storage of an entire database by using a symmetric key called the database encryption key. In SQL Database the database encryption key is protected by a built-in server certificate. The built-in server certificate is unique for each SQL Database server. If a database is in a GeoDR relationship, it is protected by a different key on each server. If 2 databases are connected to the same server, they share the same built-in certificate. Microsoft automatically rotates these certificates at least every 90 days. For a general description of TDE, see Transparent Data Encryption (TDE).
Azure SQL Database does not support Azure Key Vault integration with TDE. SQL Server running on an Azure virtual machine can use an asymmetric key from the Key Vault. For more information, see Example A: Transparent Data Encryption by Using an Asymmetric Key from the Key Vault.
| Applies to: SQL Database V12 (Preview in some regions). |
Important
This is currently a preview feature. I acknowledge and agree that implementation of SQL Database transparent data encryption in my database(s) is subject to the preview terms in my license agreement (e.g. the Enterprise Agreement, Microsoft Azure Agreement, or Microsoft Online Subscription Agreement), as well as any applicable Supplemental Terms of Use for Microsoft Azure Preview.
The preview of status of TDE applies even in the subset of geographic regions where version family V12 of SQL Database is announced as now being in general availability status. TDE for SQL Database is not intended for use in production databases until Microsoft announces that TDE is promoted from preview to GA. For more information about SQL Database V12, see What's new in Azure SQL Database.
Permissions
To sign up for the preview and to configure TDE through the Azure portal, by using the REST API, or by using PowerShell, you must be connected as the Azure Owner, Contributor, or SQL Security Manager.
To configure TDE by using Transact-SQL requires the following:
You must be already signed up for the TDE preview.
To create the database encryption key you must be a SQL Database administrator or you must be a member of the dbmanager role in the master database and have the CONTROL permission on the database.
To execute the ALTER DATABASE statement with the SET option only requires membership in the dbmanager role.
Sign Up for the Preview of TDE and Enable TDE on a Database
Visit the Azure Portal at https://portal.azure.com and sign-in with your Azure Administrator or Contributor account.
On the left banner, click to BROWSE, and then click SQL databases.
With SQL databases selected in the left pane, click your user database.
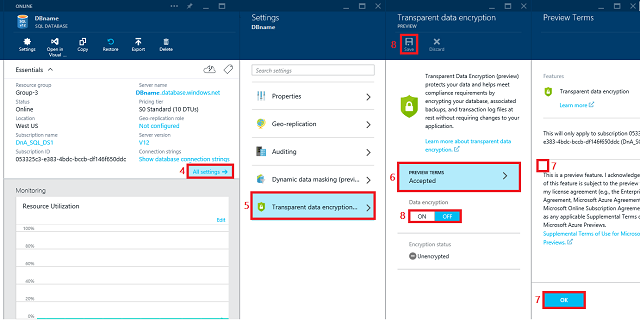
In the database blade, click All settings.
In the Settings blade, click Transparent data encryption (preview) part to open the Transparent data encryption PREVIEW blade. If you have not already signed up for the TDE preview, the data encryption settings will be disabled until you complete signup.
Click PREVIEW TERMS.
Read the terms of the preview, and if you agree to the terms, select the Transparent Data encryptionPreview terms check box, and then click OK near the bottom of the page. Returning to the Data encryptionPREVIEW blade, where the Data encryption button should now be enabled.
In the Data encryption PREVIEW blade, move the Data encryption button to On, and then click Save (at the top of the page) to apply the setting. The Encryption status will approximate the progress of the transparent data encryption.
You can also monitor the progress of encryption by connecting to SQL Database using a query tool such as SQL Server Management Studio as a database user with the VIEW DATABASE STATE permission. Query the
encryption_statecolumn of the sys.dm_database_encryption_keys view.
Enabling TDE on SQL Database by Using Transact-SQL
The following steps, assume you have already signed up for the preview.
Connect to the database using a login that is an administrator or a member of the dbmanager role in the master database.
Execute the following statements to create a database encryption key and encrypt the database.
-- Create the database encryption key that will be used for TDE. CREATE DATABASE ENCRYPTION KEY WITH ALGORITHM = AES_256 ENCRYPTION BY SERVER CERTIFICATE ##MS_TdeCertificate##; -- Enable encryption ALTER DATABASE [AdventureWorks] SET ENCRYPTION ON; GOTo monitor the progress of encryption on SQL Database, database users with the VIEW DATABASE STATE permission can query the
encryption_statecolumn of the sys.dm_database_encryption_keys view.
Enabling TDE on SQL Database by Using PowerShell
Using the Azure PowerShell you can run the following command to turn TDE on/off. You do have to connect your account to the PS window before running the command. The following steps, assume you have already signed up for the preview. For additional information about PowerShell, see How to install and configure Azure PowerShell.
To enable TDE, return the TDE status, and view the encryption activity.
Switch-AzureMode -Name AzureResourceManager Set-AzureSqlDatabaseTransparentDataEncryption -ServerName "myserver" -ResourceGroupName "Default-SQL-WestUS" -DatabaseName "database1" -State "Enabled" Get-AzureSqlDatabaseTransparentDataEncryption -ServerName "myserver" -ResourceGroupName "Default-SQL-WestUS" -DatabaseName "database1" Get-AzureSqlDatabaseTransparentDataEncryptionActivity -ServerName "myserver" -ResourceGroupName "Default-SQL-WestUS" -DatabaseName "database1"To disable TDE:
Set-AzureSqlDatabaseTransparentDataEncryption -ServerName "myserver" -ResourceGroupName "Default-SQL-WestUS" -DatabaseName "database1" -State "Disabled" Switch-AzureMode -Name AzureServiceManagement
Decrypting a TDE Protected Database on SQL Database
To Disable TDE by Using the Azure Portal
Visit the Azure Portal at https://portal.azure.com and sign-in with your Azure Administrator or Contributor account.
On the left banner, click to BROWSE, and then click SQL databases.
With SQL databases selected in the left pane, click your user database.
In the database blade, click All settings.
In the Settings blade, click Transparent data encryption (preview) part to open the Transparent data encryption PREVIEW blade.
In the Transparent data encryption PREVIEW blade, move the Data encryption button to Off, and then click Save (at the top of the page) to apply the setting. The Encryption status will approximate the progress of the transparent data decryption.
You can also monitor the progress of decryption by connecting to SQL Database using a query tool such as Management Studio as a database user with the VIEW DATABASE STATE permission. Query the
encryption_statecolumn of the sys.dm_database_encryption_keysview.
To Disable TDE by Using Transact-SQL
Connect to the database using a login that is an administrator or a member of the dbmanager role in the master database.
Execute the following statements to decrypt the database.
-- Enable encryption ALTER DATABASE [AdventureWorks] SET ENCRYPTION OFF; GOTo monitor the progress of encryption on SQL Database, database users with the VIEW DATABASE STATE permission can query the
encryption_statecolumn of the sys.dm_database_encryption_keys view.
Working with TDE Protected Databases on SQL Database
You do not need to decrypt databases for operations within Azure. The TDE settings on the source database or primary database are transparently inherited on the target. This includes operations involving:
Geo-Restore
Self-Service Point in Time Restore
Restore a Deleted Database
Active Geo_Replication
Creating a Database Copy
Moving a TDE Protected Database on using .Bacpac Files
When exporting a TDE protected database using the Export Database function in the Azure SQL Database Portal or the SQL Server Import and Export Wizard, the content of the database is not encrypted. The content is stored in .bacpac files which are not encrypted. Be sure to protect the .bacpac files appropriately and enable TDE once import of the new database is completed.
Related SQL Server Topic
See Also
Transparent Data Encryption (TDE) CREATE CREDENTIAL (Transact-SQL) CREATE ASYMMETRIC KEY (Transact-SQL) CREATE DATABASE ENCRYPTION KEY (Transact-SQL) ALTER DATABASE (Transact-SQL) ALTER DATABASE SET Options (Transact-SQL)