R Server 9.1 installation instructions for Teradata Servers
Microsoft R Server 9.1 for Teradata is an R-based analytical engine embedded in your Teradata data warehouse. This article provides detailed instructions for installing Microsoft R Server 9.1 for Teradata in the Teradata data warehouse. For configuring local workstations to submit jobs to run within your Teradata data warehouse, see Microsoft R Server Client Installation Manual for Teradata.
Microsoft R Server for Teradata is required for running Microsoft R Server scalable analytics in-database. If you do not need to run your analytics in-database, but simply need to access Teradata data via Teradata Parallel Transport or ODBC, you do not need to install Microsoft R Server in your Teradata data warehouse. You will, however, need to configure your local workstations as described in Microsoft R Server Client Installation Manual for Teradata.
Important
The Teradata compute context was discontinued in Machine Learning Server 9.2.1. If you have R Server 9.1 and use the Teradata compute context, you are covered by Microsoft's service support policy. For future compatibility, we recommend modifying existing code to run in other compute contexts, and create a Teradata data source object to work with your data. For more information about Teradata as a data source, see RxTeradata.
System Requirements
Microsoft R Server for Teradata has the following system requirements:
Processor: 64-bit processor with x86-compatible architecture (variously known as AMD64, Intel64, x86-64, IA-32e, EM64T, or x64 chips). Itanium-architecture chips (also known as IA-64) are not supported. Multiple-core chips are recommended.
Operating System: SUSE Linux Enterprise Server SLES11 SP1 64-bit is supported.
Teradata Version: Teradata 15.10, 15.00, or 14.10.
Memory: A minimum of 1 GB of RAM is required; 4 GB or more are recommended.
Disk Space: A minimum of 500 MB of disk space is required
The following specific libraries must be installed on the Teradata appliance from the SLES 11 installation DVDs:
SLES-11-SP1-DVD-x86_64-GM-DVD1.iso/suse/x86_64/ghostscript-fonts-std-8.62-32.27.31.x86_64.rpm
SLES-11-SP1-DVD-x86_64-GM-DVD1.iso/suse/x86_64/libicu-4.0-7.24.11.x86_64.rpm
SLE-11-SP1-SDK-DVD-x86_64-GM-DVD1.iso/suse/x86_64/libstdc++45-4.5.0_20100414-1.2.7.x86_64.rpm
SLE-11-SP1-SDK-DVD-x86_64-GM-DVD1.iso/suse/x86_64/libgfortran43-4.3.4_20091019-0.7.35.x86_64.rpm
SLE-11-SP1-SDK-DVD-x86_64-GM-DVD1.iso/suse/x86_64/gcc43-fortran-4.3.4_20091019-0.7.35.x86_64.rpm
SLE-11-SP1-SDK-DVD-x86_64-GM-DVD1.iso/suse/x86_64/gcc-fortran-4.3-62.198.x86_64.rpm
Dependency: The file libstdc++6-5.3.1.x86_64.rpm is included with MRS 9.1. This may cause conflicts with existing rpms. If you opt to perform this install, the rpm needs to be installed on each node. If you cannot install this, rpm MRS 9.1 will not work.
A method of doing so is to execute the following command on each node:
zypper -n install --force-resolution libstdc++6-5.3.1.x86_64.rpm
Download software
First, download the version of Microsoft R Open. For this release, you must have Microsoft R Open 3.3.3 for SLES 11 (found at the mro repository.
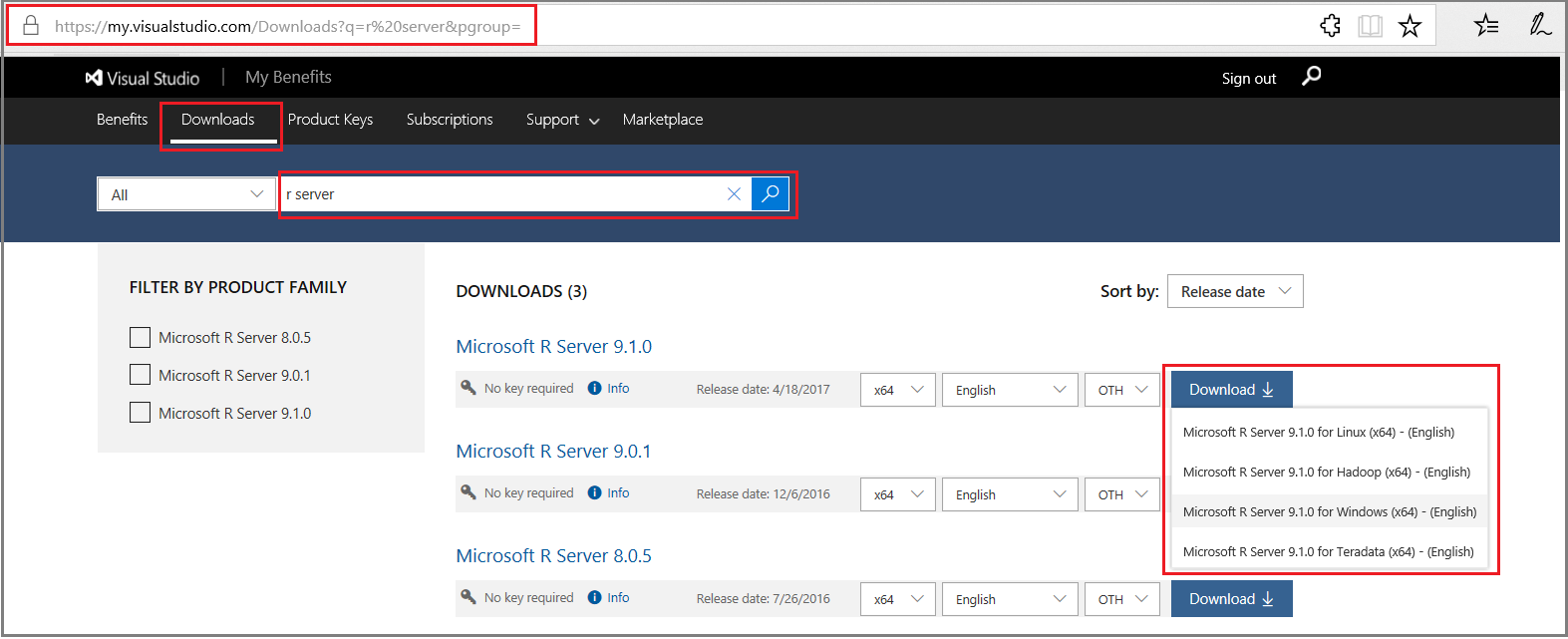
Second, download R Server 9.1 for Teradata from Visual Studio Dev Essentials.
- Click Join or access now to sign up for download benefits.
- Check the URL to verify it changed to https://my.visualstudio.com/.
- Click Downloads to search for R Server.
- Click Downloads for a specific version to select the platform.
Installing the Microsoft R Server rpms
We recommend using the Teradata Parallel Update Tool (PUT) to install the Microsoft R Server rpms.
PUT is a browser-based utility, and we recommend that you upgrade to the latest version. Newer versions contain the PUT Customer Mode, which is the easiest way to install Microsoft R Server.
If you have an iso file, you must first mount the file. The following commands create a mount point and mount the file to that mount point (replacing MSDN with the name of the current ISO downloaded):
mkdir /mnt/mrsimage mount –o loop MSDN.iso /mnt/mrsimage
If you have a gzipped tar file, you should unpack the file as follows (be sure you have downloaded the file to a writable directory, such as /tmp):
tar -zxf en_r_server_910_for_teradata_x64_10324043.tar.gz
This creates the directory MRS91Teradata. This is where you can find the libstdc++6-5.3.1.x86_64.rpm (dependency discussed above). If you cannot install this rpm MRS 9.1 will not work.
Agree to license agreements: /MRS90Teradata/ MRO_EULA.txt /MRS90Teradata/ MRO_EULA.txt
Copy the following files to the Customer Mode directory (which you may need to create) /var/opt/teradata/customermodepkgs:
microsoft-r-open-3.3.3.tar.gz MRS90Teradata/RPM/microsoft-r-server-packages-9.1.rpm MRS90Teradata/RPM/microsoft-r-server-teradata-9.1.rpm
Point your Java-enabled browser to
https://<HOSTIP>:8443/putwhere<HOSTIP>is the IP address of your Teradata data warehouse node and log in to Customer Mode using a Linux account such as root (not a database account).
To install the Microsoft R Server rpms on all the nodes, do the following:
The initial PUT screen asks you to select an operation. Select Install/Upgrade Software.
At the Install/Upgrade Software: Customer Mode step, confirm the summary and click Next.
You may receive a dialog box saying that PUT was unable to find any packages to auto-select. If you see this dialog box, click OK.
Select microsoft-r-server-teradata-9.1.
Select all Groups and click >> to install on all groups, then click Next.
Review the list of dependencies and files to be installed, then click Yes.
Click Next
Clear the “Restore normal Teradata Vital Infrastructure (TVI) escalation path (recommended)” check box.
Click Finish.
Setting Up the Revolution Analytics Database
After you have installed the rpms, change directory to the "teradata" directory and run the revoTdSetup.sh script as follows:
Depending on Teradata version cd to:
/usr/lib64/microsoft-r/3.3.3/teradata/1510 or
/usr/lib64/microsoft-r/3.3.3/teradata/1500 or
/usr/lib64/microsoft-r/3.3.3/teradata/1410
chmod u+x ./revoTdSetup.sh
./revoTdSetup.sh
Enter the parent user database name and password at the prompts. Do not modify this script, and in particular, do not modify the name of the revoAnalytics_Zqht2 database. The database administrator running the script must have specific grants, as described in the next section
If you have previously run Microsoft R Server on your Teradata database, restart the database before proceeding.
Adding and Configuring Users
All users who interact with the database, including the database administrator, need to have specific grants. The following example provides an existing “sysdba” user the required grants to run the revoTdSetup.sh script:
grant all on sysdba to sysdba with grant option;
If you don’t already have such a user, the following example creates a database administrator user named "sysdba" with the required grants to run the revoTdSetup.sh script:
# Create the user who will run revoTdSetup.sh (e.g., sysdba):
bteq .logon localhost/dbc,dbc
create user SYSDBA from dbc as perm=25E9, spool=15E9, temporary=15E9, password=sysdba;
grant select, execute on dbc to sysdba with grant option;
grant all on sysdba to sysdba with grant option;
grant select on sys_calendar to sysdba with grant option;
grant select on dbc to public;
You will often want to allow a user account to run jobs on data in other databases also. The lines shown as follows are examples of the types of permissions your Revolution users may require. (For convenience, these steps are organized according to the purpose of the permissions granted.)
First, you need to grant permissions for the user account to work with the Revolution database. Log on to bteq with your admin account, and run the following lines. Substitute the new user account name for 'ut1' in the sample lines as follows:
-- grant ut1 various permissions on revoAnalytics_Zqht2 DB grant execute procedure on revoAnalytics_Zqht2.InitRevoJob to ut1; grant execute procedure on revoAnalytics_Zqht2.StartRevoJobXsp to ut1; grant execute procedure on revoAnalytics_Zqht2.GetRevoJobState to ut1; grant execute procedure on revoAnalytics_Zqht2.RemoveRevoJobResults to ut1; grant execute function on revoAnalytics_Zqht2.FinishRevoJob to ut1; grant execute function on revoAnalytics_Zqht2.DistributeRevoJobDataUdf to ut1; grant execute function on revoAnalytics_Zqht2.revoAnalyticsTblOp to ut1; grant select on revoAnalytics_Zqht2.RevoAnalyticsJobResults to ut1; -- the following two create view and drop view grants are for the -- table operator PARTITION BY work-around -- for Teradata's Issue DR166609, which was fixed in 14.10.02d grant create view on revoAnalytics_Zqht2 to ut1; grant drop view on revoAnalytics_Zqht2 to ut1;Next you need to grant permissions for the user account and the revolution database to work with data in the user account database. Run the following lines, substituting your user account name for 'ut1'.
-- grant ut1 rights on db with data to be analyzed - -- in this case itself grant all on ut1 to ut1; -- give revoAnalytics_Zqht2 rights on database with data to -- be analyzed - in this case ut1 grant select on ut1 to revoAnalytics_Zqht2; grant create table on ut1 to revoAnalytics_Zqht2; grant drop table on ut1 to revoAnalytics_Zqht2;Finally, you want to grant permissions on any other databases you wish that account to have access to. Run the following lines, substituting your user account name for 'ut1', and your other database name for 'RevoTestDB'.
-- grant ut1 rights on db with data to be analyzed grant select on RevoTestDB to ut1; -- give revoAnalytics_Zqht2 rights on database with data to -- be analyzed grant select on RevoTestDB to revoAnalytics_Zqht2; grant create table on RevoTestDB to revoAnalytics_Zqht2;
Managing Memory in In-Teradata Computations
Because a Teradata cluster node typically has many worker processes (AMPs) running constantly, it is important to limit how much memory a distributed analysis consumes. Microsoft R Server provides stored procedures in the revoAnalytics_Zqht2 scheduler database that allow a database administrator to set the memory limits for master and worker processes working on a RevoScaleR job. By default, the master process memory limit is 2000 MB (2GB) and the worker process memory limit is 1000 MB (1GB).
These limits may be customized by a database administrator using the SetMasterMemoryLimitMB() and SetWorkerMemoryLimitMB() stored procedures, defined in the revoAnalytics_Zqht2 database created on installation.
For example, to set the master memory limit to 3000 MB:
call revoAnalytics_Zqht2.SetMasterMemoryLimitMB(3000);
To set the worker memory limit to 1500 MB:
call revoAnalytics_Zqht2.SetWorkerMemoryLimitMB(1500);
The current memory limits can be viewed in the revoAnalytics_Zqht2.Properties table.
Memory limits that have been changed are in effect immediately, and no restart of the database is required.
Maintaining the Revolution Database
Two tables in the revoAnalytics_Zqht2 database may require periodic cleanup:
RevoJobs – one row is added to this table for each job. Each job is assigned a job ID between 1 and 2,147,483,647. The table is not automatically cleaned up. If never cleaned up, it can grow to up to 2,147,483,647 rows. In version 8.0.0 and earlier, values did not recycle unless old rows were deleted, and the next ID was always computed as the max ID in the table plus 1, which could result in integer overflow. In version 8.0.1 and later, after reaching the maximum value, the job IDs cycle back to 1 (or a relatively low number) harmlessly.
RevoAnalyticsJobResults – multiple rows are added for each job. It is automatically cleaned up if wait = TRUE in RxInTeradata(), but not if wait = FALSE. In version 8.0.1 and later, if the job IDs have cycled, then any rows matching a recycled ID are deleted before the ID is reused.
Installing Additional R Packages
The R community is an active, open-source community, and new packages extending R’s capacity for statistics, data analysis, graphics, and interconnectivity are added frequently. The most up-to-date source for these third-party packages is the Comprehensive R Archive Network (CRAN), a network of servers around the world that store open-source R distributions, extensions, documentation, and binaries. The repository (https://cran.r-project.org/) has grown from only 12 packages in 1997 to over 5300 packages currently. However, CRAN does not maintain source packages by R version, and Microsoft R Server for Teradata is seldom the latest R version, so packages from CRAN may be incompatible with Microsoft R Server for Teradata. Microsoft’s MRAN archive (https://mran.microsoft.com), however, maintains daily snapshots of the CRAN repository. Users may take advantage of this repository and download the chosen packages from any specific date, but notice that they are external to Teradata.
In most cases, the natural place to install additional R packages is to the client workstation. Installation to the Teradata data warehouse is required only if you plan to use the package’s functions as transform functions inside RevoScaleR functions, in which case the packages will need to be loaded in-database. If you need a package for this purpose, you can do so as follows:
To manually distribute and install the package:
- Download the package and any required dependencies from https://mran.microsoft.com/.
- Copy the downloaded packages to each node of your data warehouse.
- For each package, run the command “R CMD INSTALL package.tar.gz” on each node. (If your data warehouse is equipped with the psh command, you can use that to run the command on all the nodes in parallel.)
Removing Microsoft R Server
To remove Microsoft R Server from your computer, run the following commands:
psh rpm -e microsoft-r-server-teradata-9.1
psh rpm -e microsoft-r-server-packages-9.1
psh rpm -e microsoft-r-open-foreachiterators-3.3.3
psh rpm -e microsoft-r-open-mkl-3.3.3
psh rpm -e microsoft-r-open-mro-3.3.3
Restart the DBS to unload MRS from udfsectsk processes.