WIF Claims Programming Model
ASP.NET and Windows Communication Foundation (WCF) developers ordinarily use the IIdentity and IPrincipal interfaces to work with the user’s identity information. In .NET 4.5, Windows Identity Foundation (WIF) has been integrated such that claims are now always present for any principal as illustrated in the following diagram:
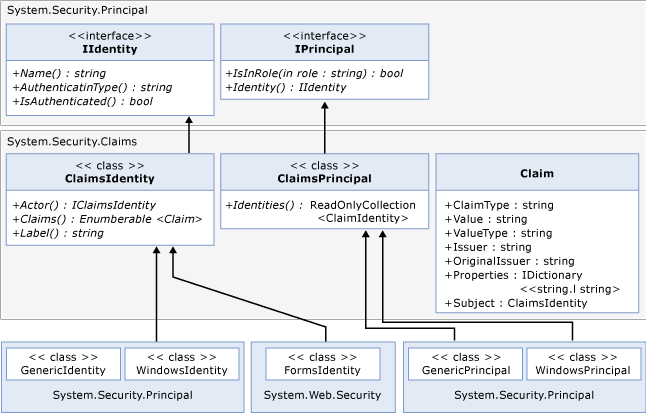
In .NET 4.5, System.Security.Claims contains the new ClaimsPrincipal and ClaimsIdentity classes (see diagram above). All principals in .NET now derive from ClaimsPrincipal. All built-in identity classes, like FormsIdentity for ASP.NET and WindowsIdentity now derive from ClaimsIdentity. Similarly, all built-in principal classes like GenericPrincipal and WindowsPrincipal derive from ClaimsPrincipal.
A claim is represented by Claim class. This class has the following important properties:
Type represents the type of claim and is typically a URI. For example, the email address claim is represented as
https://schemas.microsoft.com/ws/2008/06/identity/claims/email.Value contains the value of the claim and is represented as a string. For example, the email address can be represented as "someone@contoso.com".
ValueType represents the type of the claim value and is typically a URI. For example, the string type is represented as
http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string. The value type must be a QName according to the XML schema. The value should be of the formatnamespace#formatto enable WIF to output a valid QName value. If the namespace is not a well-defined namespace, the generated XML probably cannot be schema validated, because there will not be a published XSD file for that namespace. The default value type ishttp://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string. For information about well-known value types that you can use safely, see the W3C XML Schema page.Issuer is the identifier of the security token service (STS) that issued the claim. This can be represented as URL of the STS or a name that represents the STS, such as
https://sts1.contoso.com/sts.OriginalIssuer is the identifier of the STS that originally issued the claim, regardless of how many STSs are in the chain. This is represented just like Issuer.
Subject is the subject whose identity is being examined. It contains a ClaimsIdentity.
Properties is a dictionary that lets the developer provide application-specific data to be transferred on the wire together with the other properties, and can be used for custom validation.
Identity Delegation
An important property of ClaimsIdentity is Actor. This property enables the delegation of credentials in a multi-tier system in which a middle tier acts as the client to make requests to a back-end service.
Accessing Claims through Thread.CurrentPrincipal
To access the current user’s set of claims in an RP application, use Thread.CurrentPrincipal.
The following code sample shows the usage of this method to get a System.Security.Claims.ClaimsIdentity:
ClaimsPrincipal claimsPrincipal = Thread.CurrentPrincipal as ClaimsPrincipal;
For more information, see System.Security.Claims.
Role Claim Type
Part of configuring your RP application is to determine what your role claim type should be. This claim type is used by System.Security.Claims.ClaimsPrincipal.IsInRole(System.String). The default claim type is https://schemas.microsoft.com/ws/2008/06/identity/claims/role.
Claims Extracted by Windows Identity Foundation from Different Token Types
WIF supports several combinations of authentication mechanisms out of the box. The following table lists the claims that WIF extracts from different token types.
| Token Type | Claim Generated | Map To Windows Access Token |
|---|---|---|
| SAML 1.1 | 1. All claims from System.IdentityModel.SecurityTokenService.GetOutputClaimsIdentity(System.Security.Claims.ClaimsPrincipal,System.IdentityModel.Protocols.WSTrust.RequestSecurityToken,System.IdentityModel.Scope). 2. The https://schemas.microsoft.com/ws/2008/06/identity/claims/confirmationkey claim that contains the XML serialization of the confirmation key, if the token contains a proof token.3. The https://schemas.microsoft.com/ws/2008/06/identity/claims/samlissuername claim from the Issuer element.4. AuthenticationMethod and AuthenticationInstant claims, if the token contains an authentication statement. |
In addition to the claims listed in "SAML 1.1", except claims of type https://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2005/05/identity/claims/name, Windows authentication related claims will be added and the identity will be represented by WindowsClaimsIdentity. |
| SAML 2.0 | Same as "SAML 1.1". | Same as "SAML 1.1 Mapped to Windows Account". |
| X509 | 1. Claims with the X500 distinguished name, emailName, dnsName, SimpleName, UpnName, UrlName, thumbprint, RsaKey (this can be extracted using the RSACryptoServiceProvider.ExportParameters method from the X509Certificate2.PublicKey.Key property), DsaKey (this can be extracted using the DSACryptoServiceProvider.ExportParameters method from the X509Certificate2.PublicKey.Key property), SerialNumber properties from the X509 Certificate. 2. AuthenticationMethod claim with value https://schemas.microsoft.com/ws/2008/06/identity/authenticationmethod/x509. AuthenticationInstant claim with the value of the time when the certificate was validated in XmlSchema DateTime format. |
1. It uses the Windows account fully qualified domain name as the https://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2005/05/identity/claims/name claim value. .2. Claims from the X509 Certificate not mapped to Windows, and claims from the windows account obtained by mapping the certificate to Windows. |
| UPN | 1. Claims are similar to the claims in the Windows authentication section. 2. AuthenticationMethod claim with value https://schemas.microsoft.com/ws/2008/06/identity/authenticationmethod/password. The AuthenticationInstant claim with the value of the time when the password was validated in XmlSchema DateTime format. |
|
| Windows (Kerberos or NTLM) | 1. Claims generated from the access token such as: PrimarySID, DenyOnlyPrimarySID, PrimaryGroupSID, DenyOnlyPrimaryGroupSID, GroupSID, DenyOnlySID, and Name 2. AuthenticationMethod with the value https://schemas.microsoft.com/ws/2008/06/identity/authenticationmethod/windows. AuthenticationInstant with the value of the time when the Windows access token was created in the XMLSchema DateTime format. |
|
| RSA Key Pair | 1. The https://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2005/05/identity/claims/rsa claim with the value of RSAKeyValue.2. AuthenticationMethod claim with the value https://schemas.microsoft.com/ws/2008/06/identity/authenticationmethod/signature. AuthenticationInstant claim with the value of the time when the RSA key was authenticated (that is, the signature was verified) in the XMLSchema DateTime format. |
| Authentication Type | URI emitted in "AuthenticationMethod" claim |
|---|---|
| Password | urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:1.0:am:password |
| Kerberos | urn:ietf:rfc:1510 |
| SecureRemotePassword | urn:ietf:rfc:2945 |
| TLSClient | urn:ietf:rfc:2246 |
| X509 | urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:1.0:am:X509-PKI |
| PGP | urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:1.0:am:PGP |
| Spki | urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:1.0:am:SPKI |
| XmlDSig | urn:ietf:rfc:3075 |
| Unspecified | urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:1.0:am:unspecified |