Median Filter
Important
Support for Machine Learning Studio (classic) will end on 31 August 2024. We recommend you transition to Azure Machine Learning by that date.
Beginning 1 December 2021, you will not be able to create new Machine Learning Studio (classic) resources. Through 31 August 2024, you can continue to use the existing Machine Learning Studio (classic) resources.
- See information on moving machine learning projects from ML Studio (classic) to Azure Machine Learning.
- Learn more about Azure Machine Learning.
ML Studio (classic) documentation is being retired and may not be updated in the future.
Creates a median filter used to smooth data for trend analysis
Category: Data Transformation / Filter
Note
Applies to: Machine Learning Studio (classic) only
Similar drag-and-drop modules are available in Azure Machine Learning designer.
Module overview
This article describes how to use the Median Filter module in Machine Learning Studio (classic), to define a median filter for applying to a series of values that represent a digital input signal or image.
Median filters are widely used in image recognition to reduce noise so that features can more easily be detected.
Note
A filter is a transfer function that takes an input signal and creates an output signal based on the filter characteristics. In digital signal processing, the use of filters can improve the results of image or voice recognition. For more information, see Filter.
After you have defined a filter transformation that meets your needs by using the Median Filter module, you can apply the filter to data by connecting a dataset and the filter to the Apply Filter module.
Tip
Need to filter data from a dataset or remove missing values? Use these modules instead:
- Clean Missing Data: Use this module to remove missing values or replace missing values with placeholders.
- Partition and Sample: Use this module to divide or filter your dataset by criteria such as a range of dates, a specific value, or regular expressions.
- Clip Values: Use this module to set a range and keep only the values within that range.
How to configure Median Filter
Add the Median Filter to your experiment. You can find this module under Data Transformation, in the Filter category.
For Length, type an integer value that defines the total size of the window across which the filter is applied. This is also called the filter mask.
The value should be an odd, positive-valued integer. If you specify an even number, the mask size is reduced by one.
By default the mask begins at the current value and creates a window centered on the current value.
For example, if you type 5 as the Length or window size, the median value is computed across a sliding window consisting of 5 values centered on the current value. If you type 4, the mask is reduced to 3 values, centered on the index value.
Connect the filter to Apply Filter, and connect a dataset.
Use the column selector to specify which columns of the dataset to which the filter should be applied. By default, the Apply Filter module will use the filter for all selected numeric columns.
Run the experiment. The following operations are applied to the selected columns:
- For each set of values included in the window or mask, the filter algorithm computes the median.
- The current (or index) value is replaced with the median value.
Examples
For examples of how filters are used in machine learning, see this experiment in the Azure AI Gallery:
- Filters: This experiment demonstrates all filter types, using an engineered waveform dataset.
Technical notes
This section contains implementation details, tips, and answers to frequently asked questions.
Implementation details
Each entry in the output signal is equal to the median of the entries in a subset (mask) of the input signal, and centered at the corresponding index. The mask size should be an odd, positive-valued integer.
If you provide this method with an even-valued mask size, it is reduced by one. For example, given m=2q+1, the filter is defined as: yi = median[{xi-q,…, xi+q}]
Values beyond the borders of the input signal are assumed to equal the value at the border. That is, if n is the length of the input signal:
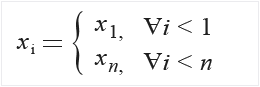
For more information about median filters, this Wikipedia article provides a good explanation of the theory and application:
Module parameters
| Name | Range | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Length | >=1 | Integer | 5 | Length of the filter window |
Output
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Filter | IFilter interface | Filter implementation |