Configure rooms and workspaces for Room Finder in Outlook
Note
This article is for Exchange administrators and Microsoft 365 administrators only. For information about how to use Room Finder to reserve meeting rooms and workspaces, see Use the Scheduling Assistant and Room Finder for meetings in Outlook.
Room Finder is a web-based feature to help your users find available meeting rooms and workspaces that are suitable for their use. Every meeting room and workspace must be set up in Exchange Online so that it displays in Room Finder. Each of these spaces is configured to have either a room mailbox or a workspace mailbox as a specific type of resource mailbox. To reserve these spaces, users must include the associated mailbox in their meeting request.
Because rooms and workspaces are physical locations, and there can be multiple such spaces in a building, it's best to organize these spaces into logical groups called room lists to manage them easily in Room Finder.
Each room list is a specially designated distribution group. Its members are the resource mailboxes for each room and workspace that's part of the list. While there is no hard limit on the number of rooms and workspaces that can be added to a room list, the maximum number of rooms and workspaces that can be returned in a search on Room Finder is 100. To ensure optimal performance, restrict each room list to a maximum of 50 room mailboxes and workspace mailboxes.
Room lists can be organized by the following elements:
- Buildings
- Floor ranges within a building
- Wings within a building
- Similar rooms within a building
Set up properties for rooms and workspaces
One of the significant advantages of using Room Finder is that you can browse for rooms and workspaces by city and room list. Then, you can further refine those results by filtering by the facilities that these spaces provide, such as conferencing devices and accessibility features.
Important
For Room Finder to work effectively, it's important to configure the attributes for rooms and workspaces. Make sure that you configure the City, Floor, and Capacity properties. The other attributes can be configured as appropriate for each room and workspace.
After you set the City, Floor, and Capacity properties for all the rooms and workspaces, you'll be able to browse room lists by a specific city in Room Finder, and filter rooms and workspaces by capacity and floor level on which they're located. Optionally, you can also set the FloorLabel property to provide a friendly name for the floor information such as Ground, Basement, Lobby etc. However, it's important that each room list includes rooms and workspaces from the same city only.
If the rooms and workspaces in a room list are from different cities, then the room list will display in the results only when you filter by the city in which the majority of its rooms and workspaces are located. For example, if a room list includes Room1 in City A, Room2 in City A, and Room 3 in City B, the room list will display only when you filter for rooms in City A.
Room Finder displays room lists as the values for the Building filter. It doesn't use the Building property that might be specified for rooms and workspaces. Room lists help to support backward compatibility for existing room lists. To ensure forward compatibility, we recommend that you populate the Building property when you configure rooms and workspaces.
To add information about features in the rooms and workspaces that are specific to your organization, such as coffee makers and conference tables, use the Tags property. The tags that you define will display in the drop-down menu for the Features filter in Room Finder.
Note
It will take 24 to 48 hours for these settings to take effect after you either configure or modify them. During this period, Room Finder might not show the expected results.
List of tasks to set up rooms and workspaces
To set up rooms and workspaces correctly, you must complete the following tasks:
Set up rooms and create room mailboxes and workspace mailboxes, as appropriate.
If you have to set up room mailboxes in a hybrid environment, see the More information section.
Configure properties such as CountryOrRegion, State, City, Building, Floor, FloorLabel, and Capacity for the rooms and workspaces.
For example, consider that for an organization that uses contoso.com as the domain, you have to set up meeting rooms and workspaces in Building A. This building is located in the city of Seattle that is in the state of Washington in the United States of America. If Building A has a total of 50 rooms and workspaces across three floors, you must complete the following tasks so that your users can find these spaces in Room Finder:
Create a room mailbox for each meeting room, and set "Seattle" as the City, "Washington" as the State, "United States of America" as the CountryorRegion, a room capacity value for the Capacity property, and values for the Floor and FloorLabel properties. If room1 is on floor 1 and has a capacity of 5, run the following cmdlets:
New-Mailbox -Organization contoso.com -Name room1 -DisplayName "Conference Room 1" -Room Set-Place room1@contoso.com -CountryOrRegion "US" -State "Washington" -City "Seattle" -Floor 1 -FloorLabel “Ground” -Capacity 5
Note: In the Set-Place cmdlet,use the Floor property to specify the floor where a room or workspace is located. In the Places API room resource type, use the FloorNumber parameter.
Create a workspace mailbox for each workspace in the building, and set "Seattle" as the City, "Washington" as the State, "United States of America" as the CountryOrRegion, a workspace capacity value for the Capacity property, and values for the Floor and FloorLabel properties. If workspace1 is on floor 1 and has a capacity of 5, run the following cmdlets:
New-Mailbox -Organization contoso.com -Name workspace1 -DisplayName "Workspace 1" -Room | Set-Mailbox -Type Workspace Set-Place workspace1@contoso.com -CountryOrRegion "US" -State "Washington" -City "Seattle" -Floor 1 -FloorLabel "Ground" -Capacity 5Also, you can set up automatic workspace capacity evaluation by running the following cmdlet:
Set-CalendarProcessing workspace1@contoso.com -EnforceCapacity $trueSelect one of the following options:
Create one room list that uses a name such as Building A, and then add all 50 rooms and workspaces to it. To create the room list and add room1 to it, run the following cmdlets:
New-DistributionGroup -Organization contoso.com -Name "Building A" -RoomList -ManagedBy admin@contoso.com Add-DistributionGroupMember -Identity BuildingA@contoso.com -Member room1@contoso.comCreate a different room list for each floor of the building, such as Building A-Floor 1, and add all rooms and workspaces on each floor to the corresponding room list. Run the following cmdlets:
New-DistributionGroup -Organization contoso.com -Name "Building A-Floor 1" -RoomList -ManagedBy admin@contoso.com Add-DistributionGroupMember -Identity BuildingA-Floor1@contoso.com -Member room1@contoso.com
For the room named room1:
The primary SMTP address is room1@contoso.com.
The displayed name in Room Finder is Conference Room 1.
For the room list named Building A:
The primary SMTP address is BuildingA@contoso.com.
The displayed name in Room Finder is Building A.
For the room list named Building A-Floor 1:
The primary SMTP address is BuildingAFloor1@contoso.com.
The displayed name in Room Finder will be Building A-Floor 1.
Verify the properties for rooms and workspaces
If a room or workspace that's configured doesn't display in the results in Room Finder, verify that it's configured properly.
Run the following commands on the room list that the room mailbox or workspace mailbox belongs to:
$FormatEnumerationLimit=-1
Get-DistributionGroup -Identity BuildingA@contoso.com
Get-DistributionGroupMember -Identity BuildingA@contoso.com
$members = Get-DistributionGroupMember -Identity BuildingA@contoso.com | select Name | foreach {Get-Place -Identity $_.Name | Format-List}
$members
If you see the following results in the output from these cmdlets, then the room or workplace is set up correctly:
For all rooms and workspaces, the segment of their SMTP address that follows the "@" character is identical to the SMTP address that's listed for the room list in the Localities property.
All rooms and workspaces have the same value for the City property.
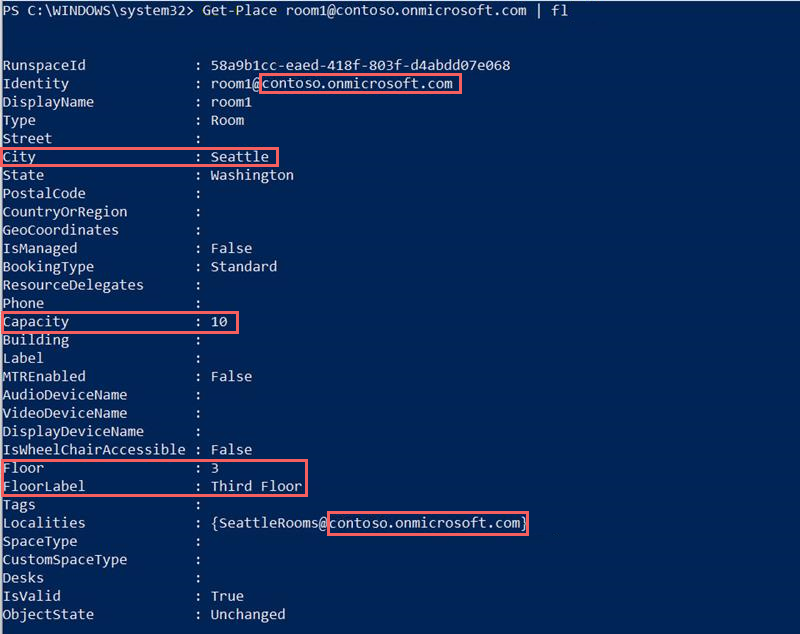
If you don't see these results for all the rooms and workspaces, reconfigure the properties only for the rooms and workspaces that don't have the same results as the others.
Find rooms and workspaces
After the properties for the rooms and workspaces are configured correctly and grouped into room lists, users can see these values in the following Outlook clients:
- Outlook for Windows
- Outlook on the web
- Outlook for Mac
- Outlook for iOS
- Outlook for Android
For information about how to use Room Finder in these clients, see Use the Scheduling Assistant and Room Finder for meetings in Outlook.
More information
If you have a hybrid environment that includes on-premises Exchange Server and Exchange Online, use the following instructions to set up room mailboxes and room lists:
- Create a room list on an on-premises server, and sync it to the cloud.
- Create an on-premises room mailbox, and sync it to the cloud.
- Create a remote synced room mailbox in Exchange Online by running the
New-RemoteMailboxcmdlet together with the-Roomswitch in Exchange Management Shell. - Add both the on-premises room mailbox and the remote synced room mailbox to the on-premises room list by running the
Add-DistributionGroupMembercmdlet in Exchange Management Shell. - Configure the properties on both room mailboxes by using the
Set-Usercmdlet in Exchange Management Shell.