2.1.24 Model Function Parameter
Function elements in conceptual schema definition language (CSDL) only support inbound parameters. CSDL does not allow setting the FunctionParameter mode. It is always set to Mode="In".
The type of a Parameter can be declared either as an attribute or as a child element.
The following is an example of the type of a Parameter declared as an attribute.
-
<Parameter Name="Age" Type="Edm.Int32"/>
The following is an example of the type of a Parameter declared as a child element.
-
<Parameter Name="Owner"> <TypeRef Name="Model.Person" /> </Parameter>
The following rules apply to the Parameter element:
Parameter MUST have a Name attribute defined that is of type SimpleIdentifier and represents the name of this Parameter.
Parameter MUST define the type either as an attribute or as a child element.
Parameter can define facets if the type is a scalar type.
Parameter can contain any number of AnnotationAttribute attributes. The full names of the AnnotationAttribute attributes cannot collide.
A function parameter MUST be one of the following types:
A scalar type or a collection of scalar types.
An entity type or collection of entity types.
A complex type or collection of complex types.
A row type or collection of row types.
A reference type or collection of reference types.
Parameter can contain a maximum of one CollectionType element.
Parameter can contain a maximum of one ReferenceType element.
Parameter can contain a maximum of one RowType element.
Parameter can contain any number of AnnotationElement elements.
In CSDL 3.0, Parameter can contain any number of ValueAnnotation elements.
AnnotationElement elements are last in the sequence of child elements of a Parameter.
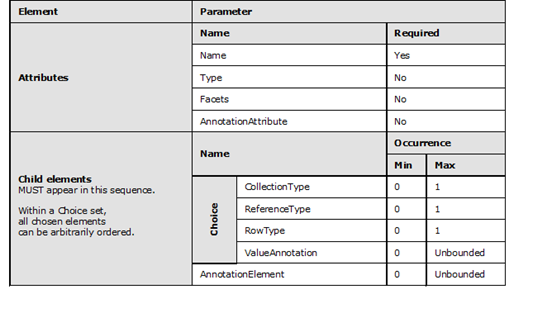
All child elements are to appear in the order indicated. For all child elements within a given choice, the child elements can be ordered arbitrarily.