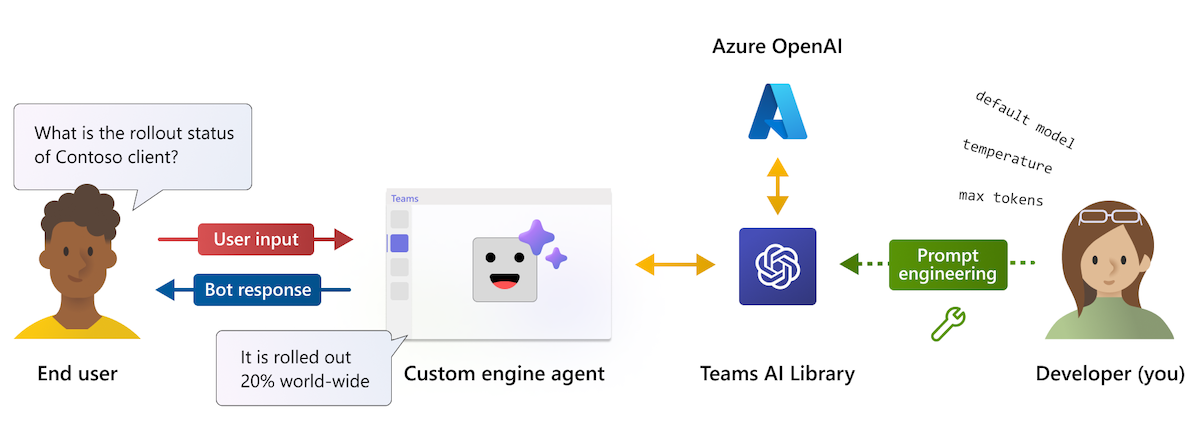
Teams AI library
Teams AI library is a Teams-centric interface for integrating GPT-based language models and user intent engines. It simplifies the development process by reducing the need to write and maintain complex conversational bot logic.
You can leverage prebuilt, reusable code snippets that allow you to quickly build intelligent apps. This capabilities-driven approach allows you to focus on business logic rather than learning the intricacies of Microsoft Teams conversational frameworks.
Why use Teams AI library?
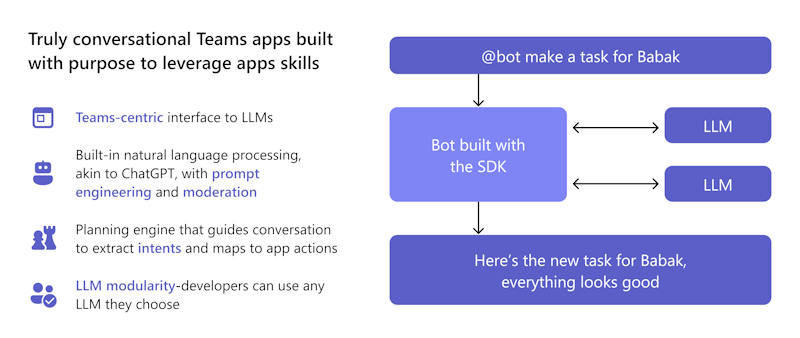
Teams AI library enables your apps to engage users in natural and conversational interactions. These interactions can be guided toward specific app functionalities or tasks, allowing your app to better understand and process user intent.
You can rely on the built-in conversational bot capabilities in Teams (such as Power Virtual Agents or the Bot Framework) to handle the complexities of natural language processing.
You can leverage Teams AI library to:
- Use prebuilt templates to add Teams app capabilities.
- Use techniques like prompt engineering to add ChatGPT like conversational experiences to your bot and built-in safety features, like moderation, help ensure your bot always responds in an appropriate manner.
- Use the library's planning engine that allows the model to identify the user's intent and then maps that intent to actions that you implement.
- Add support for any LLM of your choice without changing the bot logic.
Teams AI library supports both JavaScript and C#. It allows you to harness AI capabilities to build intelligent, user-friendly applications for Microsoft Teams. The library provides the flexibility to create AI-powered experiences using the tools and languages that best suits your project needs and ensures the best possible outcomes for your Teams users.
How do Teams AI library features benefit me?
Teams AI library offers a variety of features that can simplify the development of your custom engine agent.
As a developer, I want to build an intelligent lightbot that controls the light in response to the user's command. I'm considering using Teams AI library because of its features that can make building my custom engine agent a breeze. I want my AI-powered lightbot to make the user experience better and keep them more involved.
How can I use Teams AI library to make sure my custom engine agent runs smoothly and gives users a fun and interactive experience?
Localization
Teams AI library uses OpenAI's GPT model for localization. User inputs in any language are translated to intents, entities, and actions. This approach eliminates the need for maintaining localization records.
LLM modularity
An LLM generates coherent and diverse natural language text using latent variables. Teams AI library uses OpenAI's GPT model but it allows you to swap it with any LLM without changing the bot logic. This means you can keep your app's content outside the public domain and confined to your preferred LLM model.
Responsible AI
Teams AI library helps build conversational apps with moderation hooks, conversation sweeping, and feedback loops. It supports both low code and complex scenarios. The library extends capabilities with AI constructs for natural language modeling, user intent, personalization, and automated context-aware conversations.
Predictive engine for mapping intents to actions
A simple interface for actions and predictions allows a bot to react when needed. Ambient presence lets a bot learn intent, use business logic prompts, and generate responses. For example, if a user is out of office and needs to summarize a thread, Teams AI library:
- Understands the intent as summarization.
- Uses prompts to make summarizations over time, focused on the user’s interactions.
- Provides actions to summarize the chat content.
Action Planner
Action Planner is the main component that calls your LLM and includes several features to enhance and customize your model. Model plugins simplify configuring your selected LLM to the planner and ships with an OpenAIModel that supports both OpenAI and Azure OpenAI LLMs. Add more plugins for other models like Llama-2 to give you the flexibility to choose the best model for your use case. An internal feedback loop increases reliability by fixing the subpar responses from the LLM.
Assistants API
Note
Teams AI library supports both OpenAI and Azure OpenAI Assistants API in public developer preview for you to get started with building intelligent assistants.
Assistants API allows you to create powerful AI assistants capable of performing tasks that are difficult to code using traditional methods. It provides programmatic access to OpenAI’s GPT system for tasks ranging from chat to image processing, audio processing, and building custom assistants. The API supports natural language interaction to enable the development of assistants that can understand and respond in a conversational manner.
Follow the quick start guide for Assistants API to create an assistant that specializes in mathematics.
Prompt management
Dynamic prompt management allows the bot to adjust the size and content of the prompt sent to the LLM, based on the available token budget and the data sources or augmentations. It improves the efficiency and accuracy of the prompt by ensuring that it doesn't include irrelevant information or exceed the context window.
Augmentation
Enhance your AI model’s responses with Augmentation. Tailor your model using different modes for accuracy and desired outcomes:
- Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG): Incorporate real-time, dynamic external data sources for up-to-date, accurate results without re-training.
- Monologue: Create AutoGPT-style agents for multi-step actions with full schema validation and automatic repair.
- Sequence: Enable your AI assistant to return a sequence of actions with schema validation for reliability.
- Functions: Produce structured responses using customizable user-defined functions. The Action Planner assesses and repairs model responses for reliability and consistency.
Vector data sources
Vector databases are designed to store vectors to enable efficient search. They return the most relevant results for a user's query. They allow RAG to use LLMs and custom data or domain-specific information. This involves extracting relevant information from a custom data source and integrating it into the model request through prompt engineering. Before sending a request to the LLM, the user input is transformed into an embedding, and vector search techniques are used to find the most similar embedding in the database.
Enhanced reasoning
Teams AI library offers an integrated fact-checking system to tackle bot hallucinations. When a user interacts with your AI assistant, it prompts the bot to critically evaluate its potential responses before sending. The bot identifies inaccuracies and corrects its answers, which improves accuracy, quality, and contextual relevance. Advanced reasoning ensures that your AI assistant becomes a dependable source of information and judgment that builds trust in the product and increases user engagement.
Feedback loop
The feedback loop allows a bot to validate and correct the output of the language model. It checks the structure and parameters of the plan or monologue that the model returns and provides feedback on errors or missing information. The model attempts to fix its mistakes and return a valid output. The feedback loop can improve the reliability and accuracy of the AI system and reduce the chances of hallucinations or invalid actions.
Updates to Teams AI library
The following table lists the updates to Teams AI library:
| Type | Description | .NET | JavaScript | Python |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OpenAIModel | The OpenAIModel class allows you to call both OpenAI and Azure OpenAI with one single component. New models can be defined for other model types like Llama2. | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Embeddings | The OpenAIEmbeddings class allows you to generate embeddings using either OpenAI or Azure OpenAI. New embeddings can be defined for things like OSS Embeddings. | ❌ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Prompts | A new object-based prompt system enables better token management and reduces the likelihood of overflowing the model's context window. | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Augmentation | Augmentations simplify prompt engineering tasks by letting the developer add named augmentations to their prompt. Only functions, sequence, and monologue style augmentations are supported. |
✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Data Sources | A new DataSource plugin makes it easy to add RAG to any prompt. You can register a named data source with the planner and then specify the names of the data sources they wish to augment the prompt. | ❌ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
Function calls using AI SDK
Function calls, implemented within the AI SDK, unlock numerous capabilities, enabling the AI model to generate accurate responses seamlessly. It enables direct connection with external tools, thereby making AI even more powerful. These capabilities include performing complex calculations, retrieving important data, creating smoother workflows, and enabling dynamic interactions with users.
Note
Structured outputs aren't supported.
To use function calling with the Chat Completions API:
Set up the planner where the default prompt uses the Tools Augmentation. Update one of the following files of your bot app:
- For a JavaScript app: Update
index.ts. - For a C# bot app: Update
Program.cs. - For a Python app: Update
bot.py.
The following code snippet shows how to set up the
ToolsAugmentationclass:const planner = new ActionPlanner({ model, prompts, defaultPrompt: 'tools' });- For a JavaScript app: Update
Specify tools augmentation in the
config.jsonfile.{ "schema": 1.1, "description": "", "type": "", "completion": { + "tool_choice": "auto", + "parallel_tool_calls": true, }, + "augmentation": { + "augmentation_type": "tools" + } }Specify all your
function definitionsin theactions.jsonfile, which is in thepromptsfolder. Ensure that you follow the schema to avoid errors when the action is called by the LLM.[{ "name": "CreateList", "description": "Creates a list" }]Register your
handlersin yourapplicationclass.- Each handler is a callback function that runs when a specific event happens. The function call handler executes code in response to the event.
- The function call must return a string as the output of the function call.
- When the model requests to invoke any functions, these are mapped to
DOcommands within aPlanand are invoked in the AI classrunfunction. The outputs are then returned to the model with tool call IDs to show that the tools were used.
The following code snippet shows how to register
handlers:app.ai.action("createList", async (context: TurnContext, state: ApplicationTurnState, parameters: ListAndItems) => { // Ex. create a list with name "Grocery Shopping". ensureListExists(state, parameters.list); return `list created and items added. think about your next action`; });
Enable tool options
You can enable the following tool options:
Enable Tool Choice: Allow the model to select the function it must call by enabling tool selection. In the
config.jsonfile:- Set
tool_choiceasrequiredto mandate the model to always call at least one function. - Set
tool_choiceto a specific function using its definition for using that function. - Set
tool_choiceasnoneto disable the tool.
The default value of
tool_choiceisauto. It enables the model to select the functions that it must call.- Set
Toggle Parallel Tool Calls: Executing tools in parallel is faster and reduces the number of back-and-forth calls to the API. In the
config.jsonfile, you can setparallel_tool_callstotrueorfalse. By default, theparallel_tool_callsparameter is set totrue.
The following code snippet shows how to enable tool choice and to toggle parallel tool calls:
{
"schema": 1.1,
"description": "",
"type": "",
"completion": {
+ "tool_choice": "auto",
+ "parallel_tool_calls": true,
},
+ "augmentation": {
+ "augmentation_type": "tools"
+ }
}
Note
As a developer utilizing the AI SDK, you can share valuable feedback or seek support to enhance your experience.
Code samples
| Sample name | Description | .NET | Node.js | Python |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Echo bot | This sample shows how to incorporate a conversational flow into a Microsoft Teams application using Bot Framework and Teams AI library. | View | View | View |
| Search command message extension | This sample shows how to incorporate a basic Message Extension app into a Microsoft Teams application using Bot Framework and Teams AI library. | View | View | View |
| Typeahead bot | This sample shows how to incorporate the typeahead search functionality in Adaptive Cards into a Microsoft Teams application using Bot Framework and Teams AI library. | View | View | View |
| Conversational bot with AI: Teams chef | This sample shows how to incorporate conversational bot behavior into Microsoft Teams. The bot is built to allow GPT to facilitate the conversation on its behalf, using only a natural language prompt file to guide it. | View | View | |
| Message extensions: GPT-ME | This sample is a message extension for Microsoft Teams that uses the text-davinci-003 model to help users generate and update posts. | View | View | View |
| Light bot | This sample illustrates more complex conversational bot behavior into Microsoft Teams. The bot is built to allow GPT to facilitate the conversation on its behalf and manually defined responses, and maps user intents to user defined actions. | View | View | View |
| List bot | This sample shows how to incorporate conversational bot behavior into Microsoft Teams. The bot harnesses the power of AI to simplify your workflow and bring order to your daily tasks and showcases the action chaining capabilities. | View | View | View |
| DevOps bot | This sample shows how to incorporate conversational bot behavior in Microsoft Teams. The bot uses the gpt-3.5-turbo model to chat with Teams users and perform DevOps actions such as create, update, triage and summarize work items. | View | View | View |
| Twenty questions | This sample shows showcases the incredible capabilities of language models and the concept of user intent. Challenge your skills as a human player and try to guess a secret within 20 questions, while the AI-powered bot answers your queries about the secret. | View | View | View |
| Math tutor assistant | This example shows how to create a conversational experience using OpenAI's Assistants APIs. It uses OpenAI's Code Interpreter tool to create an assistant that's an expert on math. | View | View | View |
| Food ordering assistant | This example shows how to create a conversational assistant that uses tools to call actions in your bot's code. It's a food ordering assistant for a fictional restaurant called The Pub and is capable of complex interactions with the user as it takes their order. | View | View | View |
Next step
See also
Platform Docs