Integrate new applications with existing solutions
Note
This is article 4 of 6 in Build applications on the Microsoft Cloud.
It’s rare that new applications don't connect to existing applications and data. High-quality apps that people want to use typically interact with what already exists. In this article, we consider various ways that you can use Microsoft Cloud to connect to applications and data.
- Use Azure API Management to connect to your existing applications and data
- Use Microsoft 365 and Microsoft Graph to connect to your modern work applications and data
- Use Dynamics 365 to connect to your line-of-business solutions and data
Use Azure API Management to connect to your existing applications and data
Azure API Management provides a simple, general, and manageable way to connect to applications and data. You can use it to create a standard interface that provides a single point of access for other applications to use. API Management also makes it possible to manage and secure your application APIs in a standard way, and gives developers a single place to learn how to use those APIs.
In our example application, suppose that both the pro-code customer-facing component and the low-code employee-facing component need to access existing applications and data. Figure 6 shows how API Management fits into the picture.
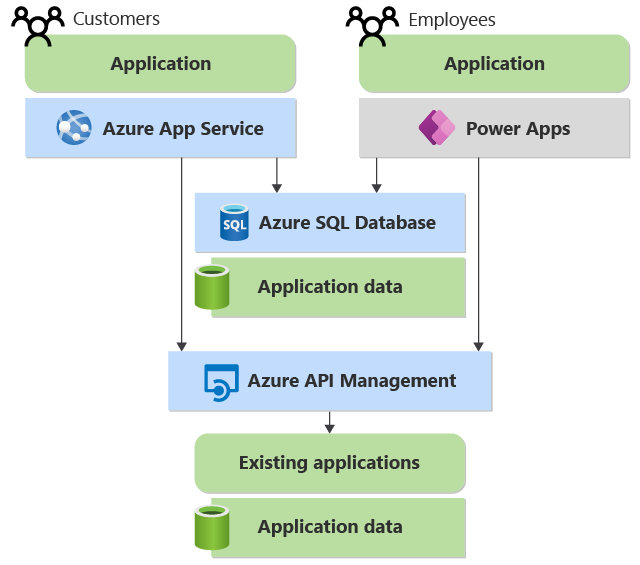
Figure 6: Azure API Management provides a uniform way to wrap existing applications and data.
These existing applications can be running on Azure, on another vendor’s cloud platform, in your own datacenter, or elsewhere. it doesn’t matter whether the applications were created by Microsoft, by your internal developers, or by another company. Wrapping them with API Management hides these differences so that applications access other applications and data in a standard way.
The benefits of using API Management include:
- Both pro-code and low-code applications can call the APIs directly. In Figure 6, for example, the customer-facing component and the employee-facing component both access existing applications and data through API Management.
- Power Platform applications can use a standard connector to connect to API Management. Like other connectors, this one can be added to a low-code app, providing a simple and consistent way to connect to existing applications.
- Pro-code developers can create custom API wrappers for existing applications and then publish them for use by low-code applications through the API Management connector. Visual Studio provides a dialog that makes this easy to do.
Connecting new applications to your existing applications and data is important. The Microsoft Cloud provides Azure API Management to solve this problem effectively.
Microsoft Cloud in a hybrid world
Cloud computing is a mainstream approach today, but many organizations still have a substantial investment in on-premises technology. Creating successful applications by using the Microsoft Cloud often requires integrating with this existing investment.
Microsoft Cloud components can connect to your on-premises world in a variety of ways. Here are some examples:
- Azure: Many aspects of Azure can connect to your on-premises environment. You can use VPN Gateway to connect your on-premises network to Azure. Azure DevOps pipelines can deploy code to the cloud or on-premises. You can run a subset of Azure services on-premises by using Azure Stack Hub, Azure Stack HCI, or Azure Stack Edge.
- Power Platform: Microsoft provides an on-premises gateway so that your low-code apps can access data stored in your datacenter. For example, an application created with Power Apps can use the gateway to access on-premises SQL Server data, and a Power BI solution can use it to combine data from on-premises data sources with data stored in the cloud.
- Microsoft 365: Various Microsoft 365 components, including Exchange and SharePoint, can provide hybrid deployment by using connections between cloud and on-premises software.
- Dynamics 365: Some Dynamics 365 components, such as Supply Chain Management, allow for a hybrid deployment.
- Microsoft Entra ID : It’s common today to connect this cloud-based identity service with an existing on-premises Active Directory, creating a hybrid solution for managing identity. Identity information can be automatically synchronized between the two services.
Your organization can also use Microsoft Sentinel and various aspects of Azure Arc to secure and manage your infrastructure on Azure, on other public clouds, or in your own datacenter. This ensures that applications you deploy in a hybrid fashion can still be effectively managed.
Use Microsoft 365 and Microsoft Graph to connect to your modern work applications and data
High-quality internal applications help employees do their jobs well. Your pro-code and low-code applications can be more useful if they give employees direct access to their organizational data, such as emails, calendar entries, and spreadsheets. This data is often stored in Microsoft 365 tools such as Exchange, SharePoint, and OneDrive.
For example, a custom application can make its users more productive by providing built-in access to calendar data, emails, and chats. This minimizes the time users spend switching between the application and Outlook or Teams. Applications can also show employees relevant documents from OneDrive to help them make better decisions. They get the data that they need without having to search.
To access this kind of data, your custom applications can use the unified API provided by Microsoft Graph. Figure 7 illustrates this idea in our sample application.
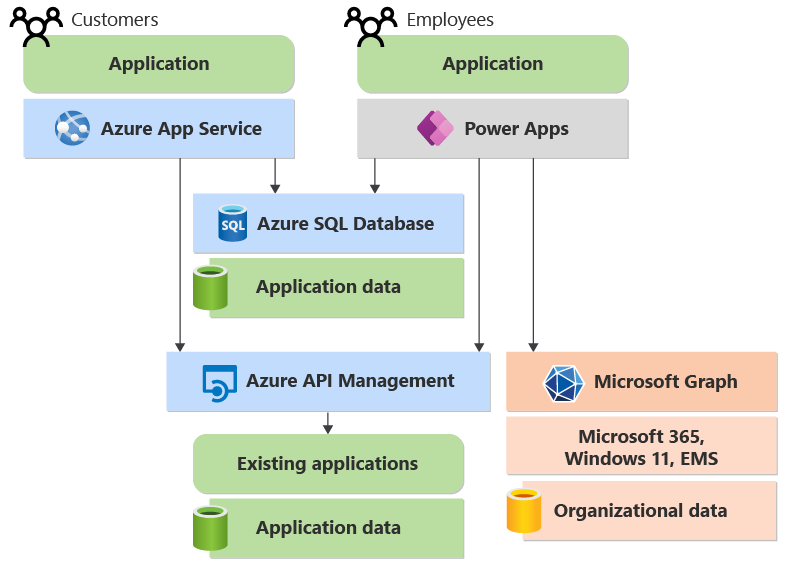
Figure 7: Microsoft Graph gives applications access to the organizational data in Microsoft 365.
Applications can use Microsoft Graph to access data in Microsoft 365, Windows 11, and Enterprise Mobility + Security. The data that this API exposes can come from many different cloud services, including Exchange, SharePoint, Teams, OneDrive, OneNote, Planner, Microsoft Search, and Microsoft Entra ID. Because Microsoft 365 already meets compliance requirements for e-discovery and records management, building applications that use its content and services gives you solutions that are more compliant. Microsoft Graph can be used both by pro-code and low-code apps.
In our example application, customers and employees work together in some way. Suppose that employees exchange mail or engage in Teams chats with these customers. If an employee needs to look up information from a prior mail exchange or chat with a customer, the application can use Microsoft Graph to get it from Microsoft 365. By selecting a customer in the employee-facing application interface, the employee can view the relevant mail exchange or chat.
Applications can use the data accessed via Microsoft Graph in many other ways. For example:
- A custom application can personalize interactions with employees by displaying employee names and pictures rather than just names.
- A custom application can check an internal user’s calendar, then automatically suggest times for a meeting with customers. The application can subscribe to changes in the user’s calendar and advise of a need to adjust scheduled meetings.
- A custom application can automate employee onboarding. It can automatically add a new employee to appropriate Teams channels, email lists, and other areas in Microsoft 365.
- A custom application that needs to store data can use SharePoint instead of an Azure data service. The application can then use SharePoint features such as permission management and improved compliance.
Microsoft Graph can connect to external data sources including Google Drive, Box, Jira, and Salesforce, so that your custom applications can index and search information stored outside of your Microsoft environment. Microsoft also provides Microsoft Graph Data Connect for moving large amounts of organizational data into Azure datastores. You can then use the data to create machine learning models and do other analysis, helping you better understand what’s happening in your organization.
Microsoft Graph is yet another example of the value provided by building applications on the unified services of Microsoft Cloud. You can use it to create better applications that make employees more productive.
Use Dynamics 365 to connect to your line-of-business solutions and data
Dynamics 365 is a set of services that can provide a range of business solutions. Here’s a partial list of what it includes:
- Dynamics 365 Sales for managing sales pipelines, onboarding new sellers, and supporting sales professionals in other ways.
- Dynamics 365 Customer Insights to help you understand your customers better. For example, it can provide a view of each customer and predict customer needs.
- Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management for building and running a resilient supply chain that optimizes your inventory and improves demand planning.
- Dynamics 365 Customer Service to support your customer service organization. For example, it can get your representatives faster answers and create virtual agents (chatbots).
- Dynamics 365 Finance to handle invoices, payments, and other financial matters.
- Dynamics 365 Human Resources to help manage recruitment, employee benefits, compensation, and other HR issues.
New enterprise applications often can benefit from integrating with one or more Dynamics 365 services. Because we use Power Apps to create our example application, we can integrate easily by using a connector. Figure 8 shows how this looks.
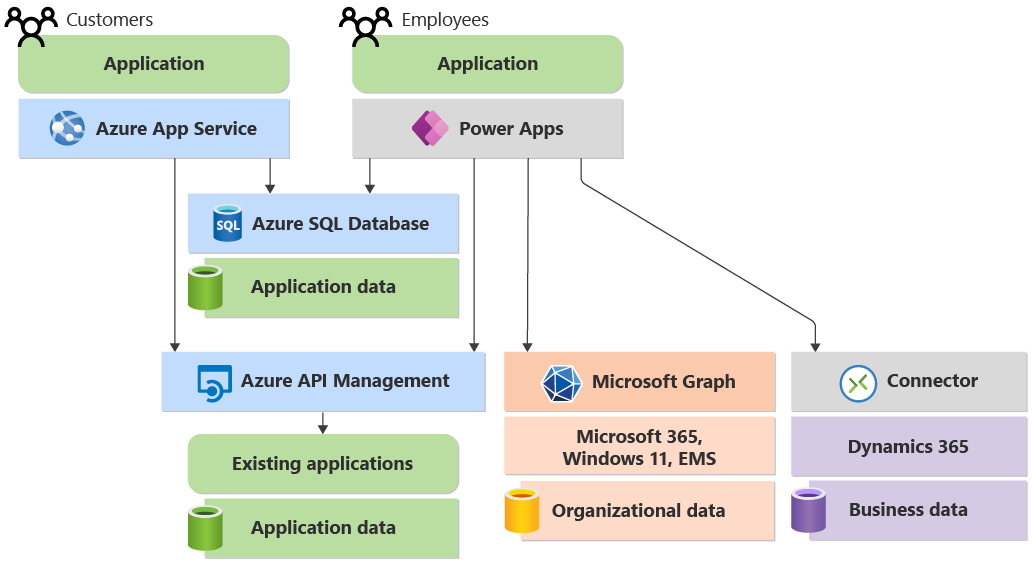
Figure 8: A low-code application can use a Power Platform connector to access Dynamics 365.
Power Platform provides various connectors for accessing Dynamics 365. One of the most widely used is the Microsoft Dataverse connector, which provides access to the data in Dynamics 365 Sales, Dynamics 365 Customer Service, and other Dynamics 365 offerings. This connector takes advantage of the fact that much of Dynamics 365 is built on Dataverse, making it simple to integrate with Power Platform. Although it’s not shown in Figure 8, Dynamics 365 also exposes APIs for pro-code apps.
Connecting an enterprise application to Dynamics 365 business applications and data can be beneficial in many ways:
- A customer-facing application can integrate with Dynamics 365 Finance so that customers can work with invoices.
- A call center application, such as an employee-facing application created with Power Apps or Azure, can provide real-time predictions of how likely a customer is to switch to a competitor. Dynamics 365 Customer Insights includes pre-built machine learning models to provide this information.
- A recruiting application with both customer-facing and employee-facing components can integrate with Dynamics 365 Human Resources to store and access information about job openings and candidates.
There are connections between Dynamics 365 and other parts of the Microsoft Cloud. For example, a field technician can use Teams to notify users of Dynamics 365 Sales—sales professionals—about customers whose products are nearing end-of-life. The sales team can proactively tell the customers about replacement options.
Microsoft Industry Clouds
The Microsoft Cloud provides a broadly useful set of services for creating custom applications. Yet the solutions your organization creates probably aren’t generic; they’re specialized for your industry. What the Microsoft Cloud provides is helpful, but you’d also like more support for the industry-specific applications you need to build.
Microsoft Industry Clouds address this need. Each Industry Cloud builds on the Microsoft Cloud by adding industry-specific components. Here are some Industry Clouds:
- Microsoft Cloud for Healthcare
- Microsoft Cloud for Manufacturing (preview)
- Microsoft Cloud for Retail
- Microsoft Cloud for Financial Services
- Microsoft Cloud for Nonprofit
- Microsoft Cloud for Sustainability
Each Industry Cloud is designed to help you get the industry-specific value and compliance that you need. Each includes applications designed for a particular industry. For example, Cloud for Nonprofit includes a pre-built Power Apps solution for volunteer management, and Cloud for Healthcare includes an extensible chatbot so that customers can describe symptoms, then get information about related medical conditions and the type of doctor to consult.
Industry clouds also include components for application developers. Here are some examples:
- Cloud for Retail includes an intelligent recommendations service that suggests products to customers. This service is accessed via an API, so that developers can create customer-specific solutions that use it.
- Cloud for Healthcare includes a Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) connector. This connector makes it easy for Power Platform solutions to connect to healthcare data that’s accessible through the industry standard FHIR interface.
- Cloud for Financial Services, Cloud for Healthcare, and others provide pre-defined data types, called entities, for Dataverse and other datastores.
Building your own applications on the services that Microsoft Industry Clouds provide can help you create better and more compliant solutions in less time.
Next steps
See how successful enterprise application development leaders create and run secure applications by using Active Directory for identity and access management.