Get started with your Microsoft Intune deployment
Microsoft Intune is a cloud-based service that helps you manage your devices and apps. For more information about what Microsoft Intune can do for your organization, go to What is Microsoft Intune.
This article provides an overview of the steps to start your Intune deployment.
Tip
As a companion to this article, the Microsoft 365 admin center also has some setup guidance. The guide customizes your experience based on your environment. To access this deployment guide, go to the Microsoft Intune setup guide in the Microsoft 365 admin center, and sign in with the Global Reader (at a minimum). For more information on these deployment guides and the roles needed, go to Advanced deployment guides for Microsoft 365 and Office 365 products.
To review best practices without signing in and activating the automated setup features, go to the M365 Setup portal.
Before you begin
To help plan your Intune deployment, use the Planning guide to move to Microsoft Intune. It covers personal devices, licensing considerations, creating a rollout plan, communicating changes to your users, and more.
The following articles are good resources:
Determine your license needs and any other prerequisites for your Intune deployment. The following list provides some of the most common prerequisites:
Intune subscription: Included with some Microsoft 365 subscriptions. You also get access to the Microsoft Intune admin center, which is a web-based console for managing your devices, apps, and users.
Microsoft 365 apps: Included with Microsoft 365 and is used for productivity apps, including Outlook and Teams.
Microsoft Entra ID: Microsoft Entra ID is used for the identity management for users, groups, and devices. It comes with your Intune subscription and possibly your Microsoft 365 subscription.
Microsoft Entra ID P1 or P2, which might cost extra, gives you more features commonly used by organizations, including Conditional Access, multifactor authentication (MFA), and dynamic groups.
Windows Autopilot: Included with some Microsoft 365 subscriptions. Windows Autopilot gives you modern OS deployment for currently supported versions of Windows client devices.
Platform specific prerequisites: Depending on the platforms of your devices, there are other requirements.
For example, if you manage iOS/iPadOS and macOS devices, you need an Apple MDM push certificate and possibly an Apple token. If you manage Android devices, you might need a managed Google Play account. If you use certificate authentication, you might need a SCEP or PKCS certificate.
For more information, go to:
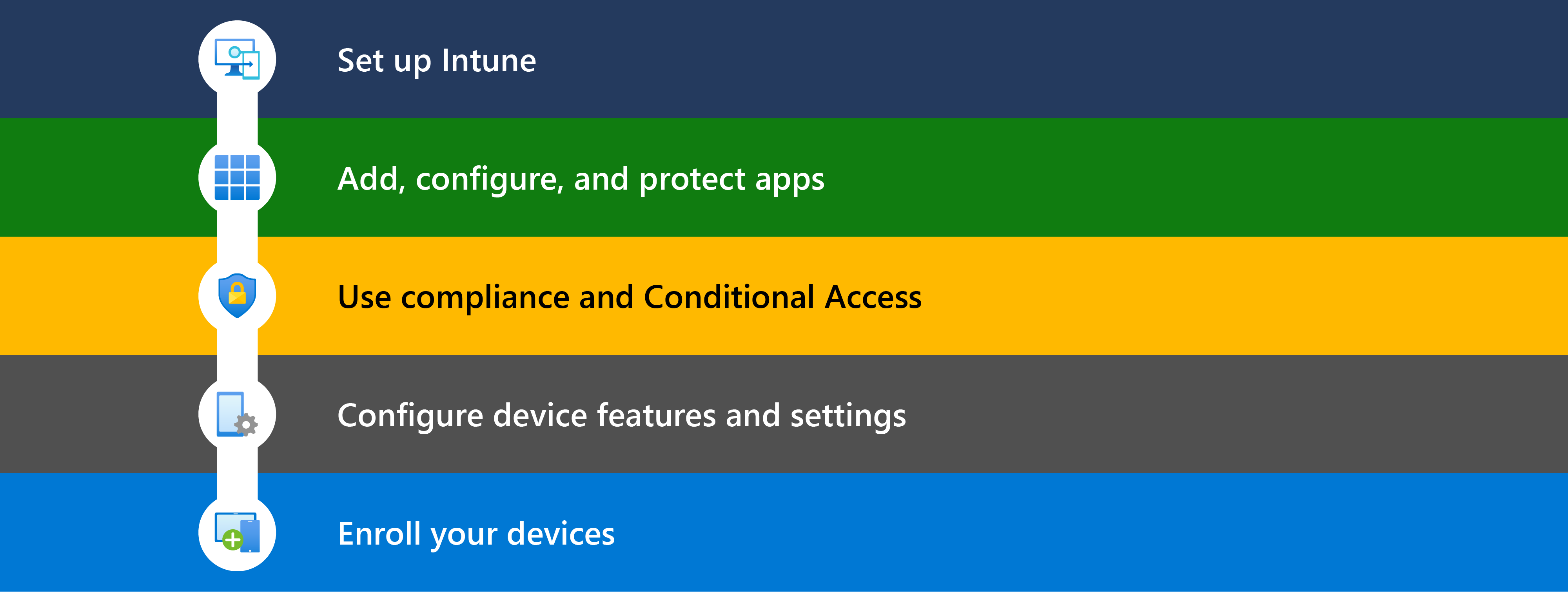
Step 1 - Set up Intune
In this step:
✅ Confirm your devices are supported, create your Intune tenant, add users & groups, assign licenses, and more.
This step focuses on setting up Intune and getting it ready for you to manage your user identities, apps, and devices. Intune uses many features in Microsoft Entra ID, including your domain, your users, and your groups.
For more information, go to Step 1 - Set up Microsoft Intune.
Step 2 - Add and protect apps
In this step:
✅ On devices that will enroll in Intune, create a baseline of apps that devices must have, and then assign these app policies during enrollment. On apps that need extra security, also use app protection policies.
✅ On devices that won't enroll in Intune, use app protection policies and multifactor authentication (MFA):
- App protection policies help protect organization data on personal devices.
- MFA helps protect your organization's data from unauthorized access.
For more information, go to Step 2 - Add, configure, and protect apps with Intune.
Every organization has a base set of apps that should be installed on devices. Before users enroll their devices, you can use Intune to assign these apps to their devices. During enrollment, the app policies are automatically deployed. When enrollment completes, the apps install and are ready to use.
If you prefer, you can enroll your devices, and then assign apps. It's your choice. The next time users check for new apps, they'll see the new apps available.
If users with their own personal devices access organization resources, then you need to protect any apps that access your organization data using mobile application management (MAM), at a minimum. You can create MAM policies for Outlook, Teams, SharePoint, and other apps. The Microsoft Intune planning guide has some guidance on managing personal devices.
Note
MFA is a feature of Microsoft Entra ID that must be enabled in your Microsoft Entra tenant. Then, you configure MFA for your apps. For more information, go to:
Step 3 - Check for compliance and turn on Conditional Access
In this step:
✅ Create a baseline of compliance policies that devices must have, and then assign these compliance policies during enrollment.
✅ Enable Conditional Access to enforce your compliance policies.
For more information, go to Step 3 – Plan for compliance policies.
MDM solutions like Intune can set rules that devices should meet, and can report the compliance states of these rules. These rules are called compliance policies. When you combine compliance policies with Conditional Access, you can require devices meet certain security requirements before they can access your organization's data.
When users enroll their devices in Intune, the enrollment process can automatically deploy your compliance policies. When enrollment completes, admins can check the compliance status and get a list of devices that don't meet your rules.
If you prefer, you can enroll your devices before checking compliance. It's your choice. At the next Intune check-in, the compliance policies are assigned.
Note
Conditional Access is a feature of Microsoft Entra ID that must be enabled in your Microsoft Entra tenant. Then, you can create Conditional Access policies for your user identities, apps, and devices. For more information, go to:
Step 4 - Configure device features
In this step:
✅ Create baseline of security features and device features that should be enabled or blocked. Assign these profiles during enrollment.
For more information, go to Step 4 - Create device configuration profiles to secure devices and access organization resources.
Your organization can have a base set of device and security features that should be configured or should be blocked. These settings are added to device configuration and endpoint security profiles. Microsoft recommends you assign key security and device configuration policies during enrollment. When enrollment starts, the device configuration profiles are automatically assigned. When enrollment completes, these device and security features are configured.
If you prefer, you can enroll your devices before creating the configuration profiles. It's your choice. At the next Intune check-in, the profiles are assigned.
In the Microsoft Intune admin center, you can create different profiles based on your device platform - Android, iOS/iPadOS, macOS, and Windows.
The following articles are good resources:
- Apply features and settings on your devices using device profiles
- Use the settings catalog to configure settings
- Manage endpoint security in Microsoft Intune
- Windows security baselines
Step 5 - Enroll your devices
In this step:
✅ Enroll your devices in Intune.
For more specific information, go to Step 5 - Enrollment guidance: Enroll devices in Microsoft Intune.
To fully manage devices, the devices must be enrolled in Intune to receive the compliance & Conditional Access policies, app policies, device configuration policies, and security policies you create. As an admin, you create enrollment policies for your users and devices. Each device platform (Android, iOS/iPadOS, Linux, macOS, and Windows) has different enrollment options. You choose what's best for your environment, your scenarios, and how your devices are used.
Depending on the enrollment option you choose, users can enroll themselves. Or, you can automate enrollment so users only need to sign in to the device with their organization account.
When a device enrolls, the device is issued a secure MDM certificate. This certificate communicates with the Intune service.
Different platforms have different enrollment requirements. The following articles can help you learn more about device enrollment, including platform-specific guidance:
Cloud attach with Configuration Manager
Microsoft Configuration Manager helps protect on-premises Windows Server, devices, apps, and data. If you need to manage a combination of cloud and on-premises endpoints, you can cloud attach your Configuration Manager environment to Intune.
If you use Configuration Manager, then there are two steps to cloud attach your on-premises devices:
Tenant attach: Register your Intune tenant with your Configuration Manager deployment. Your Configuration Manager devices are shown in the Microsoft Intune admin center. On these devices, you can run different actions, including installing apps and run Windows PowerShell scripts using the web-based Intune admin center.
Co-management: Manage Windows client devices with Configuration Manager and Microsoft Intune. Configuration Manager manages some workloads, and Intune manages other workloads.
For example, you can use Configuration Manager to manage Windows updates, and use Intune to manage compliance & Conditional Access policies.
If you currently use Configuration Manager, you get immediate value through tenant attach, and you get more value through co-management.
For guidance on the Microsoft Intune setup that's right for your organization, go to Deployment guide: Set up or move to Microsoft Intune.