Adding IP Security <add>
Overview
The <add> element of the <ipSecurity> collection defines a unique IP security restriction. Each restriction can be based on the IP version 4 address, a range of IP version 4 addresses, or a DNS domain name.
Compatibility
| Version | Notes |
|---|---|
| IIS 10.0 | The <add> element was not modified in IIS 10.0. |
| IIS 8.5 | The <add> element was not modified in IIS 8.5. |
| IIS 8.0 | The <add> element was not modified in IIS 8.0. |
| IIS 7.5 | The <add> element was not modified in IIS 7.5. |
| IIS 7.0 | The <add> element of the <ipSecurity> collection was introduced in IIS 7.0. |
| IIS 6.0 | The <ipSecurity> collection replaces the IIS 6.0 IPSecurity metabase property. |
Setup
The default installation of IIS does not include the role service or Windows feature for IP security. To use IP security on IIS, you must install the role service or Windows feature using the following steps:
Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2
- On the taskbar, click Server Manager.
- In Server Manager, click the Manage menu, and then click Add Roles and Features.
- In the Add Roles and Features wizard, click Next. Select the installation type and click Next. Select the destination server and click Next.
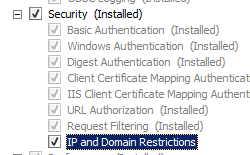
- On the Server Roles page, expand Web Server (IIS), expand Web Server, expand Security, and then select IP and Domain Restrictions. Click Next.
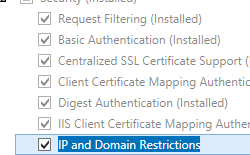 .
. - On the Select features page, click Next.
- On the Confirm installation selections page, click Install.
- On the Results page, click Close.
Windows 8 or Windows 8.1
- On the Start screen, move the pointer all the way to the lower left corner, right-click the Start button, and then click Control Panel.
- In Control Panel, click Programs and Features, and then click Turn Windows features on or off.
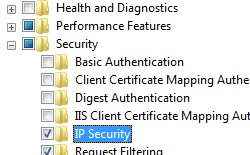
- Expand Internet Information Services, expand World Wide Web Services, expand Security, and then select IP Security.
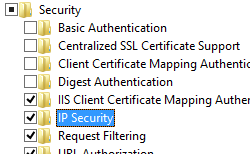
- Click OK.
- Click Close.
Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server 2008 R2
On the taskbar, click Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Server Manager.
In the Server Manager hierarchy pane, expand Roles, and then click Web Server (IIS).
In the Web Server (IIS) pane, scroll to the Role Services section, and then click Add Role Services.
On the Select Role Services page of the Add Role Services Wizard, select IP and Domain Restrictions, and then click Next.
On the Confirm Installation Selections page, click Install.
On the Results page, click Close.
Windows Vista or Windows 7
On the taskbar, click Start, and then click Control Panel.
In Control Panel, click Programs and Features, and then click Turn Windows Features on or off.
Expand Internet Information Services, then World Wide Web Services, then Security.
Select IP Security, and then click OK.
How To
How to add IP restrictions to deny access for a Web site
Open Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager:
If you are using Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2:
- On the taskbar, click Server Manager, click Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows 8 or Windows 8.1:
- Hold down the Windows key, press the letter X, and then click Control Panel.
- Click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server 2008 R2:
- On the taskbar, click Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows Vista or Windows 7:
- On the taskbar, click Start, and then click Control Panel.
- Double-click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
In the Connections pane, expand the server name, expand Sites, and then site, application or Web service for which you want to add IP restrictions.
In the Home pane, double-click the IP Address and Domain Restrictions feature.
In the IP Address and Domain Restrictions feature, click Add Deny Entry... in the Actions pane.
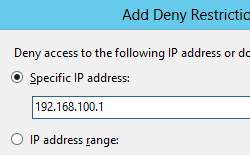
Enter the IP address that you wish to deny, and then click OK.
How to edit the IP restrictions feature settings for a Web site
Open Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager:
If you are using Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2:
- On the taskbar, click Server Manager, click Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows 8 or Windows 8.1:
- Hold down the Windows key, press the letter X, and then click Control Panel.
- Click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server 2008 R2:
- On the taskbar, click Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows Vista or Windows 7:
- On the taskbar, click Start, and then click Control Panel.
- Double-click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
In the Connections pane, expand the server name, expand Sites, and then site, application or Web service for which you want to add IP restrictions.
In the Home pane, double-click the IP Address and Domain Restrictions feature.
In the IP Address and Domain Restrictions feature, click Edit Feature Settings... in the Actions pane.
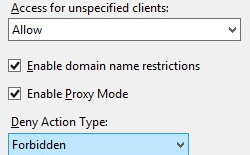
Choose the default access behavior for unspecified clients, specify whether to enable restrictions by domain name, specify whether to enable Proxy Mode, select the Deny Action Type, and then click OK.
Configuration
Rules are processed from top to bottom, in the order they appear in the list. The allowunlisted attribute is processed last. Best practice for Internet Protocol security (IPsec) restrictions is to list Deny rules first.
Attributes
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
allowed |
Optional Boolean attribute. Specifies whether to allow access to the address space. The default value is false. |
domainName |
Optional string attribute. Specifies domain name on which to impose a restriction rule. You can use an asterisk (*) as a wildcard. |
ipAddress |
Optional string attribute. Specifies the IP version 4 address on which to impose a restriction rule. |
subnetMask |
Optional string attribute. Specifies the subnet mask with which to evaluate the IP address for this restriction rule. You can use a subnet mask to identify a range of IP addresses in an address space. The default value requires a direct match of the IP address being evaluated (effectively, a range of a single address). The default value is 255.255.255.255. |
Child Elements
None.
Configuration Sample
The following configuration sample adds two IP restrictions to the Default Web Site; the first restriction denies access to the IP address 192.168.100.1, and the second restriction denies access to the entire 169.254.0.0 network.
<location path="Default Web Site">
<system.webServer>
<security>
<ipSecurity>
<add ipAddress="192.168.100.1" />
<add ipAddress="169.254.0.0" subnetMask="255.255.0.0" />
</ipSecurity>
</security>
</system.webServer>
</location>
Sample Code
The following code samples add two IP restrictions to the Default Web Site; the first restriction denies access to the IP address 192.168.100.1, and the second restriction denies access to the entire 169.254.0.0 network.
AppCmd.exe
appcmd.exe set config "Default Web Site" -section:system.webServer/security/ipSecurity /+"[ipAddress='192.168.100.1',allowed='False']" /commit:apphost
appcmd.exe set config "Default Web Site" -section:system.webServer/security/ipSecurity /+"[ipAddress='169.254.0.0',subnetMask='255.255.0.0',allowed='False']" /commit:apphost
Note
You must be sure to set the commit parameter to apphost when you use AppCmd.exe to configure these settings. This commits the configuration settings to the appropriate location section in the ApplicationHost.config file.
C#
using System;
using System.Text;
using Microsoft.Web.Administration;
internal static class Sample
{
private static void Main()
{
using (ServerManager serverManager = new ServerManager())
{
Configuration config = serverManager.GetApplicationHostConfiguration();
ConfigurationSection ipSecuritySection = config.GetSection("system.webServer/security/ipSecurity", "Default Web Site");
ConfigurationElementCollection ipSecurityCollection = ipSecuritySection.GetCollection();
ConfigurationElement addElement = ipSecurityCollection.CreateElement("add");
addElement["ipAddress"] = @"192.168.100.1";
addElement["allowed"] = false;
ipSecurityCollection.Add(addElement);
ConfigurationElement addElement1 = ipSecurityCollection.CreateElement("add");
addElement1["ipAddress"] = @"169.254.0.0";
addElement1["subnetMask"] = @"255.255.0.0";
addElement1["allowed"] = false;
ipSecurityCollection.Add(addElement1);
serverManager.CommitChanges();
}
}
}
VB.NET
Imports System
Imports System.Text
Imports Microsoft.Web.Administration
Module Sample
Sub Main()
Dim serverManager As ServerManager = New ServerManager
Dim config As Configuration = serverManager.GetApplicationHostConfiguration
Dim ipSecuritySection As ConfigurationSection = config.GetSection("system.webServer/security/ipSecurity", "Default Web Site")
Dim ipSecurityCollection As ConfigurationElementCollection = ipSecuritySection.GetCollection
Dim addElement As ConfigurationElement = ipSecurityCollection.CreateElement("add")
addElement("ipAddress") = "192.168.100.1"
addElement("allowed") = False
ipSecurityCollection.Add(addElement)
Dim addElement1 As ConfigurationElement = ipSecurityCollection.CreateElement("add")
addElement1("ipAddress") = "169.254.0.0"
addElement1("subnetMask") = "255.255.0.0"
addElement1("allowed") = False
ipSecurityCollection.Add(addElement1)
serverManager.CommitChanges()
End Sub
End Module
JavaScript
var adminManager = new ActiveXObject('Microsoft.ApplicationHost.WritableAdminManager');
adminManager.CommitPath = "MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST";
var ipSecuritySection = adminManager.GetAdminSection("system.webServer/security/ipSecurity", "MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST/Default Web Site");
var ipSecurityCollection = ipSecuritySection.Collection;
var addElement = ipSecurityCollection.CreateNewElement("add");
addElement.Properties.Item("ipAddress").Value = "192.168.100.1";
addElement.Properties.Item("allowed").Value = false;
ipSecurityCollection.AddElement(addElement);
var addElement1 = ipSecurityCollection.CreateNewElement("add");
addElement1.Properties.Item("ipAddress").Value = "169.254.0.0";
addElement1.Properties.Item("subnetMask").Value = "255.255.0.0";
addElement1.Properties.Item("allowed").Value = false;
ipSecurityCollection.AddElement(addElement1);
adminManager.CommitChanges();
VBScript
Set adminManager = WScript.CreateObject("Microsoft.ApplicationHost.WritableAdminManager")
adminManager.CommitPath = "MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST"
Set ipSecuritySection = adminManager.GetAdminSection("system.webServer/security/ipSecurity", "MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST/Default Web Site")
Set ipSecurityCollection = ipSecuritySection.Collection
Set addElement = ipSecurityCollection.CreateNewElement("add")
addElement.Properties.Item("ipAddress").Value = "192.168.100.1"
addElement.Properties.Item("allowed").Value = False
ipSecurityCollection.AddElement(addElement)
Set addElement1 = ipSecurityCollection.CreateNewElement("add")
addElement1.Properties.Item("ipAddress").Value = "169.254.0.0"
addElement1.Properties.Item("subnetMask").Value = "255.255.0.0"
addElement1.Properties.Item("allowed").Value = False
ipSecurityCollection.AddElement(addElement1)
adminManager.CommitChanges()