ODBC Logging <odbcLogging>
Overview
The <odbcLogging> element configures Open Database Connectivity (ODBC) logging for Internet Information Services (IIS) 7. ODBC logging records all HTTP activity to a user-defined database instead of to text files.
ODBC logging is implemented as a custom logging module in IIS 7, therefore enabling and configuring ODBC logging in IIS 7 consists of two separate actions:
Setting the ODBC logging attributes in the
<odbcLogging>element. Specifically, the following attributes must be configured:- The dataSource attribute must specify the System Data Source Name (DSN) for the database where the table specified by the tableName attribute is located.
- The password attribute must specify the database password that IIS 7 will use when writing log information to the database.
- The tableName attribute must specify the name of the database table in the database that is specified by the dataSource attribute.
- The userName attribute must specify the database user name that IIS 7 will use when writing log information to the database.
Setting the correct custom logging attributes in the <logFile> element. Specifically, the following attributes must be configured:
- The logFormat attribute must be set to "Custom."
- The customLogPluginClsid attribute must be set to "{FF16065B-DE82-11CF-BC0A-00AA006111E0}"
By default, IIS 7 logs all activity to text files that use the W3C extended log file format, and by default you can configure IIS to use other text file formats such as the NCSA or native IIS format. The major disadvantage of using these text-based formats is that they are more difficult to parse for activity, and generally require a utility like Microsoft's LogParser in order to retrieve any useful information from your logs. In addition, data-parsing performance with text files is also typically much slower than using a database. However, text-based logging is performed in kernel mode, which improves the performance for logging requests.
When you use ODBC logging, your server's activity is stored in a database, which should greatly improve data retrieval. This expands the possibilities for using a wide variety of database clients when data mining your server's activity. The major disadvantage to using ODBC logging is the performance for logging because when ODBC logging is enabled, IIS disables the kernel-mode cache. For this reason, implementing ODBC logging can degrade overall server performance.
Note
To create the table for ODBC logging, you can use the "%windir%\System32\inetsrv\logtemp.sql" file that is provided with IIS 7. For more information about ODBC logging, see Microsoft Knowledge Base Article 245243.
Compatibility
| Version | Notes |
|---|---|
| IIS 10.0 | The <odbcLogging> element was not modified in IIS 10.0. |
| IIS 8.5 | The <odbcLogging> element was not modified in IIS 8.5. |
| IIS 8.0 | The <odbcLogging> element was not modified in IIS 8.0. |
| IIS 7.5 | The <odbcLogging> element was not modified in IIS 7.5. |
| IIS 7.0 | The <odbcLogging> element was introduced in IIS 7.0. |
| IIS 6.0 | The attributes of the <odbcLogging> element replace the following IIS 6.0 metabase properties:
|
Setup
The <odbcLogging> element is not available on the default installation of IIS 7 and later. To install it, use the following steps.
Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2
- On the taskbar, click Server Manager.
- In Server Manager, click the Manage menu, and then click Add Roles and Features.
- In the Add Roles and Features wizard, click Next. Select the installation type and click Next. Select the destination server and click Next.
- On the Server Roles page, expand Web Server (IIS), expand Web Server, expand Health and Diagnostics, and then select ODBC Logging. Click Next.
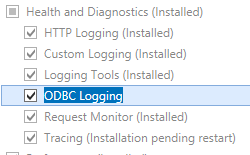 .
. - On the Select features page, click Next.
- On the Confirm installation selections page, click Install.
- On the Results page, click Close.
Windows 8 or Windows 8.1
- On the Start screen, move the pointer all the way to the lower left corner, right-click the Start button, and then click Control Panel.
- In Control Panel, click Programs and Features, and then click Turn Windows features on or off.
- Expand Internet Information Services, expand World Wide Web Services, expand Health and Diagnostics, and then select ODBC Logging.
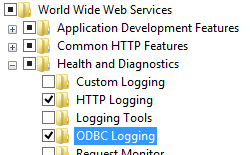
- Click OK.
- Click Close.
Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server 2008 R2
- On the taskbar, click Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Server Manager.
- In the Server Manager hierarchy pane, expand Roles, and then click Web Server (IIS).
- In the Web Server (IIS) pane, scroll to the Role Services section, and then click Add Role Services.
- On the Select Role Services page of the Add Role Services Wizard, select ODBC Logging, and then click Next.
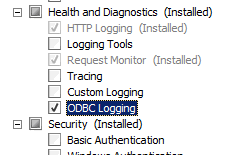
- On the Confirm Installation Selections page, click Install.
- On the Results page, click Close.
Windows Vista or Windows 7
- On the taskbar, click Start, and then click Control Panel.
- In Control Panel, click Programs and Features, and then click Turn Windows Features on or off.
- Expand Internet Information Services, then select ODBC Logging, and then click OK.
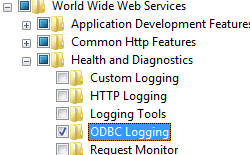
How To
There is no user interface for configuring ODBC logging for IIS 7. For examples of how to configure ODBC logging programmatically, see the Code Samples section of this document.
Configuration
Attributes
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
dataSource |
Optional string attribute. Specifies the System Data Source Name (DSN) for the database to which the log is written. The default value is InternetDb. |
password |
Optional string attribute. Specifies the ODBC database password that you use when you write information to the database during event logging. By default, this value is encrypted. The default value is [enc:AesProvider::enc]. |
tableName |
Optional string attribute. Specifies the name of the ODBC database table where Windows writes information during event logging. The default value is InternetLog. |
userName |
Optional string attribute. Specifies the ODBC database user name that is used for writing information to the database during event logging. The default value is InternetAdmin. |
Child Elements
None.
Configuration Sample
This first configuration sample for the Default Web Site configures the attributes in the <odbcLogging> element that specify the system DSN, table name, user name, and password for an ODBC logging connection.
<location path="Default Web Site">
<system.webServer>
<odbcLogging dataSource="InternetDb"
tableName="InternetLog"
userName="InternetAdmin"
password="[enc:AesProvider:57686f6120447564652c2049495320526f636b73:enc]" />
</system.webServer>
</location>
This second configuration sample configures the correct custom logging attributes in <logFile> element that enable ODBC logging for the Default Web Site.
<site name="Default Web Site" id="1" serverAutoStart="true">
<application path="/" applicationPool="DefaultAppPool">
<virtualDirectory path="/" physicalPath="%SystemDrive%\inetpub\wwwroot" />
</application>
<bindings>
<binding protocol="http" bindingInformation="*:80:" />
</bindings>
<logFile logFormat="Custom"
customLogPluginClsid="{FF16065B-DE82-11CF-BC0A-00AA006111E0}" />
</site>
Sample Code
The following code samples configure two sets of options for the Default Web Site:
- The first half of each sample configures the attributes in the
<odbcLogging>element that specify the system DSN, table name, user name, and password for an ODBC logging connection. - The second half of each sample specifies the custom logging attributes in <logFile> element that enable ODBC logging.
AppCmd.exe
appcmd.exe set config "Default Web Site" -section:system.webServer/odbcLogging /dataSource:"InternetDb" /commit:apphost
appcmd.exe set config "Default Web Site" -section:system.webServer/odbcLogging /tableName:"InternetLog" /commit:apphost
appcmd.exe set config "Default Web Site" -section:system.webServer/odbcLogging /userName:"InternetAdmin" /commit:apphost
appcmd.exe set config "Default Web Site" -section:system.webServer/odbcLogging /password:"P@ssw0rd" /commit:apphost
appcmd.exe set sites "Default Web Site" -logFile.logFormat:"Custom" /commit:apphost
appcmd.exe set sites "Default Web Site" -logFile.customLogPluginClsid:"{FF16065B-DE82-11CF-BC0A-00AA006111E0}" /commit:apphost
Note
You must be sure to set the commit parameter to apphost when you use AppCmd.exe to configure these settings. This commits the configuration settings to the appropriate location section in the ApplicationHost.config file.
C#
using System;
using System.Text;
using Microsoft.Web.Administration;
internal static class Sample
{
private static void Main()
{
using (ServerManager serverManager = new ServerManager())
{
Configuration config = serverManager.GetApplicationHostConfiguration();
ConfigurationSection odbcLoggingSection = config.GetSection("system.webServer/odbcLogging", "Default Web Site");
odbcLoggingSection["dataSource"] = @"InternetDb";
odbcLoggingSection["tableName"] = @"InternetLog";
odbcLoggingSection["userName"] = @"InternetAdmin";
odbcLoggingSection["password"] = @"P@ssw0rd";
ConfigurationSection sitesSection = config.GetSection("system.applicationHost/sites");
ConfigurationElementCollection sitesCollection = sitesSection.GetCollection();
ConfigurationElement siteElement = FindElement(sitesCollection, "site", "name", @"Default Web Site");
if (siteElement == null) throw new InvalidOperationException("Element not found!");
ConfigurationElement logFileElement = siteElement.GetChildElement("logFile");
logFileElement["customLogPluginClsid"] = @"{FF16065B-DE82-11CF-BC0A-00AA006111E0}";
logFileElement["logFormat"] = @"Custom";
serverManager.CommitChanges();
}
}
private static ConfigurationElement FindElement(ConfigurationElementCollection collection, string elementTagName, params string[] keyValues)
{
foreach (ConfigurationElement element in collection)
{
if (String.Equals(element.ElementTagName, elementTagName, StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase))
{
bool matches = true;
for (int i = 0; i < keyValues.Length; i += 2)
{
object o = element.GetAttributeValue(keyValues[i]);
string value = null;
if (o != null)
{
value = o.ToString();
}
if (!String.Equals(value, keyValues[i + 1], StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase))
{
matches = false;
break;
}
}
if (matches)
{
return element;
}
}
}
return null;
}
}
VB.NET
Imports System
Imports System.Text
Imports Microsoft.Web.Administration
Module Sample
Sub Main()
Dim serverManager As ServerManager = New ServerManager
Dim config As Configuration = serverManager.GetApplicationHostConfiguration
Dim odbcLoggingSection As ConfigurationSection = config.GetSection("system.webServer/odbcLogging", "Default Web Site")
odbcLoggingSection("dataSource") = "InternetDb"
odbcLoggingSection("tableName") = "InternetLog"
odbcLoggingSection("userName") = "InternetAdmin"
odbcLoggingSection("password") = "P@ssw0rd"
Dim sitesSection As ConfigurationSection = config.GetSection("system.applicationHost/sites")
Dim sitesCollection As ConfigurationElementCollection = sitesSection.GetCollection
Dim siteElement As ConfigurationElement = FindElement(sitesCollection, "site", "name", "Default Web Site")
If (siteElement Is Nothing) Then
Throw New InvalidOperationException("Element not found!")
End If
Dim logFileElement As ConfigurationElement = siteElement.GetChildElement("logFile")
logFileElement("customLogPluginClsid") = "{FF16065B-DE82-11CF-BC0A-00AA006111E0}"
logFileElement("logFormat") = "Custom"
serverManager.CommitChanges()
End Sub
Private Function FindElement(ByVal collection As ConfigurationElementCollection, ByVal elementTagName As String, ByVal ParamArray keyValues() As String) As ConfigurationElement
For Each element As ConfigurationElement In collection
If String.Equals(element.ElementTagName, elementTagName, StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase) Then
Dim matches As Boolean = True
Dim i As Integer
For i = 0 To keyValues.Length - 1 Step 2
Dim o As Object = element.GetAttributeValue(keyValues(i))
Dim value As String = Nothing
If (Not (o) Is Nothing) Then
value = o.ToString
End If
If Not String.Equals(value, keyValues((i + 1)), StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase) Then
matches = False
Exit For
End If
Next
If matches Then
Return element
End If
End If
Next
Return Nothing
End Function
End Module
JavaScript
var adminManager = new ActiveXObject('Microsoft.ApplicationHost.WritableAdminManager');
adminManager.CommitPath = "MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST";
var odbcLoggingSection = adminManager.GetAdminSection("system.webServer/odbcLogging", "MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST/Default Web Site");
odbcLoggingSection.Properties.Item("dataSource").Value = "InternetDb";
odbcLoggingSection.Properties.Item("tableName").Value = "InternetLog";
odbcLoggingSection.Properties.Item("userName").Value = "InternetAdmin";
odbcLoggingSection.Properties.Item("password").Value = "P@ssw0rd";
var sitesSection = adminManager.GetAdminSection("system.applicationHost/sites", "MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST");
var sitesCollection = sitesSection.Collection;
var siteElementPos = FindElement(sitesCollection, "site", ["name", "Default Web Site"]);
if (siteElementPos == -1) throw "Element not found!";
var siteElement = sitesCollection.Item(siteElementPos);
var logFileElement = siteElement.ChildElements.Item("logFile");
logFileElement.Properties.Item("customLogPluginClsid").Value = "{FF16065B-DE82-11CF-BC0A-00AA006111E0}";
logFileElement.Properties.Item("logFormat").Value = "Custom";
adminManager.CommitChanges();
function FindElement(collection, elementTagName, valuesToMatch) {
for (var i = 0; i < collection.Count; i++) {
var element = collection.Item(i);
if (element.Name == elementTagName) {
var matches = true;
for (var iVal = 0; iVal < valuesToMatch.length; iVal += 2) {
var property = element.GetPropertyByName(valuesToMatch[iVal]);
var value = property.Value;
if (value != null) {
value = value.toString();
}
if (value != valuesToMatch[iVal + 1]) {
matches = false;
break;
}
}
if (matches) {
return i;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
VBScript
Set adminManager = WScript.CreateObject("Microsoft.ApplicationHost.WritableAdminManager")
adminManager.CommitPath = "MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST"
Set odbcLoggingSection = adminManager.GetAdminSection("system.webServer/odbcLogging", "MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST/Default Web Site")
odbcLoggingSection.Properties.Item("dataSource").Value = "InternetDb"
odbcLoggingSection.Properties.Item("tableName").Value = "InternetLog"
odbcLoggingSection.Properties.Item("userName").Value = "InternetAdmin"
odbcLoggingSection.Properties.Item("password").Value = "P@ssw0rd"
Set sitesSection = adminManager.GetAdminSection("system.applicationHost/sites", "MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST")
Set sitesCollection = sitesSection.Collection
siteElementPos = FindElement(sitesCollection, "site", Array("name", "Default Web Site"))
If (siteElementPos = -1) Then
WScript.Echo "Element not found!"
WScript.Quit
End If
Set siteElement = sitesCollection.Item(siteElementPos)
Set logFileElement = siteElement.ChildElements.Item("logFile")
logFileElement.Properties.Item("customLogPluginClsid").Value = "{FF16065B-DE82-11CF-BC0A-00AA006111E0}"
logFileElement.Properties.Item("logFormat").Value = "Custom"
adminManager.CommitChanges()
Function FindElement(collection, elementTagName, valuesToMatch)
For i = 0 To CInt(collection.Count) - 1
Set element = collection.Item(i)
If element.Name = elementTagName Then
matches = True
For iVal = 0 To UBound(valuesToMatch) Step 2
Set property = element.GetPropertyByName(valuesToMatch(iVal))
value = property.Value
If Not IsNull(value) Then
value = CStr(value)
End If
If Not value = CStr(valuesToMatch(iVal + 1)) Then
matches = False
Exit For
End If
Next
If matches Then
Exit For
End If
End If
Next
If matches Then
FindElement = i
Else
FindElement = -1
End If
End Function