Adding HTTP Errors <error>
Overview
The <error> element of the <httpErrors> collection adds a unique error mapping to the HTTP errors collection.
Compatibility
| Version | Notes |
|---|---|
| IIS 10.0 | The <error> element was not modified in IIS 10.0. |
| IIS 8.5 | The <error> element was not modified in IIS 8.5. |
| IIS 8.0 | The <error> element was not modified in IIS 8.0. |
| IIS 7.5 | The <error> element was not modified in IIS 7.5. |
| IIS 7.0 | The <error> element of the <httpErrors> collection was introduced in IIS 7.0. |
| IIS 6.0 | The <httpErrors> collection replaces the IIS 6.0 HttpErrors section of the IIsWebService metabase object. |
Setup
The <error> element of the <httpErrors> collection is included in the default installation of IIS 7.
How To
How to add a custom error page
Open Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager:
If you are using Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2:
- On the taskbar, click Server Manager, click Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows 8 or Windows 8.1:
- Hold down the Windows key, press the letter X, and then click Control Panel.
- Click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server 2008 R2:
- On the taskbar, click Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows Vista or Windows 7:
- On the taskbar, click Start, and then click Control Panel.
- Double-click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
In the Connections pane, expand the server name, expand Sites, and then navigate to the Web site or application that you want to configure custom error pages for.
In the Home pane, double-click Error Pages.
In the Actions pane, click Add...
In the Add Custom Error Page dialog box, under Status code, type the number of the HTTP status code for which you want to create a custom error message.
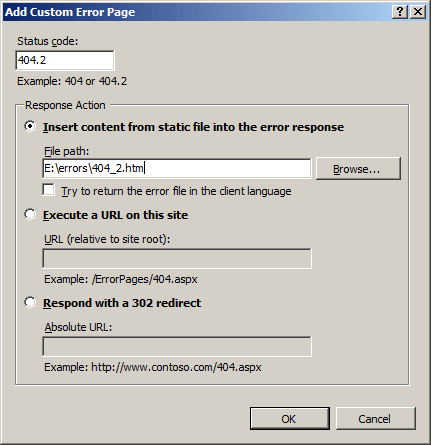
In the Response Action section, do one of the following:
- Select Insert content from static file into the error response to serve static content, for example, an .html file, for the custom error.
- Select Execute a URL on this site to serve dynamic content, for example, an .asp file for the custom error.
- Select Respond with a 302 redirect to redirect client browsers to a different URL that contains the custom error file.
In the File path text box, type the path of the custom error page if you chose Insert content from static file into the error response or the URL of the custom error page if you use either the Execute a URL on this site or Respond with a 302 redirect, and then click OK.
Note
If you select Execute a URL on this site, the path must be a relative path. If you select Respond with a 302 redirect, the URL must be an absolute URL.
Note
The following HTTP errors can't be customized: 400, 403.9, 411, 414, 500, 500.11, 500.14, 500.15, 501, 503, and 505.
Configuration
Attributes
| Attribute | Description | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
path |
Required string attribute. Specifies the file path or URL that is served in response to the HTTP error specified by the statusCode and subStatusCode attributes. If you choose the File response mode, you specify the path of the custom error page. If you choose the ExecuteURL response mode, the path has to be a server relative URL (for example, /404.htm). If you choose the Redirect response mode, you have to enter an absolute URL (for example, www.contoso.com/404.htm). |
||||||||
prefixLanguageFilePath |
Optional string attribute. Specifies the initial path segment when generating the path for a custom error. This segment appears before the language-specific portion of the custom error path. For example, in the path C:\Inetpub\Custerr\en-us\404.htm, C:\Inetpub\Custerr is the prefixLanguageFilePath. |
||||||||
responseMode |
Optional enum attribute. Specifies how custom error content is returned. The responseMode attribute can be one of the following possible values. The default is File.
|
||||||||
statusCode |
Required uint attribute. Specifies the number of the HTTP status code for which you want to create a custom error message. Acceptable values are in the range from 400 through 999. |
||||||||
subStatusCode |
Optional int attribute. Specifies the number of the HTTP substatus code for which you want to create a custom error message. Acceptable values are in the range from -1 through 999. The default value is -1. |
Child Elements
None.
Configuration Sample
The following configuration example, when included in the Web.config file for a Web site or application, uses the errorMode attribute to only allow detailed error messages to appear on the local computer. It also uses the defaultResponseMode attribute to set the response mode for the site or application. The sample then removes the inherited error message for the 500 status code. Next, it sets the prefixLanguageFilePath attribute to the directory where IIS should search of a new custom error page, and sets the path attribute to 500.htm, the file that contains the custom error message.
<configuration>
<system.webServer>
<httpErrors errorMode="DetailedLocalOnly" defaultResponseMode="File" >
<remove statusCode="500" />
<error statusCode="500"
prefixLanguageFilePath="C:\Contoso\Content\errors"
path="500.htm" />
</httpErrors>
</system.webServer>
</configuration>
Sample Code
The following examples adds a new file for all status code 404 errors with a substatus of 5, which IIS returns for "URL Sequence Denied" errors. In these examples, the prefix path is set to "%SystemDrive%\inetpub\custerr", and the file name is specified as "404.5.htm".
AppCmd.exe
appcmd.exe set config -section:system.webServer/httpErrors /+"[statusCode='404',subStatusCode='5',prefixLanguageFilePath='%SystemDrive%\inetpub\custerr',path='404.5.htm']" /commit:apphost
Note
You must be sure to set the commit parameter to apphost when you use AppCmd.exe to configure these settings. This commits the configuration settings to the appropriate location section in the ApplicationHost.config file.
C#
using System;
using System.Text;
using Microsoft.Web.Administration;
internal static class Sample
{
private static void Main()
{
using (ServerManager serverManager = new ServerManager())
{
Configuration config = serverManager.GetApplicationHostConfiguration();
ConfigurationSection httpErrorsSection = config.GetSection("system.webServer/httpErrors");
ConfigurationElementCollection httpErrorsCollection = httpErrorsSection.GetCollection();
ConfigurationElement errorElement = httpErrorsCollection.CreateElement("error");
errorElement["statusCode"] = 404;
errorElement["subStatusCode"] = 5;
errorElement["prefixLanguageFilePath"] = @"%SystemDrive%\inetpub\custerr";
errorElement["path"] = @"404.5.htm";
httpErrorsCollection.Add(errorElement);
serverManager.CommitChanges();
}
}
}
VB.NET
Imports System
Imports System.Text
Imports Microsoft.Web.Administration
Module Sample
Sub Main()
Dim serverManager As ServerManager = New ServerManager
Dim config As Configuration = serverManager.GetApplicationHostConfiguration
Dim httpErrorsSection As ConfigurationSection = config.GetSection("system.webServer/httpErrors")
Dim httpErrorsCollection As ConfigurationElementCollection = httpErrorsSection.GetCollection
Dim errorElement As ConfigurationElement = httpErrorsCollection.CreateElement("error")
errorElement("statusCode") = 404
errorElement("subStatusCode") = 5
errorElement("prefixLanguageFilePath") = "%SystemDrive%\inetpub\custerr"
errorElement("path") = "404.5.htm"
httpErrorsCollection.Add(errorElement)
serverManager.CommitChanges()
End Sub
End Module
JavaScript
var adminManager = new ActiveXObject('Microsoft.ApplicationHost.WritableAdminManager');
adminManager.CommitPath = "MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST";
var httpErrorsSection = adminManager.GetAdminSection("system.webServer/httpErrors", "MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST");
var httpErrorsCollection = httpErrorsSection.Collection;
var errorElement = httpErrorsCollection.CreateNewElement("error");
errorElement.Properties.Item("statusCode").Value = 404;
errorElement.Properties.Item("subStatusCode").Value = 5;
errorElement.Properties.Item("prefixLanguageFilePath").Value = "%SystemDrive%\\inetpub\\custerr";
errorElement.Properties.Item("path").Value = "404.5.htm";
httpErrorsCollection.AddElement(errorElement);
adminManager.CommitChanges();
VBScript
Set adminManager = createObject("Microsoft.ApplicationHost.WritableAdminManager")
adminManager.CommitPath = "MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST"
Set httpErrorsSection = adminManager.GetAdminSection("system.webServer/httpErrors", "MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST")
Set httpErrorsCollection = httpErrorsSection.Collection
Set errorElement = httpErrorsCollection.CreateNewElement("error")
errorElement.Properties.Item("statusCode").Value = 404
errorElement.Properties.Item("subStatusCode").Value = 5
errorElement.Properties.Item("prefixLanguageFilePath").Value = "%SystemDrive%\inetpub\custerr"
errorElement.Properties.Item("path").Value = "404.5.htm"
httpErrorsCollection.AddElement errorElement
adminManager.CommitChanges()