ASP Limits <limits>
Overview
The <limits> element of the <asp> element specifies the following Active Server Pages (ASP) connection and queue limits for Internet Information Services (IIS) 7:
The bufferingLimit attribute sets the maximum size of the ASP buffer. If response buffering is turned on, this attribute controls the maximum number of bytes that an ASP page can write to the response buffer before a flush occurs.
The maxRequestEntityAllowed attribute specifies the maximum number of bytes allowed in the entity body of an ASP request. If a Content-Length header is present and specifies an amount of data greater than the value of maxRequestEntityAllowed, IIS returns an HTTP 403 error response.
The processorThreadMax attribute specifies the maximum number of worker threads per processor that IIS may create.
Note
This setting can dramatically influence the scalability of your Web applications and the performance of your server in general. Because this attribute defines the maximum number of ASP requests that can execute simultaneously, this setting should remain at the default value unless your ASP applications are making extended calls to external components.
The queueConnectionTestTime attribute specifies the number of seconds that a request can be queued before ASP determines whether the client is still connected. If the request is queued longer than the number of seconds specified by the queueConnectionTestTime attribute, ASP checks to determine whether the client is still connected before executing the request. If the client is no longer connected, the request is not processed and is deleted from the queue.
Note
Most often, users do not wait more than a few seconds for ASP pages to process. Although the maximum waiting time varies from user to user, the generally accepted maximum is approximately 10 seconds. You can use the queueConnectionTestTime attribute to ensure that IIS does not waste time processing a request that has been abandoned by the user. This attribute is useful for making ASP processing efficient only up to the point at which ASP begins to process the script. Once the script is running, however, your application should continue to check for client connection at appropriate times by using the IsClientConnected method of the ASP built-in Response object.
The queueTimeout attribute specifies the amount of time (in seconds) that an ASP script request is allowed to wait in the queue. When requests are pulled from the queue, they are checked to see if they have expired (have waited longer than the value of this parameter). Expired requests are rejected with a message indicating the server is too busy.
The requestQueueMax attribute specifies the maximum number of concurrent ASP requests that are permitted into the queue. Any client browser that attempts to request ASP files when the queue is full is sent an HTTP 500 Server Too Busy error.
The scriptTimeout attribute specifies (in seconds) the default length of time that ASP pages allow a script to run before terminating the script and writing an event to the Windows Event Log. ASP scripts can override this value by using the ScriptTimeout property of the ASP built-in Session object. The ScriptTimeout property allows your ASP applications to set a higher script time-out value. For example, you can use this setting to adjust the time-out once a particular user establishes a valid session by logging in or ordering a product.
Compatibility
| Version | Notes |
|---|---|
| IIS 10.0 | The <limits> element was not modified in IIS 10.0. |
| IIS 8.5 | The <limits> element was not modified in IIS 8.5. |
| IIS 8.0 | The <limits> element was not modified in IIS 8.0. |
| IIS 7.5 | The <limits> element was not modified in IIS 7.5. |
| IIS 7.0 | The <limits> element of the <asp> element was introduced in IIS 7.0. |
| IIS 6.0 | The <limits> element replaces the following IIS 6.0 metabase properties:
|
Setup
To support and configure ASP applications on your Web server, you must install the ASP module. To install the ASP module, use the following steps.
Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2
- On the taskbar, click Server Manager.
- In Server Manager, click the Manage menu, and then click Add Roles and Features. - In the Add Roles and Features wizard, click Next. Select the installation type and click Next. Select the destination server and click Next.
- On the Server Roles page, expand Web Server (IIS), expand Web Server, expand Application Development, and then select ASP.
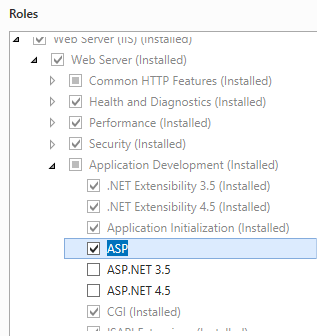
- If the Add features that are required by ASP? dialog box appears, click Add Features. (This page appears only if you have not already installed the ISAPI Extensions role service on your server.)
- On the Server Roles page, click Next.
- On the Select features page, click Next.
- On the Confirm installation selections page, click Install.
- On the Results page, click Close.
Windows 8 or Windows 8.1
On the Start screen, move the pointer all the way to the lower left corner, right-click the Start button, and then click Control Panel.
In Control Panel, click Programs and Features, and then click Turn Windows features on or off.
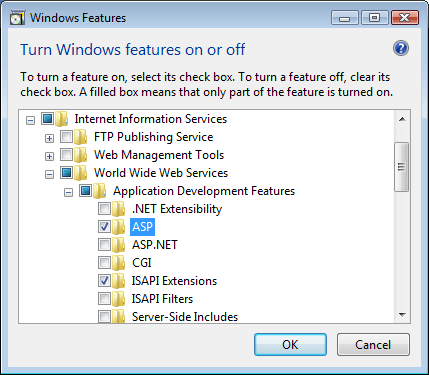
Expand Internet Information Services, expand World Wide Web Services, expand Application Development Features, and then select ASP.
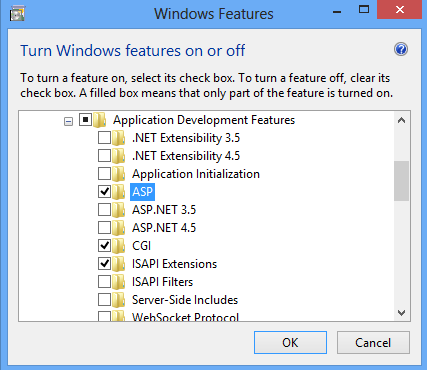
Note
The ISAPI Extensions role will be selected if it has not already been installed.
Click OK.
Click Close.
Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server 2008 R2
- On the taskbar, click Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Server Manager.
- In the Server Manager hierarchy pane, expand Roles, and then click Web Server (IIS).
- In the Web Server (IIS) pane, scroll to the Role Services section, and then click Add Role Services.
- On the Select Role Services page of the Add Role Services Wizard, select ASP.
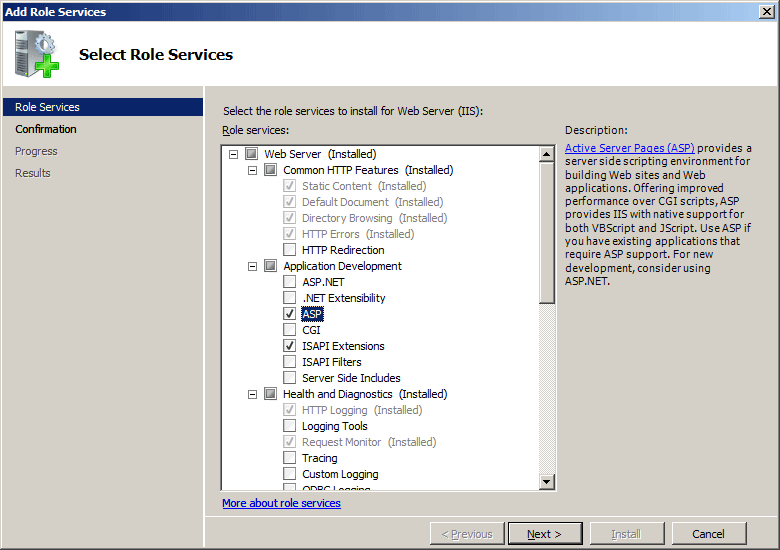
- If the Add role services required by ASP dialog box appears, click Add Required Role Services. (This page appears only if you have not already installed the ISAPI Extensions role service on your server.)
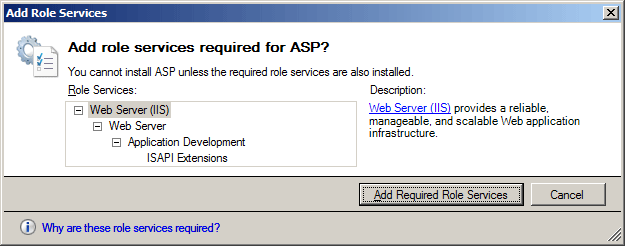
- On the Select Role Services page, click Next.
- On the Confirm Installation Selections page, click Install.
- On the Results page, click Close.
Windows Vista or Windows 7
- On the taskbar, click Start, and then click Control Panel.
- In Control Panel, click Programs and Features, and then click Turn Windows Features on or off.
- Expand Internet Information Services, then World Wide Web Services, then Application Development Features.
- Select ASP, and then click OK.
How To
How to configure the ASP cache settings for a server
Open Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager:
If you are using Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2:
- On the taskbar, click Server Manager, click Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows 8 or Windows 8.1:
- Hold down the Windows key, press the letter X, and then click Control Panel.
- Click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server 2008 R2:
- On the taskbar, click Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows Vista or Windows 7:
- On the taskbar, click Start, and then click Control Panel.
- Double-click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
In the Connections pane, highlight the name of your server.
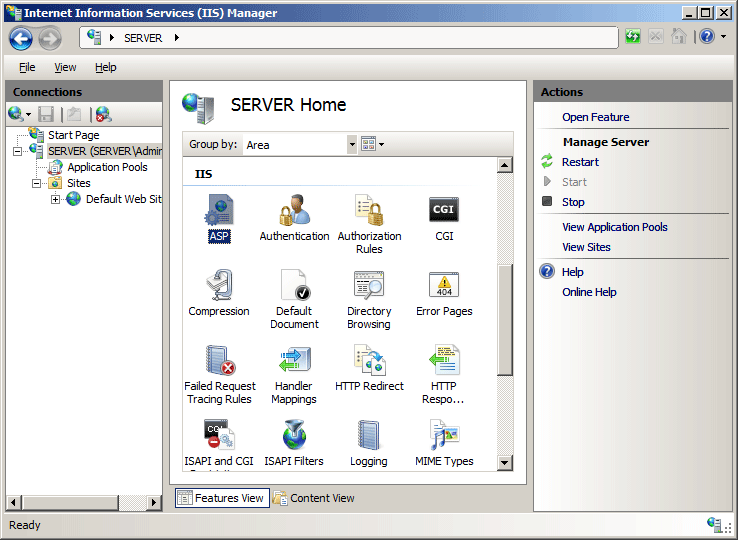
In the server's Home pane, double-click ASP.
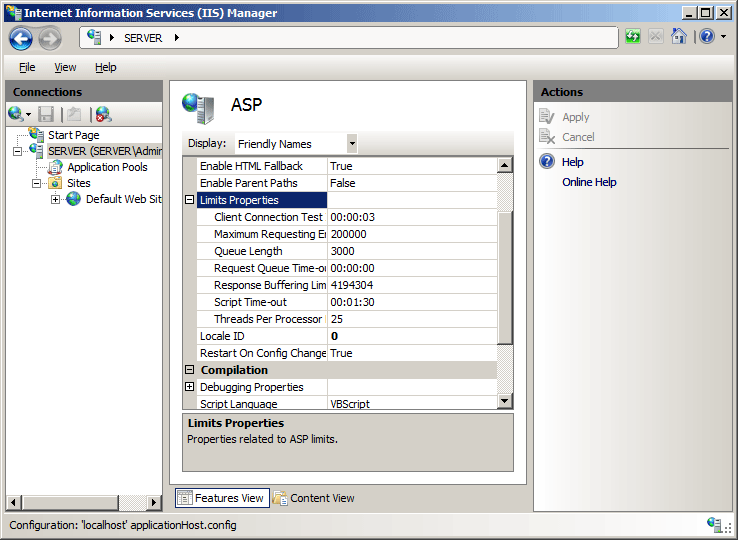
In the ASP pane, expand the Limits Properties section, configure your desired settings, then click Apply in the Actions pane.
Configuration
Attributes
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
bufferingLimit |
Optional uint attribute. Specifies the maximum size, in bytes, of the ASP buffer. If response buffering is turned on, this attribute controls the maximum number of bytes that an ASP page can write to the response buffer before a flush occurs. This value is an integer in the range from 0 to 2147483647. The default value is 4194304. |
maxRequestEntityAllowed |
Optional uint attribute. Specifies the maximum number of bytes allowed in the entire body of an ASP request. This value is an integer in the range from 0 to 2147483647. The default value is 200000. |
processorThreadMax |
Optional uint attribute. Specifies the maximum number of worker threads per processor that ASP can create. The default value is 25. |
queueConnectionTestTime |
Optional timeSpan attribute. Specifies the time interval (hh:mm:ss) after which ASP will check to see whether the client is still connected before executing a request. If the client is no longer connected, the request is not processed and is deleted from the queue. The default value is 00:00:03. |
queueTimeout |
Optional timeSpan attribute. Specifies the maximum period of time (hh:mm:ss) that an ASP request can wait in the request queue. The default value is 00:00:00. |
requestQueueMax |
Optional uint attribute. Specifies the maximum number of concurrent ASP requests that are allowed into the request queue. The default value is 3000. |
scriptTimeout |
Optional timeSpan attribute. Specifies the maximum period of time (hh:mm:ss) that ASP pages allow a script to run before terminating the script and writing an event to the Windows Event Log. The default value is 00:01:30. |
Child Elements
None.
Configuration Sample
The following configuration sample sets the ASP script time-out to 2 minutes, the amount of time that ASP will check to see whether the client is still connected before executing a request to 5 seconds, and the maximum number of concurrent ASP requests in request queue to 1,000.
<configuration>
<system.webServer>
<asp>
<cache diskTemplateCacheDirectory="%SystemDrive%\inetpub\temp\ASP Compiled Templates" />
<limits scriptTimeout="00:02:00"
queueConnectionTestTime="00:00:05"
requestQueueMax="1000" />
</asp>
<system.webServer>
<configuration>
Sample Code
The following code samples set the ASP script time-out to 2 minutes, the amount of time that ASP will check to see whether the client is still connected before executing a request to 5 seconds, and the maximum number of concurrent ASP requests in request queue to 1,000.
AppCmd.exe
appcmd.exe set config -section:system.webServer/asp /limits.scriptTimeout:"00:02:00" /commit:apphost
appcmd.exe set config -section:system.webServer/asp /limits.queueConnectionTestTime:"00:00:05" /commit:apphost
appcmd.exe set config -section:system.webServer/asp /limits.requestQueueMax:"1000" /commit:apphost
Note
You must be sure to set the commit parameter to apphost when you use AppCmd.exe to configure these settings. This commits the configuration settings to the appropriate location section in the ApplicationHost.config file.
C#
using System;
using System.Text;
using Microsoft.Web.Administration;
internal static class Sample
{
private static void Main()
{
using (ServerManager serverManager = new ServerManager())
{
Configuration config = serverManager.GetApplicationHostConfiguration();
ConfigurationSection aspSection = config.GetSection("system.webServer/asp");
ConfigurationElement limitsElement = aspSection.GetChildElement("limits");
limitsElement["scriptTimeout"] = TimeSpan.Parse("00:02:00");
limitsElement["queueConnectionTestTime"] = TimeSpan.Parse("00:00:05");
limitsElement["requestQueueMax"] = 1000;
serverManager.CommitChanges();
}
}
}
VB.NET
Imports System
Imports System.Text
Imports Microsoft.Web.Administration
Module Sample
Sub Main()
Dim serverManager As ServerManager = New ServerManager
Dim config As Configuration = serverManager.GetApplicationHostConfiguration
Dim aspSection As ConfigurationSection = config.GetSection("system.webServer/asp")
Dim limitsElement As ConfigurationElement = aspSection.GetChildElement("limits")
limitsElement("scriptTimeout") = TimeSpan.Parse("00:02:00")
limitsElement("queueConnectionTestTime") = TimeSpan.Parse("00:00:05")
limitsElement("requestQueueMax") = 1000
serverManager.CommitChanges()
End Sub
End Module
JavaScript
var adminManager = new ActiveXObject('Microsoft.ApplicationHost.WritableAdminManager');
adminManager.CommitPath = "MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST";
var aspSection = adminManager.GetAdminSection("system.webServer/asp", "MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST");
var limitsElement = aspSection.ChildElements.Item("limits");
limitsElement.Properties.Item("scriptTimeout").Value = "00:02:00";
limitsElement.Properties.Item("queueConnectionTestTime").Value = "00:00:05";
limitsElement.Properties.Item("requestQueueMax").Value = 1000;
adminManager.CommitChanges();
VBScript
Set adminManager = WScript.CreateObject("Microsoft.ApplicationHost.WritableAdminManager")
adminManager.CommitPath = "MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST"
Set aspSection = adminManager.GetAdminSection("system.webServer/asp", "MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST")
Set limitsElement = aspSection.ChildElements.Item("limits")
limitsElement.Properties.Item("scriptTimeout").Value = "00:02:00"
limitsElement.Properties.Item("queueConnectionTestTime").Value = "00:00:05"
limitsElement.Properties.Item("requestQueueMax").Value = 1000
adminManager.CommitChanges()