Web Limits <webLimits>
Overview
The <webLimits> element specifies TCP/IP connection and bandwidth limits.
Every 60 seconds, a worker process checks how long it has been idle. If its current idle time is greater than the idle time-out value specified by the Windows Process Activation Service (WAS), the worker process initiates a shutdown. When you specify a nonzero value for the dynamicIdleThreshold attribute, WAS will dynamically reduce this idle time-out depending on the amount of RAM used.
The dynamicIdleThreshold attribute represents the amount of committed physical RAM. For example, if your server has 2 gigabytes (GB) of physical memory installed and you set the dynamicIdleThreshold attribute value to 200, you have committed 200 percent (4 GB) of physical RAM for use. According to the following table, when 80 percent of 4 GB, that is, 160 percent (3.2 GB) of physical RAM is allocated, WAS will start reducing the idle time-out of all worker processes by 50 percent.
The following table lists the idle time-out reductions that occur at predetermined percentages of the dynamicIdleThreshold value.
Dynamic idle threshold percentage reached |
Dynamic idle time-out reduction |
|---|---|
| 75 or lower | WAS uses the original idle time-out settings. |
| 80 | WAS sets the idle time-out to one-half of the original value for all worker processes that have a configured idle time-out. |
| 85 | WAS sets the idle time-out to one-fourth of the original value for all worker processes that have a configured idle time-out. |
| 90 | WAS sets the idle time-out to one-eighth of the original value for all worker processes that have a configured idle time-out. |
| 95 | WAS sets the idle time-out to one-sixteenth of the original value for all worker processes that have a configured idle time-out. |
| 100 | WAS sets the idle time-out to one thirty-second of the original value for all worker processes that have a configured idle time-out. |
Dynamic Site Activation
Dynamic site activation helps IIS address scalability issues by enabling you to defer activation of Web sites. When the number of Web sites is greater than a limit, IIS will not activate any of the sites when the service is started. It will not create a queue and a binding for each configured site upon startup, as was previously done in IIS 8.0 and earlier. Instead, it creates a single queue that listens for requests for all sites, and has a single binding. WAS loads a list of the sites, their bindings, their applications, their application pools, and their application pool settings. When a request for a site arrives, IIS uses that list to create a queue and register a binding for the site. At that point, HTTP.sys places the request in the queue, WAS starts the worker process, and the request is processed.
With dynamic site activation, the IIS service will likely start more quickly and consume less memory. IIS should also take noticeably less time to restart because it will not need to release all of the registered queues and bindings with HTTP. Activation in this context refers to a process in which IIS registers a site with the HTTP protocol stack (HTTP.sys). This activation is not the same as creating a worker process, which only happens when a request for a site is received.
Dynamic site activation is enabled when the number of sites handled by a server is greater than a pre-set limit. By default, that limit is 100. If you do not change that value, a site will be activated dynamically on a server that hosts more than 100 sites. For 100 or fewer sites, on the other hand, all sites will be activated upon startup. You can change that limit by changing the dynamicRegistrationThreshold attribute. Note that the performance gain for a server with a lower number of sites will be smaller than with significantly more sites.
Note
When Dynamic site activation is enabled, users are not allowed to use an IP address to send a web request. For example, if users try to browse to HTTP://127.0.0.1, they will receive a 400 Bad Request Error.
Compatibility
| Version | Notes |
|---|---|
| IIS 10.0 | The <webLimits> element was not modified in IIS 10.0. |
| IIS 8.5 | The dynamicRegistrationThreshold attribute was added in IIS 8.5. |
| IIS 8.0 | The <webLimits> element was not modified in IIS 8.0. |
| IIS 7.5 | The <webLimits> element was not modified in IIS 7.5. |
| IIS 7.0 | The <webLimits> element was introduced in IIS 7.0. |
| IIS 6.0 | The <webLimits> element replaces the following IIS 6.0 metabase settings:
|
Setup
The <webLimits> element is included in the default installation of IIS 7 and later.
How To
How to configure the lower limit of dynamic site activation
Open Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager:
If you are using Windows Server 2012 R2:
- On the taskbar, click Server Manager, click Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows 8.1:
- Hold down the Windows key, press the letter X, and then click Control Panel.
- Click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
In the Connections pane, select the server, and then double-click Configuration Editor in the Management area.
In the Configuration Editor, for the Section, expand
system.applicationHost, and then select webLimits.Enter a value for dynamicRegistrationThreshold.
In the Action pane, click Apply.
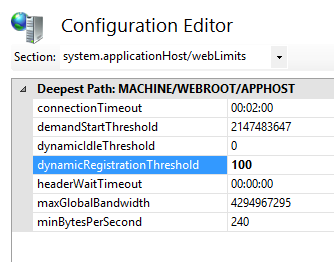
Configuration
Attributes
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
connectionTimeout |
Optional timeSpan attribute. Specifies the time that IIS waits before it disconnects a connection considered inactive. The default value is 00:02:00. |
demandStartThreshold |
Optional uint attribute. Specifies the maximum number of worker processes allowed to run concurrently on a Web server. You can use this property to prevent IIS servers from becoming unresponsive when too many worker processes have been started. The default value is 2147483647. |
dynamicIdleThreshold |
Optional uint attribute. Specifies the percentage of committed physical RAM. The valid integer range is from 0 through 10000. WAS uses this threshold value to dynamically shorten the idle time-out of worker processes. For more information, see the Remarks section. The default value is 0. |
dynamicRegistrationThreshold |
Optional uint attribute. Specifies the lower limit of dynamic site activation. When the number of configured Web sites on a server exceeds the value of this attribute, the service will not activate all of the sites when the service is started. Instead, IIS will activate each site when it receives the first request for the site. When the number of configured sites is less than or equal to this number, all configured Web sites will be activated when the service is started. The amount of system resources required by IIS is lower when sites are activated individually, especially if a large number of the sites is accessed infrequently. The first request to the site may take more time as the site is activated, but subsequent accesses will respond normally. The default value is 100. |
headerWaitTimeout |
Optional timeSpan attribute. Specifies the time that the server waits for all HTTP headers for the request to be received before disconnecting the client. The purpose of this attribute is to help prevent a common variant of the Denial of Service (DoS) attack that attempts to max out connection limits and keep those connections connected. The default value is 00:00:00. |
maxGlobalBandWidth |
Optional uint attribute. Specifies the maximum total bandwidth for the server. Setting the value to 0 enables unlimited bandwidth for the server. The default value is 4294967295. |
minBytesPerSecond |
Optional uint attribute. Specifies the minimum throughput rate, in bytes, that HTTP.sys enforces when it sends a response to the client. The minBytesPerSecond attribute prevents malicious or malfunctioning software clients from using resources by holding a connection open with minimal data. If the throughput rate is lower than the minBytesPerSecond setting, the connection is terminated. The current implementation only terminates the connection after the time it would have taken to stream the entire response back to the connecting client at the minimum bandwidth transfer rate has elapsed. If the transfer rate goes below the value specified by minBytesPerSecond only for a small period of time, but the overall transfer rate is higher, the connection will not be terminated. The default value is 240. |
Child Elements
None.
Configuration Sample
The following configuration sample sets the connection time-out to 1 minute, the percentage of committed physical RAM to 150, the header wait time-out to 30 seconds, and the minimum allowable throughput rate to 500 bytes per second.
<configuration>
<system.applicationHost>
<webLimits connectionTimeout="00:01:00"
dynamicIdleThreshold="150"
headerWaitTimeout="00:00:30"
minBytesPerSecond="500"
/>
</system.applicationHost>
</configuration>
Sample Code
The following code samples set the connection time-out to 1 minute, the percentage of committed physical RAM to 150, the header wait time-out to 30 seconds, and the minimum allowable throughput rate to 500 bytes per second.
AppCmd.exe
appcmd.exe set config -section:system.applicationHost/webLimits /connectionTimeout:"00:01:00" /commit:apphost
appcmd.exe set config -section:system.applicationHost/webLimits /dynamicIdleThreshold:"150" /commit:apphost
appcmd.exe set config -section:system.applicationHost/webLimits /headerWaitTimeout:"00:00:30" /commit:apphost
appcmd.exe set config -section:system.applicationHost/webLimits /minBytesPerSecond:"500" /commit:apphost
Note
You must be sure to set the commit parameter to apphost when you use AppCmd.exe to configure these settings. This commits the configuration settings to the appropriate location section in the ApplicationHost.config file.
C#
using System;
using System.Text;
using Microsoft.Web.Administration;
internal static class Sample
{
private static void Main()
{
using (ServerManager serverManager = new ServerManager())
{
Configuration config = serverManager.GetApplicationHostConfiguration();
ConfigurationSection webLimitsSection = config.GetSection("system.applicationHost/webLimits");
webLimitsSection["connectionTimeout"] = TimeSpan.Parse("00:01:00");
webLimitsSection["dynamicIdleThreshold"] = 150;
webLimitsSection["headerWaitTimeout"] = TimeSpan.Parse("00:00:30");
webLimitsSection["minBytesPerSecond"] = 500;
serverManager.CommitChanges();
}
}
}
VB.NET
Imports System
Imports System.Text
Imports Microsoft.Web.Administration
Module Sample
Sub Main()
Dim serverManager As ServerManager = New ServerManager
Dim config As Configuration = serverManager.GetApplicationHostConfiguration
Dim webLimitsSection As ConfigurationSection = config.GetSection("system.applicationHost/webLimits")
webLimitsSection("connectionTimeout") = TimeSpan.Parse("00:01:00")
webLimitsSection("dynamicIdleThreshold") = 150
webLimitsSection("headerWaitTimeout") = TimeSpan.Parse("00:00:30")
webLimitsSection("minBytesPerSecond") = 500
serverManager.CommitChanges()
End Sub
End Module
JavaScript
var adminManager = new ActiveXObject('Microsoft.ApplicationHost.WritableAdminManager');
adminManager.CommitPath = "MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST";
var webLimitsSection = adminManager.GetAdminSection("system.applicationHost/webLimits", "MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST");
webLimitsSection.Properties.Item("connectionTimeout").Value = "00:01:00";
webLimitsSection.Properties.Item("dynamicIdleThreshold").Value = 150;
webLimitsSection.Properties.Item("headerWaitTimeout").Value = "00:00:30";
webLimitsSection.Properties.Item("minBytesPerSecond").Value = 500;
adminManager.CommitChanges();
VBScript
Set adminManager = WScript.CreateObject("Microsoft.ApplicationHost.WritableAdminManager")
adminManager.CommitPath = "MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST"
Set webLimitsSection = adminManager.GetAdminSection("system.applicationHost/webLimits", "MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST")
webLimitsSection.Properties.Item("connectionTimeout").Value = "00:01:00"
webLimitsSection.Properties.Item("dynamicIdleThreshold").Value = 150
webLimitsSection.Properties.Item("headerWaitTimeout").Value = "00:00:30"
webLimitsSection.Properties.Item("minBytesPerSecond").Value = 500
adminManager.CommitChanges()