CI/CD for Copy job (preview) in Data Factory in Microsoft Fabric
To build successful data analytics projects with Copy job, it is very important to have source control, continuous integration, continuous deployment, and collaborative development environments.
In Fabric, there are two features we currently support in collaboration with the Application Lifecycle Management (ALM) team: Git integration and deployment pipelines. These features allow users to import/export workspace resources with individual updates.
With Git integration and deployment pipeline supported for Copy job, users can leverage their own Git repositories in Azure DevOps or GitHub and utilize Fabric’s built-in Deployment Pipelines, enabling seamless CI/CD workflows. This integration marks an important step toward expanding CI/CD capabilities across all Fabric items, empowering users with advanced, reliable development tools for their data projects.
Get started with Git integration for Copy job
Take the following steps to set up Git integration for your Copy job in Data Factory:
Prerequisites for Git integration
To access Git with your Microsoft Fabric workspace, ensure the following prerequisites for both Fabric and Git.
- Either a Power BI Premium license or Fabric capacity.
- Enabled the following tenant switches from the admin portal:
- Either an Azure DevOps organization or GitHub account.
- For an Azure DevOps organization:
- An active Azure account registered to the same user that is using the Fabric workspace. Create a free account.
- Access to an existing repository
- For a GitHub account:
- An active GitHub account. Create a free account.
- Either a fine grained token with read and write permissions for Contents, under repository permissions, or a GitHub classic token with repo scopes enabled.
- For an Azure DevOps organization:
Step 1: Connect to a Git repository
To use Git integration with Copy job in Fabric, you first need to connect to a Git repository, as described here.
Sign into Fabric and navigate to the workspace you want to connect to Git.
Select Workspace settings.
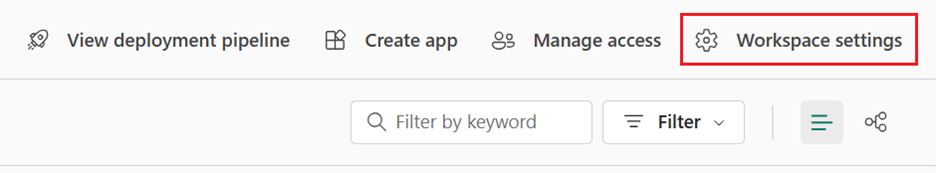
Select Git integration.
Select your Git provider. Currently, Fabric only supports Azure DevOps or GitHub. If you use GitHub, you need to select Add account to connect your GitHub account. After you sign in, select Connect to allow Fabric to access your GitHub account.
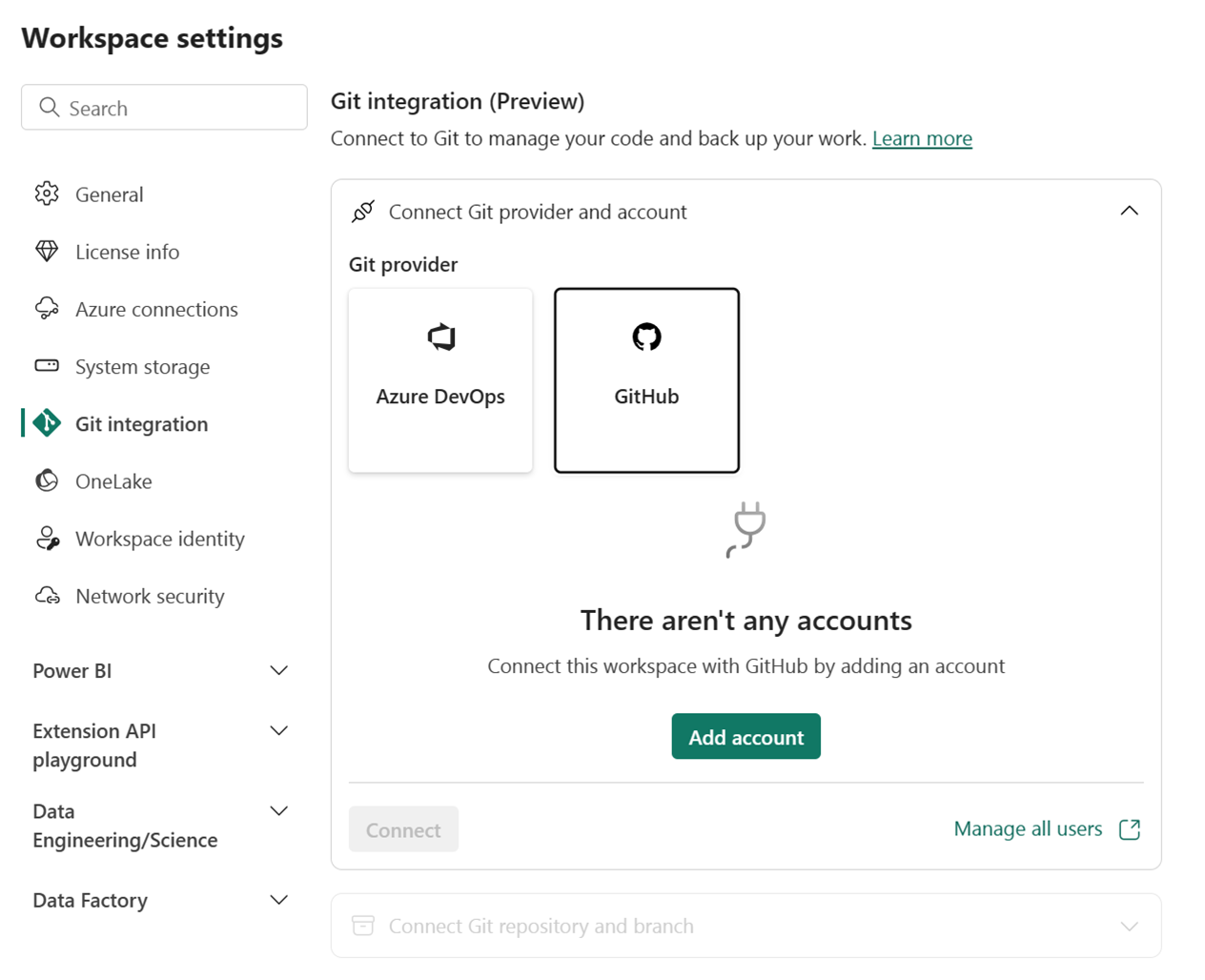
Step 2: Connect to a workspace
Once you connect to a Git repository, you need to connect to a workspace, as described here.
From the dropdown menu, specify the following details about the branch you want to connect to:
For Azure DevOps branch connections, specify the following details:
- Organization: The Azure DevOps organization name.
- Project: The Azure DevOps project name.
- Repository: The Azure DevOps repository name.
- Branch: The Azure DevOps branch name.
- Folder: The Azure DevOps folder name.
For GitHub branch connections, specify the following details:
- Repository URL: The GitHub repository URL.
- Branch: The GitHub branch name.
- Folder: The GitHub folder name.
Select Connect and sync.
After you connect, the Workspace displays information about source control that allows users to view the connected branch, the status of each item in the branch, and the time of the last sync.
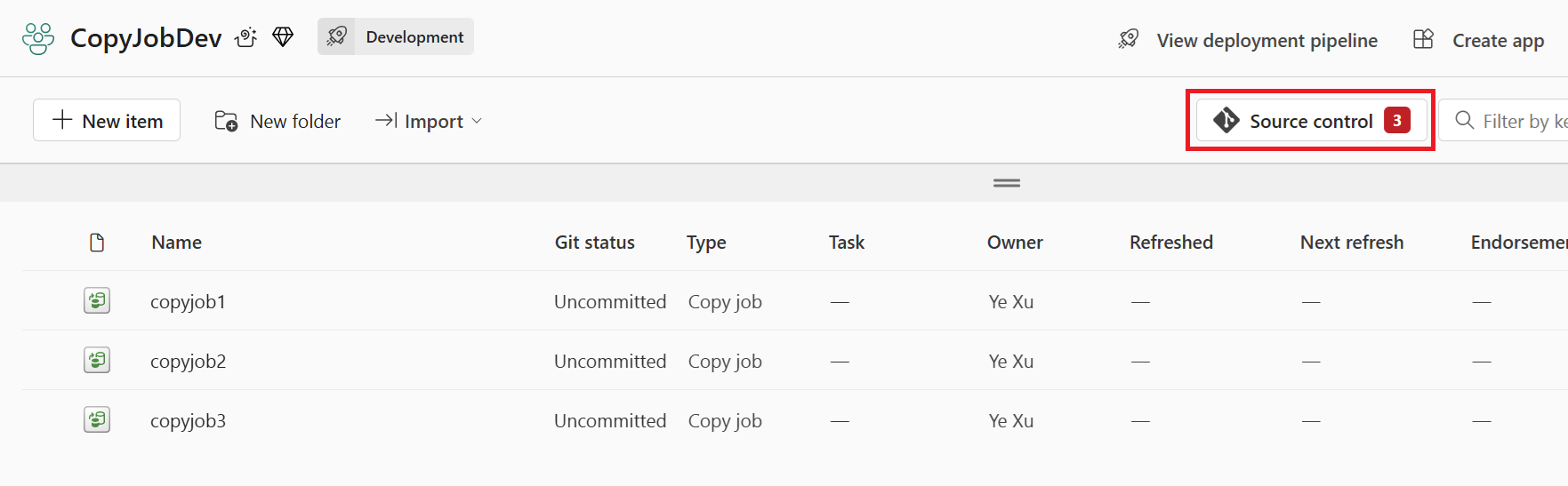
Step 3: Commit changes to Git
You can now commit changes to Git, as described here.
- Go to the workspace.
- Select the Source control icon. This icon shows the number of uncommitted changes.
- Select the Changes tab from the Source control panel. A list appears with all the items you changed, and an icon indicating the status.
- Select the items you want to commit. To select all items, check the top box.
- (Optional) Add a commit comment in the box.
- Select Commit.
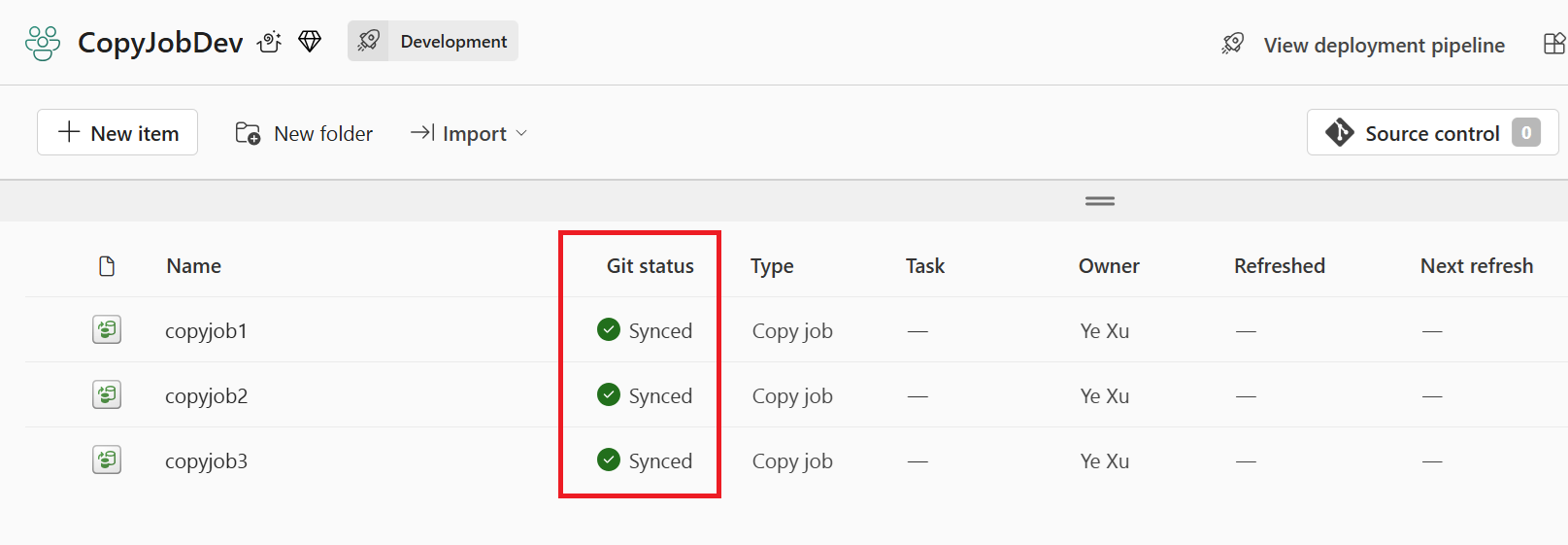
After the changes are committed, the items that were committed are removed from the list, and the workspace will point to the new commit that it synced to.
Get started with deployment pipelines for Git
Take the following steps to use Git deployment pipelines with your Fabric workspace.
Prerequisites for deployment pipelines
Before you get started, be sure to set up the following prerequisites:
- An active Microsoft Fabric subscription.
- Admin access of a Fabric workspace.
Step 1: Create a deployment pipeline
- From the Workspaces flyout, select Deployment pipelines.
Step 2: Name the pipeline and assign stages
- In the Create deployment pipeline dialog box, enter a name and description for the pipeline, and select Next.
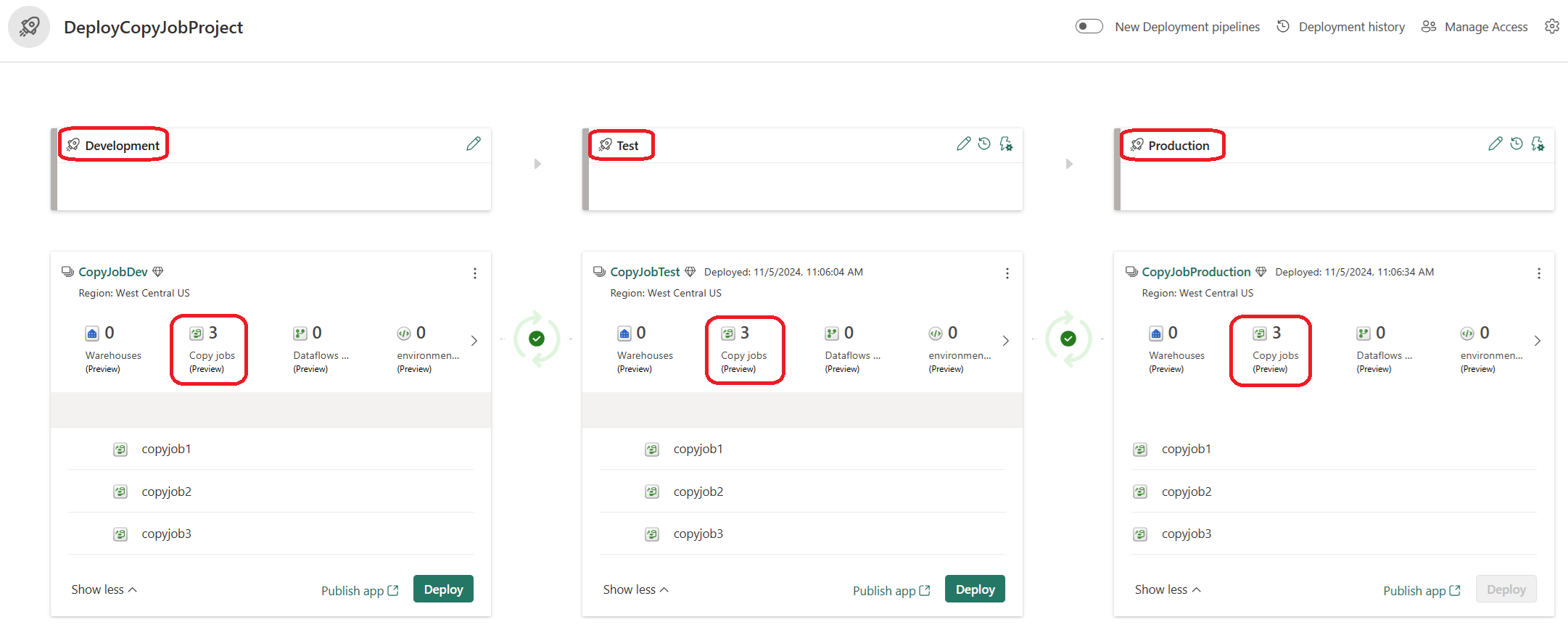
- Set your deployment pipeline’s structure by defining the required stages for your deployment pipeline. By default, the pipeline has three stages: Development, Test, and Production.
Step 3: Assign a workspace to the deployment pipeline
After creating a pipeline, you need to add content you want to manage to the pipeline. Adding content to the pipeline is done by assigning a workspace to the pipeline stage. You can assign a workspace to any stage. Follow the instructions to Assign a workspace to a pipeline.
Step 4: Deploy to an empty stage
When you finish working with content in one pipeline stage, you can deploy it to the next stage. Deployment pipelines offer three options for deploying your content:
- Full deployment: Deploy all your content to the target stage.
- Selective deployment: Select which content to deploy to the target stage.
- Backward deployment: Deploy content from a later stage to an earlier stage in the pipeline. Currently, backward deployment is only possible when the target stage is empty (has no workspace assigned to it).
After you choose how to deploy your content, you can review your deployment and leave a note.
Step 5: Deploy content from one stage to another
Once you have content in a pipeline stage, you can deploy it to the next stage, even if the next stage workspace has content. Paired items are overwritten. You can learn more about this process, in the Deploy content to an existing workspace section.
You can review the deployment history to see the last time content was deployed to each stage. To examine the differences between the two pipelines before you deploy, see Compare content in different deployment stages.
Known limitations
The following known limitations apply to CI/CD for Copy job in Data Factory in Microsoft Fabric:
- Workspace variables: CI/CD doesn't currently support workspace variables.
- Git Integration limited support: Currently, Fabric only supports Git integration with Azure DevOps and GitHub. Azure DevOps Git integration is recommended as GitHub Git integration has more limitations.