Tutorial: Add add sign-in to a Node/Express.js web app by using Microsoft identity platform
Applies to:  Workforce tenants
Workforce tenants  External tenants (learn more)
External tenants (learn more)
In this tutorial, you add sign-in and sign-out logic to your Node/Express web app. This code enables you to sign in users into your customer facing app by in an external tenant or employees in a workforce tenant.
This tutorial is part 2 of the 3-part tutorial series.
In this tutorial, you'll:
- Add sign-in and sign-out logic
- View ID token claims
- Run app and test sign-in and sign-out experience.
Prerequisites
- Complete the steps in Tutorial: Set up a Node.js web app to sign in users by using Microsoft identity platform.
Create MSAL configuration object
In your code editor, open authConfig.js file, then add the following code:
require('dotenv').config();
const TENANT_SUBDOMAIN = process.env.TENANT_SUBDOMAIN || 'Enter_the_Tenant_Subdomain_Here';
const REDIRECT_URI = process.env.REDIRECT_URI || 'http://localhost:3000/auth/redirect';
const POST_LOGOUT_REDIRECT_URI = process.env.POST_LOGOUT_REDIRECT_URI || 'http://localhost:3000';
const GRAPH_ME_ENDPOINT = process.env.GRAPH_API_ENDPOINT + "v1.0/me" || 'Enter_the_Graph_Endpoint_Here';
/**
* Configuration object to be passed to MSAL instance on creation.
* For a full list of MSAL Node configuration parameters, visit:
* https://github.com/AzureAD/microsoft-authentication-library-for-js/blob/dev/lib/msal-node/docs/configuration.md
*/
const msalConfig = {
auth: {
clientId: process.env.CLIENT_ID || 'Enter_the_Application_Id_Here', // 'Application (client) ID' of app registration in Azure portal - this value is a GUID
//For external tenant
authority: process.env.AUTHORITY || `https://${TENANT_SUBDOMAIN}.ciamlogin.com/`, // replace "Enter_the_Tenant_Subdomain_Here" with your tenant name
//For workforce tenant
//authority: process.env.CLOUD_INSTANCE + process.env.TENANT_ID
clientSecret: process.env.CLIENT_SECRET || 'Enter_the_Client_Secret_Here', // Client secret generated from the app registration in Azure portal
},
system: {
loggerOptions: {
loggerCallback(loglevel, message, containsPii) {
console.log(message);
},
piiLoggingEnabled: false,
logLevel: 'Info',
},
},
};
module.exports = {
msalConfig,
REDIRECT_URI,
POST_LOGOUT_REDIRECT_URI,
TENANT_SUBDOMAIN,
GRAPH_ME_ENDPOINT
};
The msalConfig object contains a set of configuration options that you use to customize the behavior of your authentication flows.
In your authConfig.js file, replace:
Enter_the_Application_Id_Herewith the Application (client) ID of the app you registered earlier.Enter_the_Tenant_Subdomain_Hereand replace it with the external Directory (tenant) subdomain. For example, if your tenant primary domain iscontoso.onmicrosoft.com, usecontoso. If you don't have your tenant name, learn how to read your tenant details. This value is required only for external tenant.Enter_the_Client_Secret_Herewith the app secret value you copied earlier.Enter_the_Graph_Endpoint_Herewith the Microsoft Graph API cloud instance that your app will call. Use the value https://graph.microsoft.com/ (include the trailing forward-slash)
If you use the .env file to store your configuration information:
In your code editor, open .env file, then add the following code.
CLIENT_ID=Enter_the_Application_Id_Here TENANT_SUBDOMAIN=Enter_the_Tenant_Subdomain_Here CLOUD_INSTANCE="Enter_the_Cloud_Instance_Id_Here" # cloud instance string should end with a trailing slash TENANT_ID=Enter_the_Tenant_ID_here CLIENT_SECRET=Enter_the_Client_Secret_Here REDIRECT_URI=http://localhost:3000/auth/redirect POST_LOGOUT_REDIRECT_URI=http://localhost:3000 GRAPH_API_ENDPOINT=Enter_the_Graph_Endpoint_Here # graph api endpoint string should end with a trailing slash EXPRESS_SESSION_SECRET=Enter_the_Express_Session_Secret_Here # express session secret, just any random textReplace the placeholder:
Enter_the_Application_Id_Here,Enter_the_Tenant_Subdomain_HereandEnter_the_Client_Secret_Hereas explained earlier.Enter_the_Cloud_Instance_Id_Herewith the Azure cloud instance in which your application is registered. Use https://login.microsoftonline.com/ as its value (include the trailing forward-slash). This value is required only for workforce tenant.Enter_the_Tenant_ID_herewith the workforce Tenant ID or Primary domain such as or aaaabbbb-0000-cccc-1111-dddd2222eeee or contoso.microsoft.com. This value is required only for workforce tenant.
You export msalConfig, REDIRECT_URI, TENANT_SUBDOMAIN, GRAPH_ME_ENDPOINT and POST_LOGOUT_REDIRECT_URI variables in the authConfig.js file, to make them accessible in other files.
Authority URL for your app
The application authorities for external and workforce tenants looks different. Build them as shown below:
//Authority for workforce tenant
authority: process.env.CLOUD_INSTANCE + process.env.TENANT_ID
Use custom URL domain (Optional)
Custom URL domains are not supported in workforce tenants.
Add express routes
The Express routes provide the endpoints that enable us to execute operations such as sign in, sign out and view ID token claims.
App entry point
In your code editor, open routes/index.js file, then add the following code:
const express = require('express');
const router = express.Router();
router.get('/', function (req, res, next) {
res.render('index', {
title: 'MSAL Node & Express Web App',
isAuthenticated: req.session.isAuthenticated,
username: req.session.account?.username !== '' ? req.session.account?.username : req.session.account?.name,
});
});
module.exports = router;
The / route is the entry point to the application. It renders the views/index.hbs view that you created earlier in Build app UI components. isAuthenticated is a boolean variable that determines what you see in the view.
Sign in and sign out
In your code editor, open routes/auth.js file, then add the following code:
const express = require('express'); const authController = require('../controller/authController'); const router = express.Router(); router.get('/signin', authController.signIn); router.get('/signout', authController.signOut); router.post('/redirect', authController.handleRedirect); module.exports = router;In your code editor, open controller/authController.js file, then add the following code:
const authProvider = require('../auth/AuthProvider'); exports.signIn = async (req, res, next) => { return authProvider.login(req, res, next); }; exports.handleRedirect = async (req, res, next) => { return authProvider.handleRedirect(req, res, next); } exports.signOut = async (req, res, next) => { return authProvider.logout(req, res, next); };In your code editor, open auth/AuthProvider.js file, then add the following code:
const msal = require('@azure/msal-node'); const axios = require('axios'); const { msalConfig, TENANT_SUBDOMAIN, REDIRECT_URI, POST_LOGOUT_REDIRECT_URI, GRAPH_ME_ENDPOINT} = require('../authConfig'); class AuthProvider { config; cryptoProvider; constructor(config) { this.config = config; this.cryptoProvider = new msal.CryptoProvider(); } getMsalInstance(msalConfig) { return new msal.ConfidentialClientApplication(msalConfig); } async login(req, res, next, options = {}) { // create a GUID for crsf req.session.csrfToken = this.cryptoProvider.createNewGuid(); /** * The MSAL Node library allows you to pass your custom state as state parameter in the Request object. * The state parameter can also be used to encode information of the app's state before redirect. * You can pass the user's state in the app, such as the page or view they were on, as input to this parameter. */ const state = this.cryptoProvider.base64Encode( JSON.stringify({ csrfToken: req.session.csrfToken, redirectTo: '/', }) ); const authCodeUrlRequestParams = { state: state, /** * By default, MSAL Node will add OIDC scopes to the auth code url request. For more information, visit: * https://docs.microsoft.com/azure/active-directory/develop/v2-permissions-and-consent#openid-connect-scopes */ scopes: [], }; const authCodeRequestParams = { state: state, /** * By default, MSAL Node will add OIDC scopes to the auth code request. For more information, visit: * https://docs.microsoft.com/azure/active-directory/develop/v2-permissions-and-consent#openid-connect-scopes */ scopes: [], }; /** * If the current msal configuration does not have cloudDiscoveryMetadata or authorityMetadata, we will * make a request to the relevant endpoints to retrieve the metadata. This allows MSAL to avoid making * metadata discovery calls, thereby improving performance of token acquisition process. */ if (!this.config.msalConfig.auth.authorityMetadata) { const authorityMetadata = await this.getAuthorityMetadata(); this.config.msalConfig.auth.authorityMetadata = JSON.stringify(authorityMetadata); } const msalInstance = this.getMsalInstance(this.config.msalConfig); // trigger the first leg of auth code flow return this.redirectToAuthCodeUrl( req, res, next, authCodeUrlRequestParams, authCodeRequestParams, msalInstance ); } async handleRedirect(req, res, next) { const authCodeRequest = { ...req.session.authCodeRequest, code: req.body.code, // authZ code codeVerifier: req.session.pkceCodes.verifier, // PKCE Code Verifier }; try { const msalInstance = this.getMsalInstance(this.config.msalConfig); msalInstance.getTokenCache().deserialize(req.session.tokenCache); const tokenResponse = await msalInstance.acquireTokenByCode(authCodeRequest, req.body); req.session.tokenCache = msalInstance.getTokenCache().serialize(); req.session.idToken = tokenResponse.idToken; req.session.account = tokenResponse.account; req.session.isAuthenticated = true; const state = JSON.parse(this.cryptoProvider.base64Decode(req.body.state)); res.redirect(state.redirectTo); } catch (error) { next(error); } } async logout(req, res, next) { /** * Construct a logout URI and redirect the user to end the * session with Microsoft Entra ID. For more information, visit: * https://docs.microsoft.com/azure/active-directory/develop/v2-protocols-oidc#send-a-sign-out-request */ //For external tenant //const logoutUri = `${this.config.msalConfig.auth.authority}${TENANT_SUBDOMAIN}.onmicrosoft.com/oauth2/v2.0/logout?post_logout_redirect_uri=${this.config.postLogoutRedirectUri}`; //For workforce tenant let logoutUri = `${this.config.msalConfig.auth.authority}/oauth2/v2.0/logout?post_logout_redirect_uri=${this.config.postLogoutRedirectUri}`; req.session.destroy(() => { res.redirect(logoutUri); }); } /** * Prepares the auth code request parameters and initiates the first leg of auth code flow * @param req: Express request object * @param res: Express response object * @param next: Express next function * @param authCodeUrlRequestParams: parameters for requesting an auth code url * @param authCodeRequestParams: parameters for requesting tokens using auth code */ async redirectToAuthCodeUrl(req, res, next, authCodeUrlRequestParams, authCodeRequestParams, msalInstance) { // Generate PKCE Codes before starting the authorization flow const { verifier, challenge } = await this.cryptoProvider.generatePkceCodes(); // Set generated PKCE codes and method as session vars req.session.pkceCodes = { challengeMethod: 'S256', verifier: verifier, challenge: challenge, }; /** * By manipulating the request objects below before each request, we can obtain * auth artifacts with desired claims. For more information, visit: * https://azuread.github.io/microsoft-authentication-library-for-js/ref/modules/_azure_msal_node.html#authorizationurlrequest * https://azuread.github.io/microsoft-authentication-library-for-js/ref/modules/_azure_msal_node.html#authorizationcoderequest **/ req.session.authCodeUrlRequest = { ...authCodeUrlRequestParams, redirectUri: this.config.redirectUri, responseMode: 'form_post', // recommended for confidential clients codeChallenge: req.session.pkceCodes.challenge, codeChallengeMethod: req.session.pkceCodes.challengeMethod, }; req.session.authCodeRequest = { ...authCodeRequestParams, redirectUri: this.config.redirectUri, code: '', }; try { const authCodeUrlResponse = await msalInstance.getAuthCodeUrl(req.session.authCodeUrlRequest); res.redirect(authCodeUrlResponse); } catch (error) { next(error); } } /** * Retrieves oidc metadata from the openid endpoint * @returns */ async getAuthorityMetadata() { // For external tenant //const endpoint = `${this.config.msalConfig.auth.authority}${TENANT_SUBDOMAIN}.onmicrosoft.com/v2.0/.well-known/openid-configuration`; // For workforce tenant const endpoint = `${this.config.msalConfig.auth.authority}/v2.0/.well-known/openid-configuration`; try { const response = await axios.get(endpoint); return await response.data; } catch (error) { console.log(error); } } } const authProvider = new AuthProvider({ msalConfig: msalConfig, redirectUri: REDIRECT_URI, postLogoutRedirectUri: POST_LOGOUT_REDIRECT_URI, }); module.exports = authProvider;The
/signin,/signoutand/redirectroutes are defined in the routes/auth.js file, but you implement their logic in the auth/AuthProvider.js class.
The
loginmethod handles/signinroute:It initiates sign-in flow by triggering the first leg of auth code flow.
It initializes a confidential client application instance by using MSAL configuration object,
msalConfig, that you created earlier.const msalInstance = this.getMsalInstance(this.config.msalConfig);The
getMsalInstancemethod is defined as:getMsalInstance(msalConfig) { return new msal.ConfidentialClientApplication(msalConfig); }The first leg of auth code flow generates an authorization code request URL, then redirects to that URL to obtain the authorization code. This first leg is implemented in the
redirectToAuthCodeUrlmethod. Notice how we use MSALs getAuthCodeUrl method to generate authorization code URL://... const authCodeUrlResponse = await msalInstance.getAuthCodeUrl(req.session.authCodeUrlRequest); //...We then redirect to the authorization code URL itself.
//... res.redirect(authCodeUrlResponse); //...
The
handleRedirectmethod handles/redirectroute:You set this URL as Redirect URI for the web app in the Microsoft Entra admin center earlier in Quickstart: Sign in users in a sample web app.
This endpoint implements the second leg of auth code flow uses. It uses the authorization code to request an ID token by using MSAL's acquireTokenByCode method.
//... const tokenResponse = await msalInstance.acquireTokenByCode(authCodeRequest, req.body); //...After you receive a response, you can create an Express session and store whatever information you want in it. You need to include
isAuthenticatedand set it totrue://... req.session.idToken = tokenResponse.idToken; req.session.account = tokenResponse.account; req.session.isAuthenticated = true; //...
The
logoutmethod handles/signoutroute:async logout(req, res, next) { /** * Construct a logout URI and redirect the user to end the * session with Azure AD. For more information, visit: * https://docs.microsoft.com/azure/active-directory/develop/v2-protocols-oidc#send-a-sign-out-request */ const logoutUri = `${this.config.msalConfig.auth.authority}${TENANT_SUBDOMAIN}.onmicrosoft.com/oauth2/v2.0/logout?post_logout_redirect_uri=${this.config.postLogoutRedirectUri}`; req.session.destroy(() => { res.redirect(logoutUri); }); }It initiates sign out request.
When you want to sign the user out of the application, it isn't enough to end the user's session. You must redirect the user to the logoutUri. Otherwise, the user might be able to reauthenticate to your applications without reentering their credentials. If the name of your tenant is contoso, then the logoutUri looks similar to
https://contoso.ciamlogin.com/contoso.onmicrosoft.com/oauth2/v2.0/logout?post_logout_redirect_uri=http://localhost:3000.
Logout URI and authority metadata endpoint for your app
The app's logout URI, logoutUri and authority metadata endpoint, endpoint for external and workforce tenants looks different. Build them as shown below:
//Logout URI for workforce tenant
const logoutUri = `${this.config.msalConfig.auth.authority}/oauth2/v2.0/logout?post_logout_redirect_uri=${this.config.postLogoutRedirectUri}`;
//authority metadata endpoint for workforce tenant
const endpoint = `${this.config.msalConfig.auth.authority}/v2.0/.well-known/openid-configuration`;
View ID token claims
In your code editor, open routes/users.js file, then add the following code:
const express = require('express');
const router = express.Router();
// custom middleware to check auth state
function isAuthenticated(req, res, next) {
if (!req.session.isAuthenticated) {
return res.redirect('/auth/signin'); // redirect to sign-in route
}
next();
};
router.get('/id',
isAuthenticated, // check if user is authenticated
async function (req, res, next) {
res.render('id', { idTokenClaims: req.session.account.idTokenClaims });
}
);
module.exports = router;
If the user is authenticated, the /id route displays ID token claims by using the views/id.hbs view. You added this view earlier in Build app UI components.
To extract a specific ID token claim, such as given name:
const givenName = req.session.account.idTokenClaims.given_name
Finalize your web app
In your code editor, open app.js file, then add the code from app.js to it.
In your code editor, open server.js file, then add the code from server.js to it.
In your code editor, open package.json file, then update the
scriptsproperty to:"scripts": { "start": "node server.js" }
Run and test the Node/Express.js web app
At this point, you can test your node web app.
Use the steps in Create a new user to create a test user in the workforce tenant. If you don't have access to the tenant, ask your tenant admin to create the user for you.
To start the server, run the following commands from within the project directory:
npm startOpen your browser, then go to
http://localhost:3000. You should see the page similar to the following screenshot: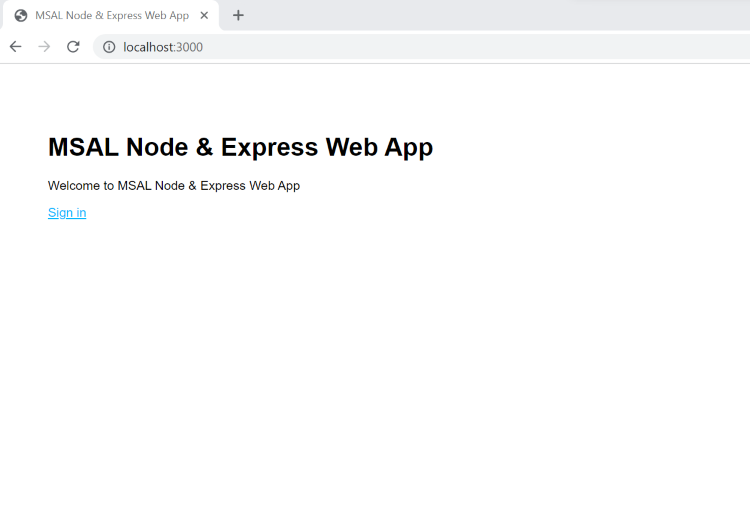
Select Sign in to start the sign-in process. The first time you sign in, you're prompted to provide your consent to allow the application to sign you in and access your profile as shown in the following screenshot:

After you're signed in successfully, you'll be redirected back to the application home page.