Use custom IoT providers
The Dynamics 365 Field Service IoT provider feature allows seamless integration with IoT (Internet of Things) devices from any IoT vendor. It integrates IoT alerts from different vendors in a unified list regardless of their origin. When users interact with an IoT device, Field Service identifies the device's provider and routes the command to the corresponding IoT system.
In Field Service, the out-of-box deployment experience integrates with Azure IoT Hub. Developers, partners, and independent software vendors (ISVs) can build custom IoT solutions on this framework and even publish them in the Microsoft AppSource marketplace.
This article describes the IoT provider data model and provides an overview of the connection methods you can use.
Prerequisites
- Experience developing model-driven apps that connect to Dynamics 365 and Microsoft Dataverse
- Programming experience with C#, .NET, and Visual Studio
- Familiarity with the REST/OData API
Field Service data model
All the methods to integrate external IoT services with Field Service must fit the Field Service IoT provider data model, which consists of three related tables (IoT Provider, IoT Provider Instance, and IoT Device) and a table of IoT settings.
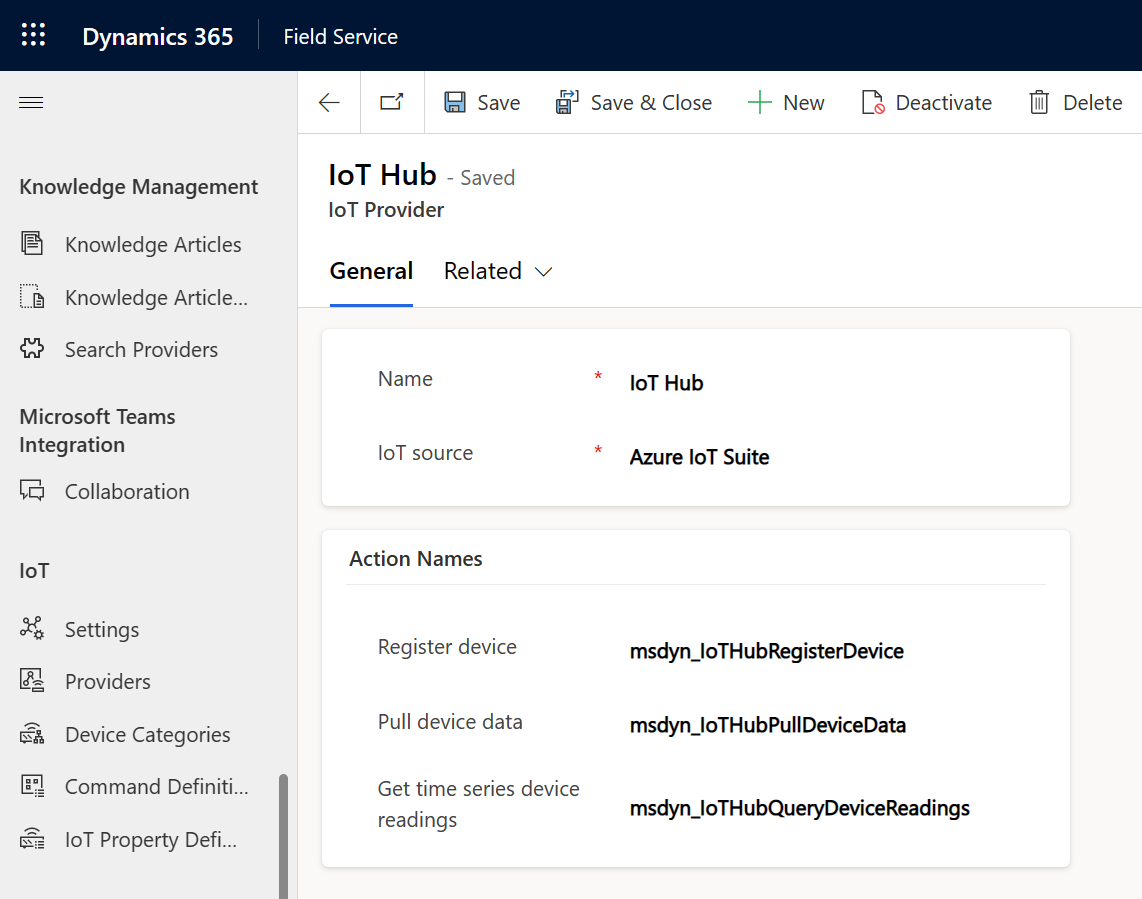
IoT Provider table
The IoT Provider table identifies your organization's IoT providers and the actions they support.
IoT Provider Instance table
A one-to-many (1:many) relationship exists between the IoT Provider table and the IoT Provider Instance table. For example, if your organization is connected to two different Azure IoT Hubs, you have one IoT provider record for Azure IoT Hub and two IoT provider instance records, one for each of your IoT Hubs. You can view the list of IoT provider instances in Field Service Settings > IoT > Providers.
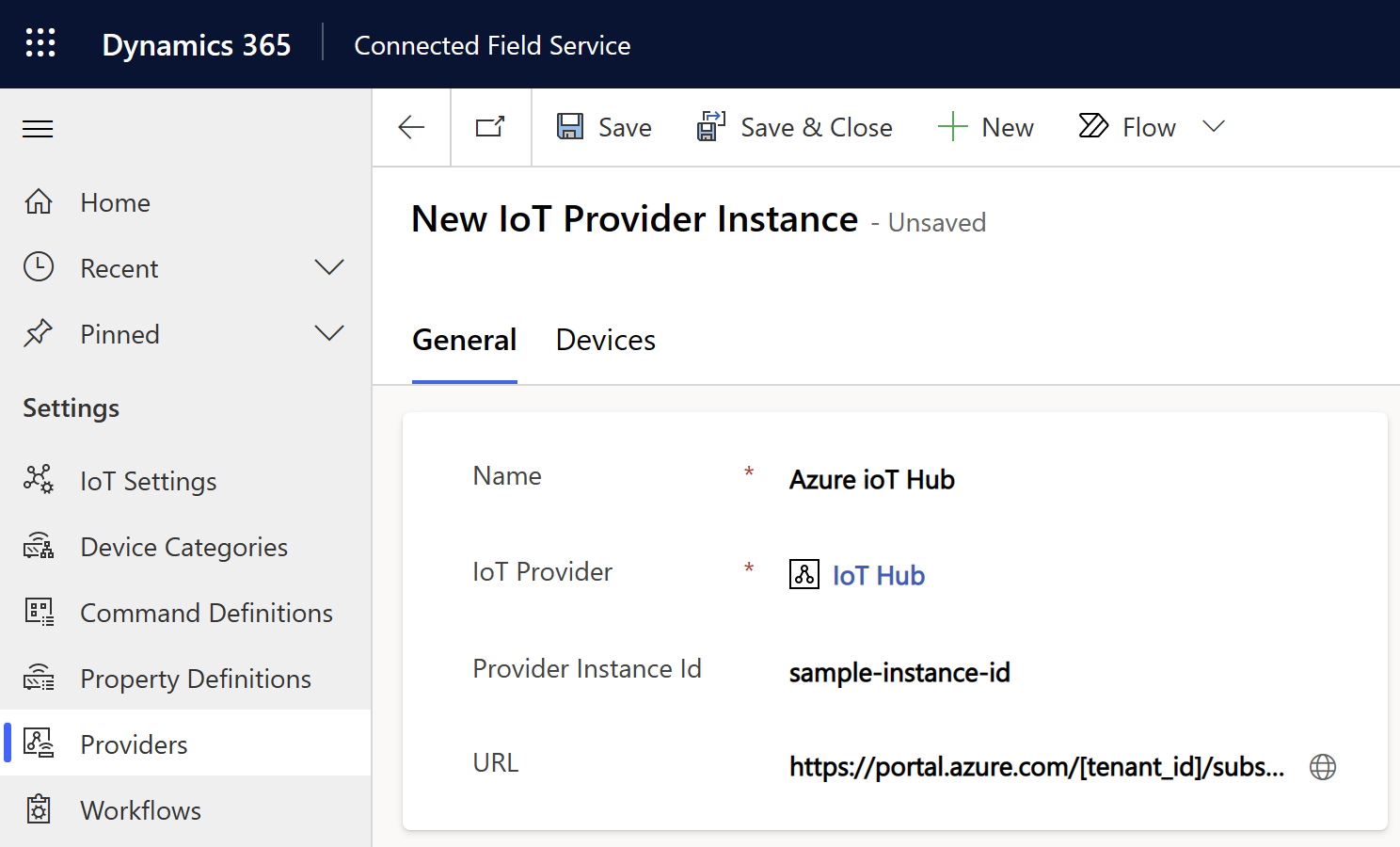
- Provider Instance Id identifies the instance in your source IoT system.
- URL could be one that's used in your provider code or the user experience; for example, an API endpoint or a link to the Azure resource group of the deployment.
IoT Device table
A 1:many relationship exists between the IoT Provider Instance table and the IoT Device table, which maps each device to an IoT provider instance.
- Account identifies the customer account in Field Service that has an association with the device.
- Category is the device category.
- Time Zone is the time zone in which the device is located.
- Device Id is used to register the device with the IoT provider.
- Simulated is used in development and testing.
Connection methods and development tools
Connection methods for custom IoT solutions come with both advantages and risks. The following table describes them.
| Method | Advantages | Risks |
|---|---|---|
| Dataverse API | - Allows direct communication between Connected Field Service and external services. - Robust protocol for building software applications. |
- External services must be able to integrate with APIs. - Requires strong understanding of Connected Field Service API capabilities. |
| Webhooks | Sends real-time updates to an external service when specific actions are taken in Connected Field Service. | External service needs to be able to receive and process webhook messages. |
| Connectors | Provides a seamless integration experience and acts as a bridge between Connected Field Service and the external service. | Requires more robust technical knowledge and development resources. |
| Custom code | Highly tailored and effective integration. | Requires high level of technical expertise; it might involve more risk than other methods. |
Commonly used development tools to build custom solutions for Connected Field Service:
Microsoft Power Apps is a low-code development platform that allows makers and pro developers to create custom business applications quickly and easily.
Microsoft Azure Functions is a service that allows developers to run code on demand without dedicated servers.
Microsoft .NET Framework is a software development framework for building and running applications on Windows.
Microsoft Visual Studio is a popular integrated development environment that supports a wide range of programming languages and frameworks, including .NET, JavaScript, and Python.
JavaScript is a widely used programming language commonly used with other tools and frameworks, such as Node.js and React.
REST APIs provide a standardized way for applications to communicate with each other over the web. Connected Field Service provides many REST APIs that can be used to integrate with external services and build custom solutions.