SearchBar
The .NET Multi-platform App UI (.NET MAUI) SearchBar is a user input control used to initiating a search. The SearchBar control supports placeholder text, query input, search execution, and cancellation. The following iOS screenshot shows a SearchBar query with results displayed in a ListView:
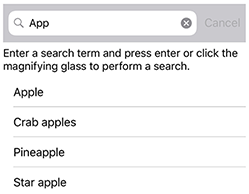
SearchBar defines the following properties:
CancelButtonColoris a Color that defines the color of the cancel button.HorizontalTextAlignmentis a TextAlignment enum value that defines the horizontal alignment of the query text.SearchCommandis an ICommand that allows binding user actions, such as finger taps or clicks, to commands defined on a viewmodel.SearchCommandParameteris anobjectthat specifies the parameter that should be passed to theSearchCommand.VerticalTextAlignmentis a TextAlignment enum value that defines the vertical alignment of the query text.
These properties are backed by BindableProperty objects, which means that they can be targets of data bindings, and styled.
In addition, SearchBar defines a SearchButtonPressed event, which is raised when the search button is clicked, or the enter key is pressed.
SearchBar derives from the InputView class, from which it inherits the following properties:
CharacterSpacing, of typedouble, sets the spacing between characters in the entered text.CursorPosition, of typeint, defines the position of the cursor within the editor.FontAttributes, of typeFontAttributes, determines text style.FontAutoScalingEnabled, of typebool, defines whether the text will reflect scaling preferences set in the operating system. The default value of this property istrue.FontFamily, of typestring, defines the font family.FontSize, of typedouble, defines the font size.IsReadOnly, of typebool, defines whether the user should be prevented from modifying text. The default value of this property isfalse.IsSpellCheckEnabled, of typebool, controls whether spell checking is enabled.IsTextPredictionEnabled, of typebool, controls whether text prediction and automatic text correction is enabled.Keyboard, of typeKeyboard, specifies the soft input keyboard that's displayed when entering text.MaxLength, of typeint, defines the maximum input length.Placeholder, of typestring, defines the text that's displayed when the control is empty.PlaceholderColor, of type Color, defines the color of the placeholder text.SelectionLength, of typeint, represents the length of selected text within the control.Text, of typestring, defines the text entered into the control.TextColor, of type Color, defines the color of the entered text.TextTransform, of typeTextTransform, specifies the casing of the entered text.
These properties are backed by BindableProperty objects, which means that they can be targets of data bindings, and styled.
In addition, InputView defines a TextChanged event, which is raised when the text in the Entry changes. The TextChangedEventArgs object that accompanies the TextChanged event has NewTextValue and OldTextValue properties, which specify the new and old text, respectively.
Create a SearchBar
To create a search bar, create a SearchBar object and set its Placeholder property to text that instructs the user to enter a search term.
The following XAML example shows how to create a SearchBar:
<SearchBar Placeholder="Search items..." />
The equivalent C# code is:
SearchBar searchBar = new SearchBar { Placeholder = "Search items..." };
Note
On iOS, the soft input keyboard can cover a text input field when the field is near the bottom of the screen, making it difficult to enter text. However, in a .NET MAUI iOS app, pages automatically scroll when the soft input keyboard would cover a text entry field, so that the field is above the soft input keyboard. The KeyboardAutoManagerScroll.Disconnect method, in the Microsoft.Maui.Platform namespace, can be called to disable this default behavior. The KeyboardAutoManagerScroll.Connect method can be called to re-enable the behavior after it's been disabled.
Perform a search with event handlers
A search can be executed using the SearchBar control by attaching an event handler to one of the following events:
SearchButtonPressed, which is called when the user either clicks the search button or presses the enter key.TextChanged, which is called anytime the text in the query box is changed. This event is inherited from the InputView class.
The following XAML example shows an event handler attached to the TextChanged event and uses a ListView to display search results:
<SearchBar TextChanged="OnTextChanged" />
<ListView x:Name="searchResults" >
In this example, the TextChanged event is set to an event handler named OnTextChanged. This handler is located in the code-behind file:
void OnTextChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
SearchBar searchBar = (SearchBar)sender;
searchResults.ItemsSource = DataService.GetSearchResults(searchBar.Text);
}
In this example, a DataService class with a GetSearchResults method is used to returnitems that match a query. The SearchBar control's Text property value is passed to the GetSearchResults method and the result is used to update the ListView control's ItemsSource property. The overall effect is that search results are displayed in the ListView.
Perform a search using a viewmodel
A search can be executed without event handlers by binding the SearchCommand property to an ICommand implementation. For more information about commanding, see Commanding.
The following example shows a viewmodel class that contains an ICommand property named PerformSearch:
public class SearchViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged
{
public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged;
protected virtual void NotifyPropertyChanged([CallerMemberName] string propertyName = "")
{
PropertyChanged?.Invoke(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(propertyName));
}
public ICommand PerformSearch => new Command<string>((string query) =>
{
SearchResults = DataService.GetSearchResults(query);
});
private List<string> searchResults = DataService.Fruits;
public List<string> SearchResults
{
get
{
return searchResults;
}
set
{
searchResults = value;
NotifyPropertyChanged();
}
}
}
Note
The viewmodel assumes the existence of a DataService class capable of performing searches.
The following XAML example consumes the SearchViewModel class:
<ContentPage ...>
<ContentPage.BindingContext>
<viewmodels:SearchViewModel />
</ContentPage.BindingContext>
<StackLayout>
<SearchBar x:Name="searchBar"
SearchCommand="{Binding PerformSearch}"
SearchCommandParameter="{Binding Text, Source={x:Reference searchBar}}"/>
<ListView x:Name="searchResults"
ItemsSource="{Binding SearchResults}" />
</StackLayout>
</ContentPage>
In this example, the BindingContext is set to an instance of the SearchViewModel class. The SearchBar.SearchCommand property binds to PerformSearch viewmodel property, and the SearchCommandParameter property binds to the SearchBar.Text property. Similarly, the ListView.ItemsSource property is bound to the SearchResults property of the viewmodel.
Hide and show the soft input keyboard
The SoftInputExtensions class, in the Microsoft.Maui namespace, provides a series of extension methods that support interacting with the soft input keyboard on controls that support text input. The class defines the following methods:
IsSoftInputShowing, which checks to see if the device is currently showing the soft input keyboard.HideSoftInputAsync, which will attempt to hide the soft input keyboard if it's currently showing.ShowSoftInputAsync, which will attempt to show the soft input keyboard if it's currently hidden.
The following example shows how to hide the soft input keyboard on a SearchBar named searchBar, if it's currently showing:
if (searchBar.IsSoftInputShowing())
await searchBar.HideSoftInputAsync(System.Threading.CancellationToken.None);
