Gradients
The .NET Multi-platform App UI (.NET MAUI) GradientBrush class derives from the Brush class, and is an abstract class that describes a gradient, which is composed of gradient stops. A gradient brush paints an area with multiple colors that blend into each other along an axis.
Classes that derive from GradientBrush describe different ways of interpreting gradient stops, and .NET MAUI provides the following gradient brushes:
- LinearGradientBrush, which paints an area with a linear gradient. For more information, see Linear gradient brushes.
- RadialGradientBrush, which paints an area with a radial gradient. For more information, see Radial gradient brushes.
The GradientBrush class defines the GradientStops property, of type GradientStopCollection, which represents the brush's gradient stops, each of which specifies a color and an offset along the brush's gradient axis. A GradientStopCollection is an ObservableCollection of GradientStop objects. The GradientStops property is backed by a BindableProperty object, which means that it can be the target of data bindings, and styled.
Note
The GradientStops property is the ContentProperty of the GradientBrush class, and so does not need to be explicitly set from XAML.
Gradient stops
Gradient stops are the building blocks of a gradient brush, and specify the colors in the gradient and their location along the gradient axis. Gradient stops are specified using GradientStop objects.
The GradientStop class defines the following properties:
Color, of type Color, which represents the color of the gradient stop.Offset, of typefloat, which represents the location of the gradient stop within the gradient vector. The default value of this property is 0, and valid values are in the range 0.0-1.0. The closer this value is to 0, the closer the color is to the start of the gradient. Similarly, the closer this value is to 1, the closer the color is to the end of the gradient.
These properties are backed by BindableProperty objects, which means that they can be targets of data bindings, and styled.
Important
The coordinate system used by gradients is relative to a bounding box for the output area. 0 indicates 0 percent of the bounding box, and 1 indicates 100 percent of the bounding box. Therefore, (0.5,0.5) describes a point in the middle of the bounding box, and (1,1) describes a point at the bottom right of the bounding box.
The following XAML example creates a diagonal LinearGradientBrush with four colors:
<LinearGradientBrush StartPoint="0,0"
EndPoint="1,1">
<GradientStop Color="Yellow"
Offset="0.0" />
<GradientStop Color="Red"
Offset="0.25" />
<GradientStop Color="Blue"
Offset="0.75" />
<GradientStop Color="LimeGreen"
Offset="1.0" />
</LinearGradientBrush>
The color of each point between gradient stops is interpolated as a combination of the color specified by the two bounding gradient stops. The following diagram shows the gradient stops from the previous example:
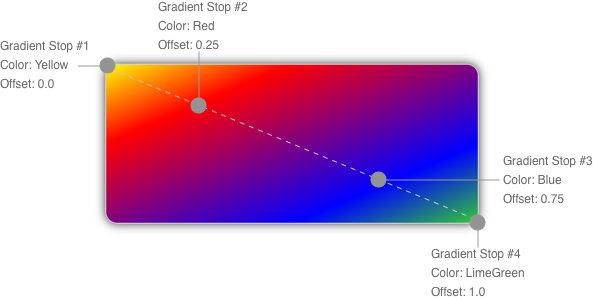
In this diagram, the circles mark the position of gradient stops, and the dashed line shows the gradient axis. The first gradient stop specifies the color yellow at an offset of 0.0. The second gradient stop specifies the color red at an offset of 0.25. The points between these two gradient stops gradually change from yellow to red as you move from left to right along the gradient axis. The third gradient stop specifies the color blue at an offset of 0.75. The points between the second and third gradient stops gradually change from red to blue. The fourth gradient stop specifies the color lime green at an offset of 1.0. The points between the third and fourth gradient stops gradually change from blue to lime green.
 Browse the sample
Browse the sample