How to create and run a long-running workflow
One of the central features of Windows Workflow Foundation (WF) is the runtime’s ability to persist and unload idle workflows to a database. The steps in How to: Run a Workflow demonstrated the basics of workflow hosting using a console application. Examples were shown of starting workflows, workflow lifecycle handlers, and resuming bookmarks. In order to demonstrate workflow persistence effectively, a more complex workflow host is required that supports starting and resuming multiple workflow instances. This step in the tutorial demonstrates how to create a Windows form host application that supports starting and resuming multiple workflow instances, workflow persistence, and provides a basis for the advanced features such as tracking and versioning that are demonstrated in subsequent tutorial steps.
Note
This tutorial step and the subsequent steps use all three workflow types from How to: Create a Workflow.
To create the persistence database
Open SQL Server Management Studio and connect to the local server, for example .\SQLEXPRESS. Right-click the Databases node on the local server, and select New Database. Name the new database WF45GettingStartedTutorial, accept all other values, and select OK.
Note
Ensure that you have Create Database permission on the local server before creating the database.
Choose Open, File from the File menu. Browse to the following folder: C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v4.0.30319\sql\en
Select the following two files and click Open.
SqlWorkflowInstanceStoreLogic.sql
SqlWorkflowInstanceStoreSchema.sql
Choose SqlWorkflowInstanceStoreSchema.sql from the Window menu. Ensure that WF45GettingStartedTutorial is selected in the Available Databases drop-down and choose Execute from the Query menu.
Choose SqlWorkflowInstanceStoreLogic.sql from the Window menu. Ensure that WF45GettingStartedTutorial is selected in the Available Databases drop-down and choose Execute from the Query menu.
Warning
It is important to perform the previous two steps in the correct order. If the queries are executed out of order, errors occur and the persistence database is not configured correctly.
To add the reference to the DurableInstancing assemblies
Right-click NumberGuessWorkflowHost in Solution Explorer and select Add Reference.
Select Assemblies from the Add Reference list, and type
DurableInstancinginto the Search Assemblies box. This filters the assemblies and makes the desired references easier to select.Check the checkbox beside System.Activities.DurableInstancing and System.Runtime.DurableInstancing from the Search Results list, and click OK.
To create the workflow host form
Right-click NumberGuessWorkflowHost in Solution Explorer and choose Add, New Item.
In the Installed templates list, choose Windows Form, type
WorkflowHostFormin the Name box, and click Add.Configure the following properties on the form.
Property Value FormBorderStyle FixedSingle MaximizeBox False Size 400, 420 Add the following controls to the form in the order specified and configure the properties as directed.
Control Property: Value Button Name: NewGame
Location: 13, 13
Size: 75, 23
Text: New GameLabel Location: 94, 18
Text: Guess a number from 1 toComboBox Name: NumberRange
DropDownStyle: DropDownList
Items: 10, 100, 1000
Location: 228, 12
Size: 143, 21Label Location: 13, 43
Text: Workflow typeComboBox Name: WorkflowType
DropDownStyle: DropDownList
Items: StateMachineNumberGuessWorkflow, FlowchartNumberGuessWorkflow, SequentialNumberGuessWorkflow
Location: 94, 40
Size: 277, 21Label Name: WorkflowVersion
Location: 13, 362
Text: Workflow versionGroupBox Location: 13, 67
Size: 358, 287
Text: GameNote
When adding the following controls, put them into the GroupBox.
Control Property: Value Label Location: 7, 20
Text: Workflow Instance IdComboBox Name: InstanceId
DropDownStyle: DropDownList
Location: 121, 17
Size: 227, 21Label Location: 7, 47
Text: GuessTextBox Name: Guess
Location: 50, 44
Size: 65, 20Button Name: EnterGuess
Location: 121, 42
Size: 75, 23
Text: Enter GuessButton Name: QuitGame
Location: 274, 42
Size: 75, 23
Text: QuitTextBox Name: WorkflowStatus
Location: 10, 73
Multiline: True
ReadOnly: True
ScrollBars: Vertical
Size: 338, 208Set the AcceptButton property of the form to EnterGuess.
The following example illustrates the completed form.
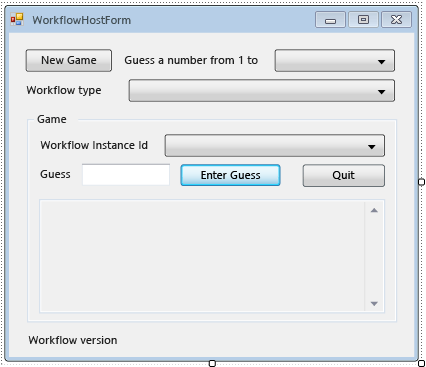
To add the properties and helper methods of the form
The steps in this section add properties and helper methods to the form class that configure the UI of the form to support running and resuming number guess workflows.
Right-click WorkflowHostForm in Solution Explorer and choose View Code.
Add the following
using(orImports) statements at the top of the file with the otherusing(orImports) statements.Imports System.Activities Imports System.Activities.DurableInstancing Imports System.Data.SqlClient Imports System.IO Imports System.Windows.Formsusing System.Activities; using System.Activities.DurableInstancing; using System.Data.SqlClient; using System.IO; using System.Windows.Forms;Add the following member declarations to the WorkflowHostForm class.
Important
Microsoft recommends that you use the most secure authentication flow available. If you're connecting to Azure SQL, Managed Identities for Azure resources is the recommended authentication method.
Const connectionString = "Server=.\SQLEXPRESS;Initial Catalog=WF45GettingStartedTutorial;Integrated Security=SSPI" Dim store As SqlWorkflowInstanceStore Dim workflowStarting As Booleanconst string connectionString = "Server=.\\SQLEXPRESS;Initial Catalog=WF45GettingStartedTutorial;Integrated Security=SSPI"; SqlWorkflowInstanceStore store; bool workflowStarting;Note
If your connection string is different, update
connectionStringto refer to your database.Add a
WorkflowInstanceIdproperty to theWorkflowFormHostclass.Public ReadOnly Property WorkflowInstanceId() As Guid Get If InstanceId.SelectedIndex = -1 Then Return Guid.Empty Else Return New Guid(InstanceId.SelectedItem.ToString()) End If End Get End Propertypublic Guid WorkflowInstanceId { get { return InstanceId.SelectedIndex == -1 ? Guid.Empty : (Guid)InstanceId.SelectedItem; } }The
InstanceIdcombo box displays a list of persisted workflow instance ids, and theWorkflowInstanceIdproperty returns the currently selected workflow.Add a handler for the form
Loadevent. To add the handler, switch to Design View for the form, click the Events icon at the top of the Properties window, and double-click Load.Private Sub WorkflowHostForm_Load(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles Me.Load End Subprivate void WorkflowHostForm_Load(object sender, EventArgs e) { }Add the following code to
WorkflowHostForm_Load.' Initialize the store and configure it so that it can be used for ' multiple WorkflowApplication instances. store = New SqlWorkflowInstanceStore(connectionString) WorkflowApplication.CreateDefaultInstanceOwner(store, Nothing, WorkflowIdentityFilter.Any) ' Set default ComboBox selections. NumberRange.SelectedIndex = 0 WorkflowType.SelectedIndex = 0 ListPersistedWorkflows()// Initialize the store and configure it so that it can be used for // multiple WorkflowApplication instances. store = new SqlWorkflowInstanceStore(connectionString); WorkflowApplication.CreateDefaultInstanceOwner(store, null, WorkflowIdentityFilter.Any); // Set default ComboBox selections. NumberRange.SelectedIndex = 0; WorkflowType.SelectedIndex = 0; ListPersistedWorkflows();When the form loads, the
SqlWorkflowInstanceStoreis configured, the range and workflow type combo boxes are set to default values, and the persisted workflow instances are added to theInstanceIdcombo box.Add a
SelectedIndexChangedhandler forInstanceId. To add the handler, switch to Design View for the form, select theInstanceIdcombo box, click the Events icon at the top of the Properties window, and double-click SelectedIndexChanged.Private Sub InstanceId_SelectedIndexChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles InstanceId.SelectedIndexChanged End Subprivate void InstanceId_SelectedIndexChanged(object sender, EventArgs e) { }Add the following code to
InstanceId_SelectedIndexChanged. Whenever the user selects a workflow by using the combo box this handler updates the status window.If InstanceId.SelectedIndex = -1 Then Return End If ' Clear the status window. WorkflowStatus.Clear() ' Get the workflow version and display it. ' If the workflow is just starting then this info will not ' be available in the persistence store so do not try and retrieve it. If Not workflowStarting Then Dim instance As WorkflowApplicationInstance = _ WorkflowApplication.GetInstance(WorkflowInstanceId, store) WorkflowVersion.Text = _ WorkflowVersionMap.GetIdentityDescription(instance.DefinitionIdentity) ' Unload the instance. instance.Abandon() End Ifif (InstanceId.SelectedIndex == -1) { return; } // Clear the status window. WorkflowStatus.Clear(); // Get the workflow version and display it. // If the workflow is just starting then this info will not // be available in the persistence store so do not try and retrieve it. if (!workflowStarting) { WorkflowApplicationInstance instance = WorkflowApplication.GetInstance(this.WorkflowInstanceId, store); WorkflowVersion.Text = WorkflowVersionMap.GetIdentityDescription(instance.DefinitionIdentity); // Unload the instance. instance.Abandon(); }Add the following
ListPersistedWorkflowsmethod to the form class.Private Sub ListPersistedWorkflows() Using localCon As New SqlConnection(connectionString) Dim localCmd As String = _ "SELECT [InstanceId] FROM [System.Activities.DurableInstancing].[Instances] ORDER BY [CreationTime]" Dim cmd As SqlCommand = localCon.CreateCommand() cmd.CommandText = localCmd localCon.Open() Using reader As SqlDataReader = cmd.ExecuteReader(CommandBehavior.CloseConnection) While (reader.Read()) ' Get the InstanceId of the persisted Workflow. Dim id As Guid = Guid.Parse(reader(0).ToString()) InstanceId.Items.Add(id) End While End Using End Using End Subusing (var localCon = new SqlConnection(connectionString)) { string localCmd = "SELECT [InstanceId] FROM [System.Activities.DurableInstancing].[Instances] ORDER BY [CreationTime]"; SqlCommand cmd = localCon.CreateCommand(); cmd.CommandText = localCmd; localCon.Open(); using (SqlDataReader reader = cmd.ExecuteReader(CommandBehavior.CloseConnection)) { while (reader.Read()) { // Get the InstanceId of the persisted Workflow. Guid id = Guid.Parse(reader[0].ToString()); InstanceId.Items.Add(id); } } }ListPersistedWorkflowsqueries the instance store for persisted workflow instances, and adds the instance ids to thecboInstanceIdcombo box.Add the following
UpdateStatusmethod and corresponding delegate to the form class. This method updates the status window on the form with the status of the currently running workflow.Private Delegate Sub UpdateStatusDelegate(msg As String) Public Sub UpdateStatus(msg As String) ' We may be on a different thread so we need to ' make this call using BeginInvoke. If InvokeRequired Then BeginInvoke(New UpdateStatusDelegate(AddressOf UpdateStatus), msg) Else If Not msg.EndsWith(vbCrLf) Then msg = msg & vbCrLf End If WorkflowStatus.AppendText(msg) ' Ensure that the newly added status is visible. WorkflowStatus.SelectionStart = WorkflowStatus.Text.Length WorkflowStatus.ScrollToCaret() End If End Subprivate delegate void UpdateStatusDelegate(string msg); public void UpdateStatus(string msg) { // We may be on a different thread so we need to // make this call using BeginInvoke. if (InvokeRequired) { BeginInvoke(new UpdateStatusDelegate(UpdateStatus), msg); } else { if (!msg.EndsWith("\r\n")) { msg += "\r\n"; } WorkflowStatus.AppendText(msg); WorkflowStatus.SelectionStart = WorkflowStatus.Text.Length; WorkflowStatus.ScrollToCaret(); } }Add the following
GameOvermethod and corresponding delegate to the form class. When a workflow completes, this method updates the form UI by removing the instance id of the completed workflow from the InstanceId combo box.Private Delegate Sub GameOverDelegate() Private Sub GameOver() If InvokeRequired Then BeginInvoke(New GameOverDelegate(AddressOf GameOver)) Else ' Remove this instance from the InstanceId combo box. InstanceId.Items.Remove(InstanceId.SelectedItem) InstanceId.SelectedIndex = -1 End If End Subprivate delegate void GameOverDelegate(); private void GameOver() { if (InvokeRequired) { BeginInvoke(new GameOverDelegate(GameOver)); } else { // Remove this instance from the combo box. InstanceId.Items.Remove(InstanceId.SelectedItem); InstanceId.SelectedIndex = -1; } }
To configure the instance store, workflow lifecycle handlers, and extensions
Add a
ConfigureWorkflowApplicationmethod to the form class.Private Sub ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp As WorkflowApplication) End Subprivate void ConfigureWorkflowApplication(WorkflowApplication wfApp) { }This method configures the
WorkflowApplication, adds the desired extensions, and adds handlers for the workflow lifecycle events.In
ConfigureWorkflowApplication, specify theSqlWorkflowInstanceStorefor theWorkflowApplication.' Configure the persistence store. wfApp.InstanceStore = store// Configure the persistence store. wfApp.InstanceStore = store;Next, create a
StringWriterinstance and add it to theExtensionscollection of theWorkflowApplication. When aStringWriteris added to the extensions it captures allWriteLineactivity output. When the workflow becomes idle, theWriteLineoutput can be extracted from theStringWriterand displayed on the form.' Add a StringWriter to the extensions. This captures the output ' from the WriteLine activities so we can display it in the form. Dim sw As New StringWriter() wfApp.Extensions.Add(sw)// Add a StringWriter to the extensions. This captures the output // from the WriteLine activities so we can display it in the form. var sw = new StringWriter(); wfApp.Extensions.Add(sw);Add the following handler for the
Completedevent. When a workflow successfully completes, the number of turns taken to guess the number is displayed to the status window. If the workflow terminates, the exception information that caused the termination is displayed. At the end of the handler theGameOvermethod is called, which removes the completed workflow from the workflow list.wfApp.Completed = _ Sub(e As WorkflowApplicationCompletedEventArgs) If e.CompletionState = ActivityInstanceState.Faulted Then UpdateStatus($"Workflow Terminated. Exception: {e.TerminationException.GetType().FullName}{vbCrLf}{e.TerminationException.Message}") ElseIf e.CompletionState = ActivityInstanceState.Canceled Then UpdateStatus("Workflow Canceled.") Else Dim turns As Integer = Convert.ToInt32(e.Outputs("Turns")) UpdateStatus($"Congratulations, you guessed the number in {turns} turns.") End If GameOver() End SubwfApp.Completed = delegate(WorkflowApplicationCompletedEventArgs e) { if (e.CompletionState == ActivityInstanceState.Faulted) { UpdateStatus($"Workflow Terminated. Exception: {e.TerminationException.GetType().FullName}\r\n{e.TerminationException.Message}"); } else if (e.CompletionState == ActivityInstanceState.Canceled) { UpdateStatus("Workflow Canceled."); } else { int turns = Convert.ToInt32(e.Outputs["Turns"]); UpdateStatus($"Congratulations, you guessed the number in {turns} turns."); } GameOver(); };Add the following
AbortedandOnUnhandledExceptionhandlers. TheGameOvermethod is not called from theAbortedhandler because when a workflow instance is aborted, it does not terminate, and it is possible to resume the instance at a later time.wfApp.Aborted = _ Sub(e As WorkflowApplicationAbortedEventArgs) UpdateStatus($"Workflow Aborted. Exception: {e.Reason.GetType().FullName}{vbCrLf}{e.Reason.Message}") End Sub wfApp.OnUnhandledException = _ Function(e As WorkflowApplicationUnhandledExceptionEventArgs) UpdateStatus($"Unhandled Exception: {e.UnhandledException.GetType().FullName}{vbCrLf}{e.UnhandledException.Message}") GameOver() Return UnhandledExceptionAction.Terminate End FunctionwfApp.Aborted = delegate(WorkflowApplicationAbortedEventArgs e) { UpdateStatus($"Workflow Aborted. Exception: {e.Reason.GetType().FullName}\r\n{e.Reason.Message}"); }; wfApp.OnUnhandledException = delegate(WorkflowApplicationUnhandledExceptionEventArgs e) { UpdateStatus($"Unhandled Exception: {e.UnhandledException.GetType().FullName}\r\n{e.UnhandledException.Message}"); GameOver(); return UnhandledExceptionAction.Terminate; };Add the following
PersistableIdlehandler. This handler retrieves theStringWriterextension that was added, extracts the output from theWriteLineactivities, and displays it in the status window.wfApp.PersistableIdle = _ Function(e As WorkflowApplicationIdleEventArgs) ' Send the current WriteLine outputs to the status window. Dim writers = e.GetInstanceExtensions(Of StringWriter)() For Each writer In writers UpdateStatus(writer.ToString()) Next Return PersistableIdleAction.Unload End FunctionwfApp.PersistableIdle = delegate(WorkflowApplicationIdleEventArgs e) { // Send the current WriteLine outputs to the status window. var writers = e.GetInstanceExtensions<StringWriter>(); foreach (var writer in writers) { UpdateStatus(writer.ToString()); } return PersistableIdleAction.Unload; };The PersistableIdleAction enumeration has three values: None, Persist, and Unload. Persist causes the workflow to persist but it does not cause the workflow to unload. Unload causes the workflow to persist and be unloaded.
The following example is the completed
ConfigureWorkflowApplicationmethod.Private Sub ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp As WorkflowApplication) ' Configure the persistence store. wfApp.InstanceStore = store ' Add a StringWriter to the extensions. This captures the output ' from the WriteLine activities so we can display it in the form. Dim sw As New StringWriter() wfApp.Extensions.Add(sw) wfApp.Completed = _ Sub(e As WorkflowApplicationCompletedEventArgs) If e.CompletionState = ActivityInstanceState.Faulted Then UpdateStatus($"Workflow Terminated. Exception: {e.TerminationException.GetType().FullName}{vbCrLf}{e.TerminationException.Message}") ElseIf e.CompletionState = ActivityInstanceState.Canceled Then UpdateStatus("Workflow Canceled.") Else Dim turns As Integer = Convert.ToInt32(e.Outputs("Turns")) UpdateStatus($"Congratulations, you guessed the number in {turns} turns.") End If GameOver() End Sub wfApp.Aborted = _ Sub(e As WorkflowApplicationAbortedEventArgs) UpdateStatus($"Workflow Aborted. Exception: {e.Reason.GetType().FullName}{vbCrLf}{e.Reason.Message}") End Sub wfApp.OnUnhandledException = _ Function(e As WorkflowApplicationUnhandledExceptionEventArgs) UpdateStatus($"Unhandled Exception: {e.UnhandledException.GetType().FullName}{vbCrLf}{e.UnhandledException.Message}") GameOver() Return UnhandledExceptionAction.Terminate End Function wfApp.PersistableIdle = _ Function(e As WorkflowApplicationIdleEventArgs) ' Send the current WriteLine outputs to the status window. Dim writers = e.GetInstanceExtensions(Of StringWriter)() For Each writer In writers UpdateStatus(writer.ToString()) Next Return PersistableIdleAction.Unload End Function End Subprivate void ConfigureWorkflowApplication(WorkflowApplication wfApp) { // Configure the persistence store. wfApp.InstanceStore = store; // Add a StringWriter to the extensions. This captures the output // from the WriteLine activities so we can display it in the form. var sw = new StringWriter(); wfApp.Extensions.Add(sw); wfApp.Completed = delegate(WorkflowApplicationCompletedEventArgs e) { if (e.CompletionState == ActivityInstanceState.Faulted) { UpdateStatus($"Workflow Terminated. Exception: {e.TerminationException.GetType().FullName}\r\n{e.TerminationException.Message}"); } else if (e.CompletionState == ActivityInstanceState.Canceled) { UpdateStatus("Workflow Canceled."); } else { int turns = Convert.ToInt32(e.Outputs["Turns"]); UpdateStatus($"Congratulations, you guessed the number in {turns} turns."); } GameOver(); }; wfApp.Aborted = delegate(WorkflowApplicationAbortedEventArgs e) { UpdateStatus($"Workflow Aborted. Exception: {e.Reason.GetType().FullName}\r\n{e.Reason.Message}"); }; wfApp.OnUnhandledException = delegate(WorkflowApplicationUnhandledExceptionEventArgs e) { UpdateStatus($"Unhandled Exception: {e.UnhandledException.GetType().FullName}\r\n{e.UnhandledException.Message}"); GameOver(); return UnhandledExceptionAction.Terminate; }; wfApp.PersistableIdle = delegate(WorkflowApplicationIdleEventArgs e) { // Send the current WriteLine outputs to the status window. var writers = e.GetInstanceExtensions<StringWriter>(); foreach (var writer in writers) { UpdateStatus(writer.ToString()); } return PersistableIdleAction.Unload; }; }
To enable starting and resuming multiple workflow types
In order to resume a workflow instance, the host has to provide the workflow definition. In this tutorial there are three workflow types, and subsequent tutorial steps introduce multiple versions of these types. WorkflowIdentity provides a way for a host application to associate identifying information with a persisted workflow instance. The steps in this section demonstrate how to create a utility class to assist with mapping the workflow identity from a persisted workflow instance to the corresponding workflow definition. For more information about WorkflowIdentity and versioning, see Using WorkflowIdentity and Versioning.
Right-click NumberGuessWorkflowHost in Solution Explorer and choose Add, Class. Type
WorkflowVersionMapinto the Name box and click Add.Add the following
usingorImportsstatements at the top of the file with the otherusingorImportsstatements.Imports System.Activities Imports NumberGuessWorkflowActivitiesusing System.Activities; using NumberGuessWorkflowActivities;Replace the
WorkflowVersionMapclass declaration with the following declaration.Public Module WorkflowVersionMap Dim map As Dictionary(Of WorkflowIdentity, Activity) ' Current version identities. Public StateMachineNumberGuessIdentity As WorkflowIdentity Public FlowchartNumberGuessIdentity As WorkflowIdentity Public SequentialNumberGuessIdentity As WorkflowIdentity Sub New() map = New Dictionary(Of WorkflowIdentity, Activity) ' Add the current workflow version identities. StateMachineNumberGuessIdentity = New WorkflowIdentity With { .Name = "StateMachineNumberGuessWorkflow", .Version = New Version(1, 0, 0, 0) } FlowchartNumberGuessIdentity = New WorkflowIdentity With { .Name = "FlowchartNumberGuessWorkflow", .Version = New Version(1, 0, 0, 0) } SequentialNumberGuessIdentity = New WorkflowIdentity With { .Name = "SequentialNumberGuessWorkflow", .Version = New Version(1, 0, 0, 0) } map.Add(StateMachineNumberGuessIdentity, New StateMachineNumberGuessWorkflow()) map.Add(FlowchartNumberGuessIdentity, New FlowchartNumberGuessWorkflow()) map.Add(SequentialNumberGuessIdentity, New SequentialNumberGuessWorkflow()) End Sub Public Function GetWorkflowDefinition(identity As WorkflowIdentity) As Activity Return map(identity) End Function Public Function GetIdentityDescription(identity As WorkflowIdentity) As String Return identity.ToString() End Function End Modulepublic static class WorkflowVersionMap { static Dictionary<WorkflowIdentity, Activity> map; // Current version identities. static public WorkflowIdentity StateMachineNumberGuessIdentity; static public WorkflowIdentity FlowchartNumberGuessIdentity; static public WorkflowIdentity SequentialNumberGuessIdentity; static WorkflowVersionMap() { map = new Dictionary<WorkflowIdentity, Activity>(); // Add the current workflow version identities. StateMachineNumberGuessIdentity = new WorkflowIdentity { Name = "StateMachineNumberGuessWorkflow", Version = new Version(1, 0, 0, 0) }; FlowchartNumberGuessIdentity = new WorkflowIdentity { Name = "FlowchartNumberGuessWorkflow", Version = new Version(1, 0, 0, 0) }; SequentialNumberGuessIdentity = new WorkflowIdentity { Name = "SequentialNumberGuessWorkflow", Version = new Version(1, 0, 0, 0) }; map.Add(StateMachineNumberGuessIdentity, new StateMachineNumberGuessWorkflow()); map.Add(FlowchartNumberGuessIdentity, new FlowchartNumberGuessWorkflow()); map.Add(SequentialNumberGuessIdentity, new SequentialNumberGuessWorkflow()); } public static Activity GetWorkflowDefinition(WorkflowIdentity identity) { return map[identity]; } public static string GetIdentityDescription(WorkflowIdentity identity) { return identity.ToString(); } }WorkflowVersionMapcontains three workflow identities that map to the three workflow definitions from this tutorial and is used in the following sections when workflows are started and resumed.
To start a new workflow
Add a
Clickhandler forNewGame. To add the handler, switch to Design View for the form, and double-clickNewGame. ANewGame_Clickhandler is added and the view switches to code view for the form. Whenever the user clicks this button a new workflow is started.Private Sub NewGame_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles NewGame.Click End Subprivate void NewGame_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { }Add the following code to the click handler. This code creates a dictionary of input arguments for the workflow, keyed by argument name. This dictionary has one entry that contains the range of the randomly generated number retrieved from the range combo box.
Dim inputs As New Dictionary(Of String, Object)() inputs.Add("MaxNumber", Convert.ToInt32(NumberRange.SelectedItem))var inputs = new Dictionary<string, object>(); inputs.Add("MaxNumber", Convert.ToInt32(NumberRange.SelectedItem));Next, add the following code that starts the workflow. The
WorkflowIdentityand workflow definition corresponding to the type of workflow selected are retrieved using theWorkflowVersionMaphelper class. Next, a newWorkflowApplicationinstance is created using the workflow definition,WorkflowIdentity, and dictionary of input arguments.Dim identity As WorkflowIdentity = Nothing Select Case WorkflowType.SelectedItem.ToString() Case "SequentialNumberGuessWorkflow" identity = WorkflowVersionMap.SequentialNumberGuessIdentity Case "StateMachineNumberGuessWorkflow" identity = WorkflowVersionMap.StateMachineNumberGuessIdentity Case "FlowchartNumberGuessWorkflow" identity = WorkflowVersionMap.FlowchartNumberGuessIdentity End Select Dim wf As Activity = WorkflowVersionMap.GetWorkflowDefinition(identity) Dim wfApp = New WorkflowApplication(wf, inputs, identity)WorkflowIdentity identity = null; switch (WorkflowType.SelectedItem.ToString()) { case "SequentialNumberGuessWorkflow": identity = WorkflowVersionMap.SequentialNumberGuessIdentity; break; case "StateMachineNumberGuessWorkflow": identity = WorkflowVersionMap.StateMachineNumberGuessIdentity; break; case "FlowchartNumberGuessWorkflow": identity = WorkflowVersionMap.FlowchartNumberGuessIdentity; break; }; Activity wf = WorkflowVersionMap.GetWorkflowDefinition(identity); WorkflowApplication wfApp = new WorkflowApplication(wf, inputs, identity);Next, add the following code which adds the workflow to the workflow list and displays the workflow's version information on the form.
' Add the workflow to the list and display the version information. workflowStarting = True InstanceId.SelectedIndex = InstanceId.Items.Add(wfApp.Id) WorkflowVersion.Text = identity.ToString() workflowStarting = False// Add the workflow to the list and display the version information. workflowStarting = true; InstanceId.SelectedIndex = InstanceId.Items.Add(wfApp.Id); WorkflowVersion.Text = identity.ToString(); workflowStarting = false;Call
ConfigureWorkflowApplicationto configure the instance store, extensions, and workflow lifecycle handlers for thisWorkflowApplicationinstance.' Configure the instance store, extensions, and ' workflow lifecycle handlers. ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp)// Configure the instance store, extensions, and // workflow lifecycle handlers. ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp);Finally, call
Run.' Start the workflow. wfApp.Run()// Start the workflow. wfApp.Run();The following example is the completed
NewGame_Clickhandler.Private Sub NewGame_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles NewGame.Click ' Start a new workflow. Dim inputs As New Dictionary(Of String, Object)() inputs.Add("MaxNumber", Convert.ToInt32(NumberRange.SelectedItem)) Dim identity As WorkflowIdentity = Nothing Select Case WorkflowType.SelectedItem.ToString() Case "SequentialNumberGuessWorkflow" identity = WorkflowVersionMap.SequentialNumberGuessIdentity Case "StateMachineNumberGuessWorkflow" identity = WorkflowVersionMap.StateMachineNumberGuessIdentity Case "FlowchartNumberGuessWorkflow" identity = WorkflowVersionMap.FlowchartNumberGuessIdentity End Select Dim wf As Activity = WorkflowVersionMap.GetWorkflowDefinition(identity) Dim wfApp = New WorkflowApplication(wf, inputs, identity) ' Add the workflow to the list and display the version information. workflowStarting = True InstanceId.SelectedIndex = InstanceId.Items.Add(wfApp.Id) WorkflowVersion.Text = identity.ToString() workflowStarting = False ' Configure the instance store, extensions, and ' workflow lifecycle handlers. ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp) ' Start the workflow. wfApp.Run() End Subprivate void NewGame_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { var inputs = new Dictionary<string, object>(); inputs.Add("MaxNumber", Convert.ToInt32(NumberRange.SelectedItem)); WorkflowIdentity identity = null; switch (WorkflowType.SelectedItem.ToString()) { case "SequentialNumberGuessWorkflow": identity = WorkflowVersionMap.SequentialNumberGuessIdentity; break; case "StateMachineNumberGuessWorkflow": identity = WorkflowVersionMap.StateMachineNumberGuessIdentity; break; case "FlowchartNumberGuessWorkflow": identity = WorkflowVersionMap.FlowchartNumberGuessIdentity; break; }; Activity wf = WorkflowVersionMap.GetWorkflowDefinition(identity); var wfApp = new WorkflowApplication(wf, inputs, identity); // Add the workflow to the list and display the version information. workflowStarting = true; InstanceId.SelectedIndex = InstanceId.Items.Add(wfApp.Id); WorkflowVersion.Text = identity.ToString(); workflowStarting = false; // Configure the instance store, extensions, and // workflow lifecycle handlers. ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp); // Start the workflow. wfApp.Run(); }
To resume a workflow
Add a
Clickhandler forEnterGuess. To add the handler, switch to Design View for the form, and double-clickEnterGuess. Whenever the user clicks this button a workflow is resumed.Private Sub EnterGuess_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles EnterGuess.Click End Subprivate void EnterGuess_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { }Add the following code to ensure that a workflow is selected in the workflow list, and that the user's guess is valid.
If WorkflowInstanceId = Guid.Empty Then MessageBox.Show("Please select a workflow.") Return End If Dim userGuess As Integer If Not Int32.TryParse(Guess.Text, userGuess) Then MessageBox.Show("Please enter an integer.") Guess.SelectAll() Guess.Focus() Return End Ifif (WorkflowInstanceId == Guid.Empty) { MessageBox.Show("Please select a workflow."); return; } int guess; if (!Int32.TryParse(Guess.Text, out guess)) { MessageBox.Show("Please enter an integer."); Guess.SelectAll(); Guess.Focus(); return; }Next, retrieve the
WorkflowApplicationInstanceof the persisted workflow instance. AWorkflowApplicationInstancerepresents a persisted workflow instance that has not yet been associated with a workflow definition. TheDefinitionIdentityof theWorkflowApplicationInstancecontains theWorkflowIdentityof the persisted workflow instance. In this tutorial, theWorkflowVersionMaputility class is used to map theWorkflowIdentityto the correct workflow definition. Once the workflow definition is retrieved, aWorkflowApplicationis created, using the correct workflow definition.Dim instance As WorkflowApplicationInstance = _ WorkflowApplication.GetInstance(WorkflowInstanceId, store) ' Use the persisted WorkflowIdentity to retrieve the correct workflow ' definition from the dictionary. Dim wf As Activity = _ WorkflowVersionMap.GetWorkflowDefinition(instance.DefinitionIdentity) ' Associate the WorkflowApplication with the correct definition Dim wfApp As New WorkflowApplication(wf, instance.DefinitionIdentity)WorkflowApplicationInstance instance = WorkflowApplication.GetInstance(WorkflowInstanceId, store); // Use the persisted WorkflowIdentity to retrieve the correct workflow // definition from the dictionary. Activity wf = WorkflowVersionMap.GetWorkflowDefinition(instance.DefinitionIdentity); // Associate the WorkflowApplication with the correct definition var wfApp = new WorkflowApplication(wf, instance.DefinitionIdentity);Once the
WorkflowApplicationis created, configure the instance store, workflow lifecycle handlers, and extensions by callingConfigureWorkflowApplication. These steps must be done every time a newWorkflowApplicationis created, and they must be done before the workflow instance is loaded into theWorkflowApplication. After the workflow is loaded, it is resumed with the user's guess.' Configure the extensions and lifecycle handlers. ' Do this before the instance is loaded. Once the instance is ' loaded it is too late to add extensions. ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp) ' Load the workflow. wfApp.Load(instance) ' Resume the workflow. wfApp.ResumeBookmark("EnterGuess", userGuess)// Configure the extensions and lifecycle handlers. // Do this before the instance is loaded. Once the instance is // loaded it is too late to add extensions. ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp); // Load the workflow. wfApp.Load(instance); // Resume the workflow. wfApp.ResumeBookmark("EnterGuess", guess);Finally, clear the guess textbox and prepare the form to accept another guess.
' Clear the Guess textbox. Guess.Clear() Guess.Focus()// Clear the Guess textbox. Guess.Clear(); Guess.Focus();The following example is the completed
EnterGuess_Clickhandler.Private Sub EnterGuess_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles EnterGuess.Click If WorkflowInstanceId = Guid.Empty Then MessageBox.Show("Please select a workflow.") Return End If Dim userGuess As Integer If Not Int32.TryParse(Guess.Text, userGuess) Then MessageBox.Show("Please enter an integer.") Guess.SelectAll() Guess.Focus() Return End If Dim instance As WorkflowApplicationInstance = _ WorkflowApplication.GetInstance(WorkflowInstanceId, store) ' Use the persisted WorkflowIdentity to retrieve the correct workflow ' definition from the dictionary. Dim wf As Activity = _ WorkflowVersionMap.GetWorkflowDefinition(instance.DefinitionIdentity) ' Associate the WorkflowApplication with the correct definition Dim wfApp As New WorkflowApplication(wf, instance.DefinitionIdentity) ' Configure the extensions and lifecycle handlers. ' Do this before the instance is loaded. Once the instance is ' loaded it is too late to add extensions. ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp) ' Load the workflow. wfApp.Load(instance) ' Resume the workflow. wfApp.ResumeBookmark("EnterGuess", userGuess) ' Clear the Guess textbox. Guess.Clear() Guess.Focus() End Subprivate void EnterGuess_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { if (WorkflowInstanceId == Guid.Empty) { MessageBox.Show("Please select a workflow."); return; } int guess; if (!Int32.TryParse(Guess.Text, out guess)) { MessageBox.Show("Please enter an integer."); Guess.SelectAll(); Guess.Focus(); return; } WorkflowApplicationInstance instance = WorkflowApplication.GetInstance(WorkflowInstanceId, store); // Use the persisted WorkflowIdentity to retrieve the correct workflow // definition from the dictionary. Activity wf = WorkflowVersionMap.GetWorkflowDefinition(instance.DefinitionIdentity); // Associate the WorkflowApplication with the correct definition var wfApp = new WorkflowApplication(wf, instance.DefinitionIdentity); // Configure the extensions and lifecycle handlers. // Do this before the instance is loaded. Once the instance is // loaded it is too late to add extensions. ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp); // Load the workflow. wfApp.Load(instance); // Resume the workflow. wfApp.ResumeBookmark("EnterGuess", guess); // Clear the Guess textbox. Guess.Clear(); Guess.Focus(); }
To terminate a workflow
Add a
Clickhandler forQuitGame. To add the handler, switch to Design View for the form, and double-clickQuitGame. Whenever the user clicks this button the currently selected workflow is terminated.Private Sub QuitGame_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles QuitGame.Click End Subprivate void QuitGame_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { }Add the following code to the
QuitGame_Clickhandler. This code first checks to ensure that a workflow is selected in the workflow list. Then it loads the persisted instance into aWorkflowApplicationInstance, uses theDefinitionIdentityto determine the correct workflow definition, and then initializes theWorkflowApplication. Next the extensions and workflow lifecycle handlers are configured with a call toConfigureWorkflowApplication. Once theWorkflowApplicationis configured, it is loaded, and thenTerminateis called.If WorkflowInstanceId = Guid.Empty Then MessageBox.Show("Please select a workflow.") Return End If Dim instance As WorkflowApplicationInstance = _ WorkflowApplication.GetInstance(WorkflowInstanceId, store) ' Use the persisted WorkflowIdentity to retrieve the correct workflow ' definition from the dictionary. Dim wf As Activity = WorkflowVersionMap.GetWorkflowDefinition(instance.DefinitionIdentity) ' Associate the WorkflowApplication with the correct definition. Dim wfApp As New WorkflowApplication(wf, instance.DefinitionIdentity) ' Configure the extensions and lifecycle handlers. ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp) ' Load the workflow. wfApp.Load(instance) ' Terminate the workflow. wfApp.Terminate("User resigns.")if (WorkflowInstanceId == Guid.Empty) { MessageBox.Show("Please select a workflow."); return; } WorkflowApplicationInstance instance = WorkflowApplication.GetInstance(WorkflowInstanceId, store); // Use the persisted WorkflowIdentity to retrieve the correct workflow // definition from the dictionary. Activity wf = WorkflowVersionMap.GetWorkflowDefinition(instance.DefinitionIdentity); // Associate the WorkflowApplication with the correct definition var wfApp = new WorkflowApplication(wf, instance.DefinitionIdentity); // Configure the extensions and lifecycle handlers ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp); // Load the workflow. wfApp.Load(instance); // Terminate the workflow. wfApp.Terminate("User resigns.");
To build and run the application
Double-click Program.cs (or Module1.vb) in Solution Explorer to display the code.
Add the following
using(orImports) statement at the top of the file with the otherusing(orImports) statements.Imports System.Windows.Formsusing System.Windows.Forms;Remove or comment out the existing workflow hosting code from How to: Run a Workflow, and replace it with the following code.
Sub Main() Application.EnableVisualStyles() Application.Run(New WorkflowHostForm()) End Substatic void Main(string[] args) { Application.EnableVisualStyles(); Application.Run(new WorkflowHostForm()); }Right-click NumberGuessWorkflowHost in Solution Explorer and choose Properties. In the Application tab, specify Windows Application for the Output type. This step is optional, but if it is not followed the console window is displayed in addition to the form.
Press Ctrl+Shift+B to build the application.
Ensure that NumberGuessWorkflowHost is set as the startup application, and press Ctrl+F5 to start the application.
Select a range for the guessing game and the type of workflow to start, and click New Game. Enter a guess in the Guess box and click Go to submit your guess. Note that the output from the
WriteLineactivities is displayed on the form.Start several workflows using different workflow types and number ranges, enter some guesses, and switch between the workflows by selecting from the Workflow Instance Id list.
Note that when you switch to a new workflow, the previous guesses and progress of the workflow are not displayed in the status window. The reason the status is not available is because it is not captured and saved anywhere. In the next step of the tutorial, How to: Create a Custom Tracking Participant, you create a custom tracking participant that saves this information.
