What is code analysis with .NET Upgrade Assistant?
This article provides an overview of the code analysis function of .NET Upgrade Assistant. Code analysis generates a report based on your project configuration, dependencies, and code. The report contains information about potential issues and problems you might encounter during the upgrade, and what steps you could take to remediate those problems.
Types of analysis
There are two types of analysis you can perform on your code:
Source code and settings
Analyzes your source code, configuration, and settings.
Binary dependencies
Analyzes the external binary dependencies (such as NuGet packages) for your projects.
Reports
A dashboard report is generated after the analysis completes. This report breaks down the results by project, file, incident, and story points. An aggregate view is also available, to group like-issues together regardless of what project they were detected in.
Tip
Story points are an Agile concept that helps estimate complexity and effort required to fix a problem. For more information, see the Incident story points section.
Each issue in the report is categorized by severity to assist you in prioritizing any fixes you need to make. Issues are either mandatory or optional. Mandatory issues block the upgrade. Optional issues provide an opportunity to upgrade to a newer feature, library, or code enhancement.
The following sections describe areas of the report in detail.
Dashboard
The Dashboard page provides a view of the incidents detected by the scan, grouped into panels:
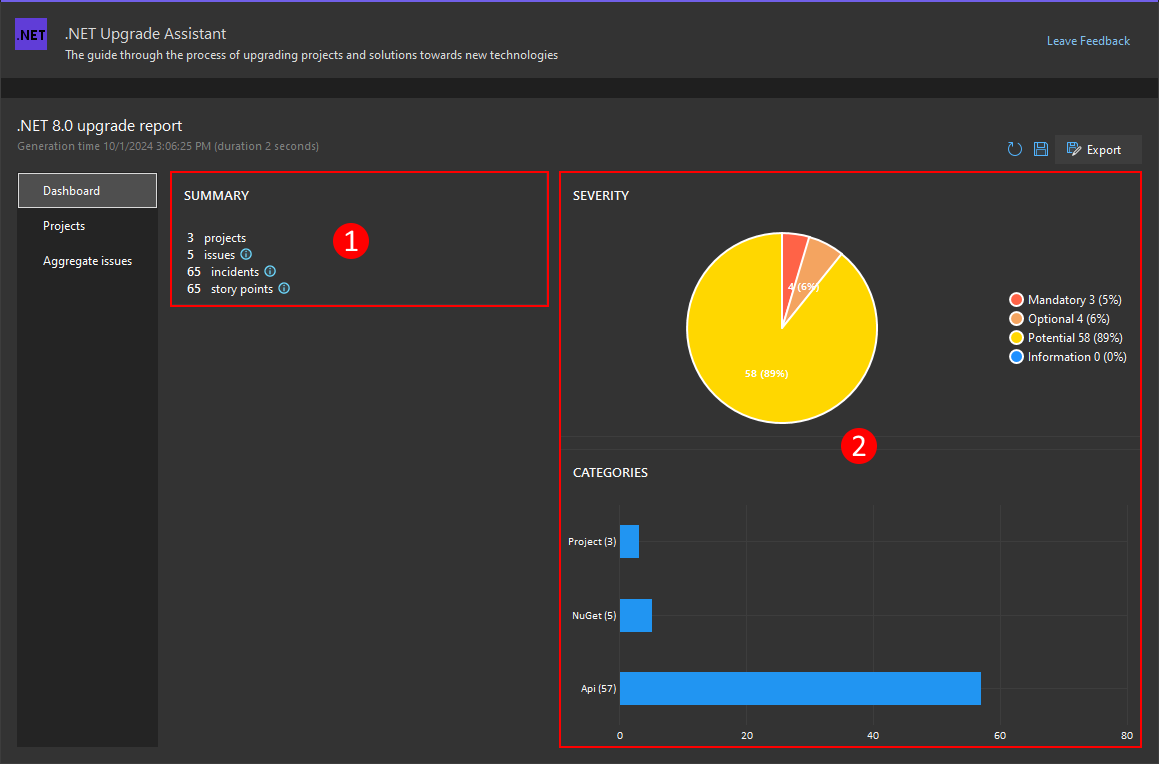
Summary
Projects
This is the number of projects where an incident was detected.
Issues
The number of unique rules that triggered during the scan. Each issue has its own severity and story point, along with each detected instance (incident).
Incidents
An incident is an instance of a detected issue at a specific location, such as a piece of code or binary file. Each incident contains the contextual information that triggered the issue.
Story Points
The total number of story points required to complete the upgrade. For more information about what a story point is, see the Incident story points section.
Severity and Categories
These two panels show charts that group the incidents by severity and category. For more information about severity, see the Incident severity section.
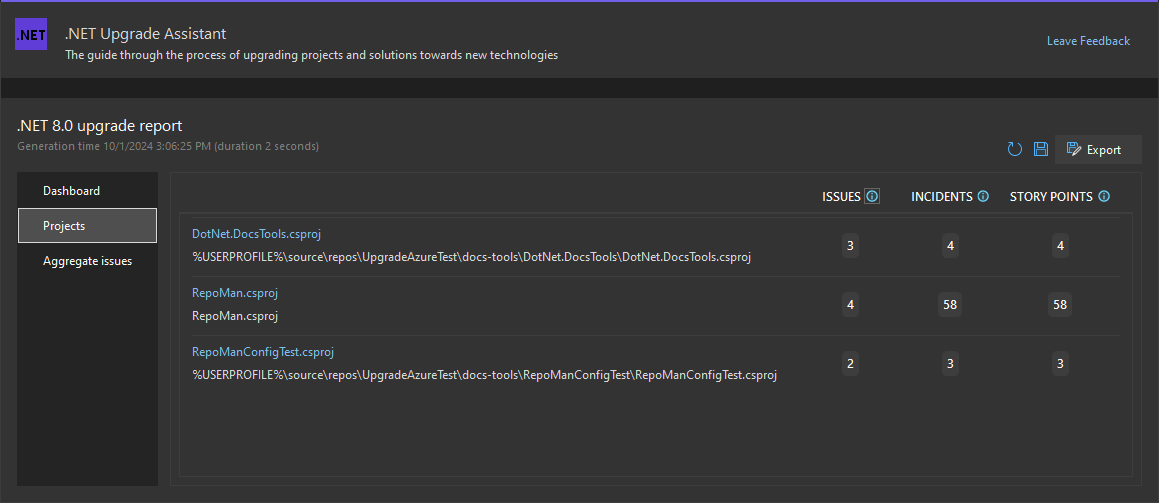
Projects
The Projects page breaks down the issues, incidents, and story points, by project. Each project is a link that opens a drill-down report filtered to that project.
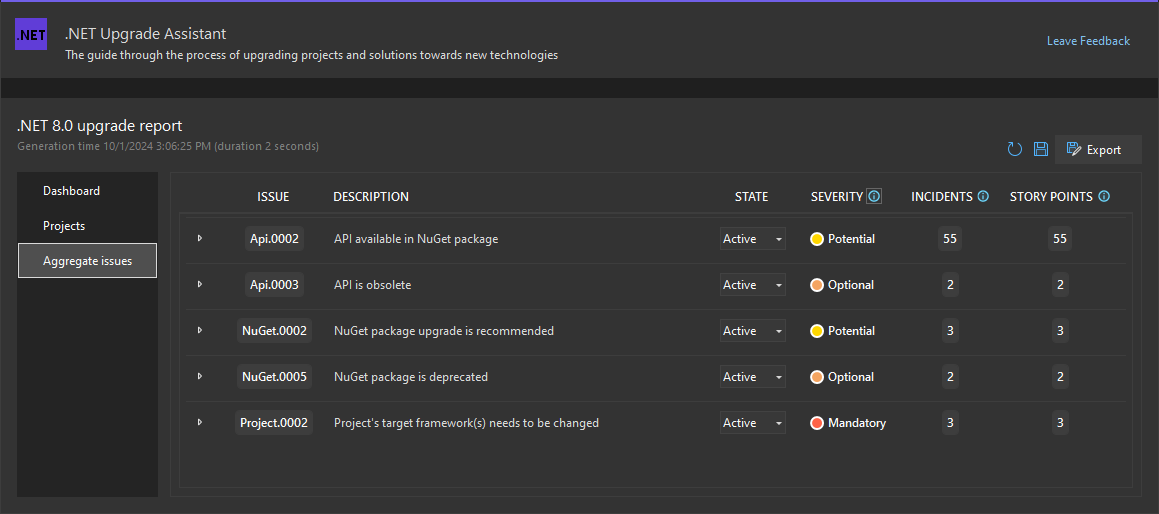
Aggregate issues
The Aggregate issues page details each issue that was triggered. Each issue can be expanded to list every incident of that issue. The State column helps you track which issues you've fixed or deemed not applicable.
Incident severity
Each issue incident has an associated severity, which might block the upgrade. The severity helps you understand what must be updated for the upgrade to succeed.
| Severity | Description |
|---|---|
| Mandatory | Must be addressed. The upgrade process might handle these issues for you, such as updating the target framework runtime (TFM). |
| Optional | These shouldn't pose a problem with upgrading, but you might want to consider addressing them before or after the upgrade. |
| Potential | Problems that might cause issue after upgrading, if you don't address them now. |
| Information | Extra information related to the upgrade. |
Incident story points
Each issue incident has an associated story point. A story point is a unit of measure to gauge the complexity of an incident, which helps estimate the time involved to resolve that incident. .NET Upgrade Assistant defines story point values by the following table:
| Story Points | Size |
|---|---|
| 1 | Trivial |
| 3 | Complex |
| 5 | Redesign |
| 7 | Rearchitecture |
| 13 | Unknown |
