Investigate and respond to container threats in the Microsoft Defender portal
Important
Some information in this article relates to a prereleased product, which may be substantially modified before it's commercially released. Microsoft makes no warranties expressed or implied, with respect to the information provided here
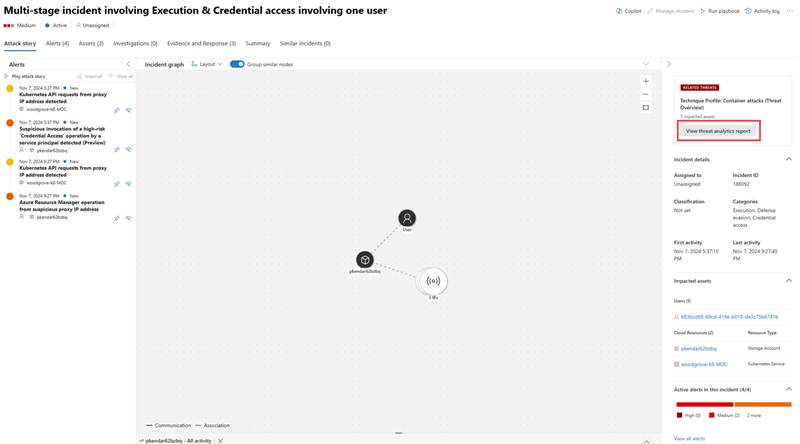
Security operations can now investigate and respond to container-related alerts in near real-time and hunt for related activities with the integration of cloud-native response actions and investigation logs in the Microsoft Defender portal. The availability of attack paths can also help analysts immediately investigate and address critical security issues to prevent a potential breach.
As organizations use containers and Kubernetes on platforms like Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS), Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE), ad Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS), the attack surface expands, increasing security challenges. Containers can also be targeted by threat actors and used for malicious purposes.
Security operations center (SOC) analysts can now easily track container threats with near real-time alerts and immediately respond to these threats by isolating or terminating container pods. This integration allows analysts to instantly mitigate a container attack from their environment in a click.
Analysts can then investigate the full scope of the attack with the ability to hunt for related activities within the incident graph. They can also further apply preventive actions with the availability of potential attack paths in the incident graph. Using the information from the attack paths allows security teams to inspect the paths and prevent possible breaches. In addition, Threat analytics reports specific to container threats and attacks are available for analysts to gain more information and apply recommendations for container attack response and prevention.
Prerequisites
Users on AKS, EKS, and GKE platforms can take advantage of the cloud response actions, cloud-related investigation logs, and attack paths in the Microsoft Defender portal with the following licenses:
| Required license | Actions |
|---|---|
| Microsoft Defender for Containers | View container-related alerts View container-related data for investigation in advanced hunting Isolate pod Terminate pod |
| Microsoft Defender for Cloud Security Posture Management | View attack paths in the incident graph |
| Microsoft Security Copilot | View and apply guided responses to investigate and remediate container threats |
The following Microsoft Defender for Containers are required for the cloud response actions in the Microsoft Defender portal:
- Defender sensor
- Kubernetes API access
For more information about these components, see Configure Microsoft Defender for Containers components.
Network policy requirement
The isolate pod response action supports Kubernetes cluster version 1.27 and later. The following network plugins are also required:
| Network plugin | Minimum version required |
|---|---|
| Azure-NPM | 1.5.34 |
| Calico | 3.24.1 |
| Cilium | 1.13.1 |
| AWS-node | 1.15.1 |
The isolate pod response action requires a network policy enforcer for your Kubernetes cluster. The following documentation provides specific steps on how to install and check network policies depending on your platform:
- Azure Kubernetes Service: Secure traffic between pods by using network policies in AKS
- Google Kubernetes Engine: Control communication between Pods and Services using network policies
- Amazon Kubernetes Engine: Limit pod traffic with Kubernetes network policies
To verify your network plugins are supported, follow the steps to access your platform's Cloud Shell and check your network plugins in the Troubleshoot issues section.
The terminate pod response action functions regardless of the presence of a network policy.
Permissions
To perform any of the response actions, users must have the following permissions for Microsoft Defender for Cloud in the Microsoft Defender XDR unified role-based access control:
| Permission name | Level |
|---|---|
| Alerts | Manage |
| Response | Manage |
For more information on these permissions, see Permissions in Microsoft Defender XDR Unified role-based access control (RBAC).
Investigate container threats
To investigate container threats in the Microsoft Defender portal:
- Select Investigation & response > Incidents and alerts in the left-hand navigation menu to open the incident or alert queues.
- In the queue, select Filter and choose Microsoft Defender for Cloud > Microsoft Defender for Containers under Service source.
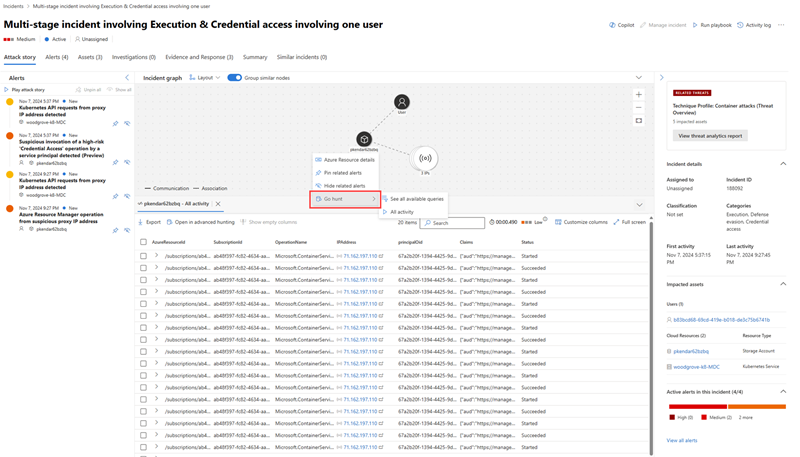
- In the incident graph, select the pod/service/cluster entity you need to investigate. Select Kubernetes service details, Kubernetes pod details, Kubernetes cluster details, or Container registry details to view relevant information about the service, pod, or registry.
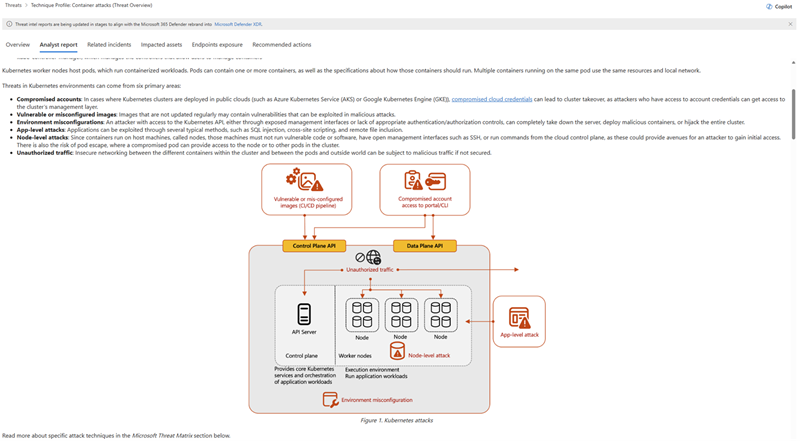
Using Threat analytics reports, analysts can utilize threat intelligence from expert Microsoft security researchers to learn about active threat actors and campaigns exploiting containers, new attack techniques that might affect containers, and prevalent threats that affect containers.
Access threat analytics reports from Threat intelligence > Threat analytics. You can also open a specific report from the incident page by selecting View threat analytics report under Related threats on the incident side pane.
Threat analytics reports also contain relevant mitigation, recovery, and prevention methods that analysts can assess and apply to their environment. Using the information in threat analytics reports helps SOC teams defend and protect their environment from container attacks. Here's an example of an analyst report about a container attack.
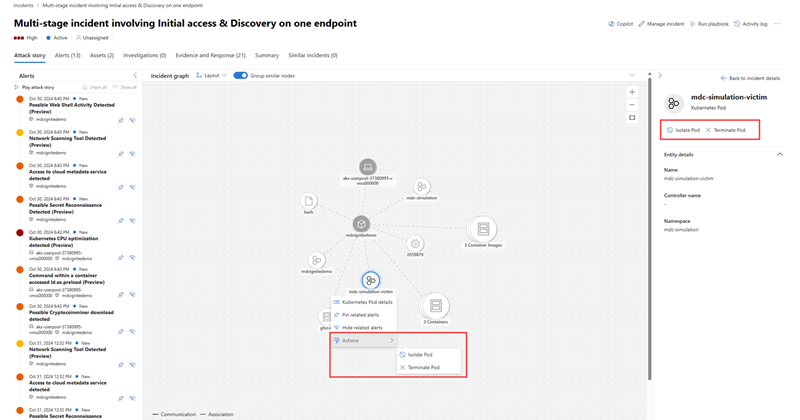
Respond to container threats
You can isolate or terminate a pod once you determine that a pod is compromised or malicious. In the incident graph, select the pod then go to Actions to view the available response actions. You can also find these response actions on the entity side pane.
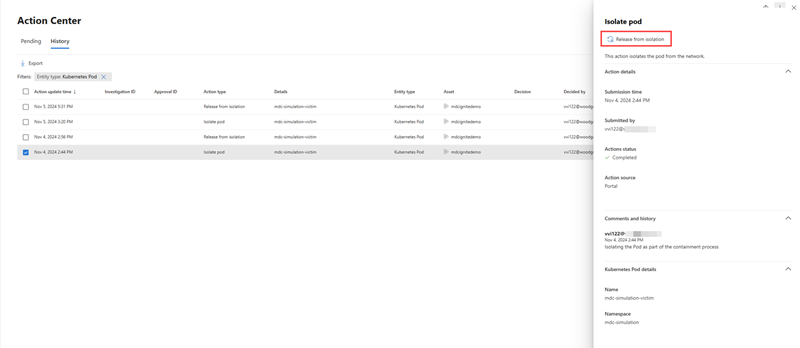
You can release a pod from isolation with the release from isolation action once your investigation is complete. This option appears on the side pane for isolated pods.
Details of all response actions can be viewed in the Action center. In the Action center page, select the response action you want to inspect to view more information about the action like which entity was acted on, when the action was done, and view the comments on the action. For isolated pods, the release from isolation action is also available in the Action center details pane.
Hunt for container-related activities
To determine the full scope of a container attack, you can deepen your investigation with the Go hunt action available in the incident graph. You can immediately view all process events and activities related to container-related incidents from the incident graph.
In the Advanced hunting page, you can extend your search for container-related activities using the CloudProcessEvents and CloudAuditEvents tables.
The CloudProcessEvents table contains information about process events in multi-cloud hosted environments such as Azure Kubernetes Service, Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service, and Google Kubernetes Engine.
The CloudAuditEvents table contains cloud audit events from cloud platforms protected by Microsoft Defender for Cloud. It also contains Kubeaudit logs, which holds information about Kubernetes-related events.
Troubleshoot issues
The following section addresses issues that you might encounter when investigating and responding to container threats.
The isolate pod action is not available
If the isolate pod action is grayed out, you need to verify that you have the necessary permissions to perform this action. Refer to the Permissions section to check and validate that you have the correct permissions.
See Permissions in Microsoft Defender XDR Unified role-based access control (RBAC) for more information.
The isolate pod action failed
- Check the Kubernetes cluster version. The isolate pod action supports Kubernetes clusters from version 1.27 and later.
- Check that you are using the required network plugins and that it matches the minimum versions supported. To check your plugins, access the Cloud Shell in your platform and run the command to check your network plugins.
- Ensure the target pod is in a valid or active state.
Learn how to access the Cloud Shell and check your network plugins by following these steps based on your platform:
On Microsoft Azure
Sign in to the Azure portal then navigate to your cluster.
Above the Essential information, select Connect button and follow the instructions.
The Cloud Shell opens at the bottom of your browser. In the command line interface, run the following command to check your network plugins:
kubectl get pods --all-namespaces -o json | jq -r '.items[].metadata.labels["k8s-app"]' | uniq | grep -E 'azure-npm|calico-node|cilium|aws-node' | head -n 1
The results should mention any of the specified plugins in the network policy requirement. An empty line means that the supported plugin is not installed.
On Google Cloud Platform
Navigate your cluster in Google Cloud Portal.
Select Connect above the name of the cluster. In the small window that appears, copy the following command and run it in your local terminal.
kubectl get pods --all-namespaces -o json | jq -r '.items[].metadata.labels["k8s-app"]' | uniq | grep -E 'azure-npm|calico-node|cilium|aws-node' | head -n 1
You can also choose Run in Cloud Shell to run a shell session that opens at the bottom of your browser. You can copy the command in the interface to check your network plugins.
The results should mention any of the specified plugins in the network policy requirement. An empty line means that the supported plugin is not installed.
On Amazon Web Services
Navigate to your cluster in AWS Cloud Portal.
Select CloudShell on the top-right corner. A Cloud Shell session opens at the bottom of your browser, which provides a command-line interface to manage your AWS resources.
Connect to your cluster by running the following command:
aws eks --region <cluster region> update-kubeconfig --name <cluster name>**
Note
Ensure that the aws-node is deleted or disabled for the Calico and Cilium plugins.
The terminate pod action failed
You need to confirm that the target pod's state is active or valid. To check if the pod is active, run the following command in the Cloud Shell:
kubectl get pod <pod-name>