Use Microsoft Sentinel functions, saved queries, and custom rules
Use functions
To use a function from Microsoft Sentinel, go to the Functions tab and scroll until you find the function that you want. Double-click the function name to insert the function in the query editor.
You can also select the vertical ellipses (  ) to the right of the function and select Insert to query to insert the function into a query in the query editor.
) to the right of the function and select Insert to query to insert the function into a query in the query editor.
Other options include:
- View details – Opens the function side pane containing its details.
- Load function code – Opens a new tab containing the function code.
For editable functions, more options are available when you select the vertical ellipses:
- Edit details – Opens the function side pane to allow you to edit details about the function (except folder names for Sentinel functions).
- Delete – Deletes the function.
Use adx() operator for Azure Data Explorer queries (Preview)
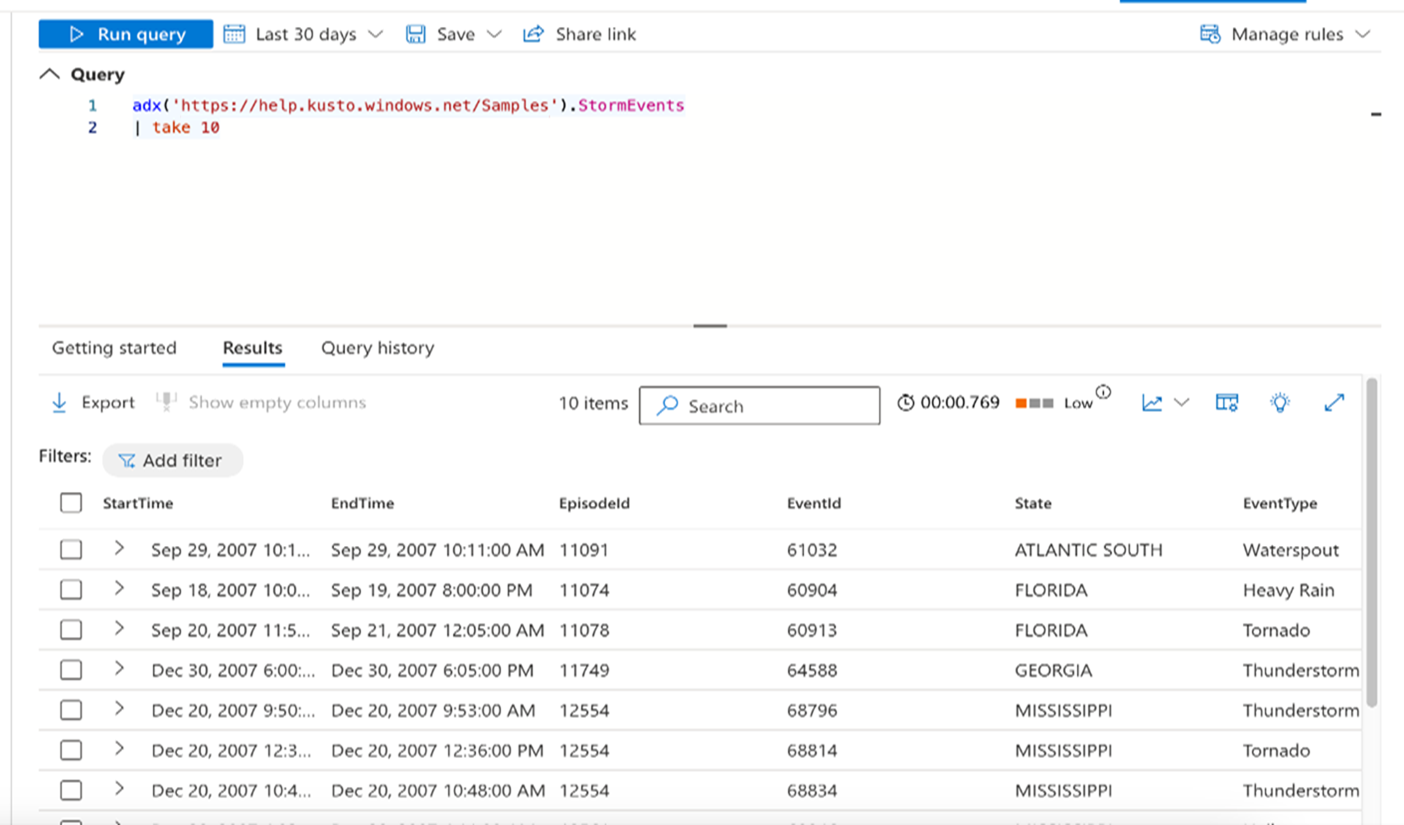
Use the adx() operator to query tables stored in Azure Data Explorer. Read What is Azure Data Explorer? for more details.
This feature was previously only available in log analytics in Microsoft Sentinel. Users can now use the operator in advanced hunting in the unified Microsoft Defender portal without needing to manually open a Microsoft Sentinel window.
In the query editor, enter the query in the following format:
adx('<Cluster URI>/<Database Name>').<Table Name>
For example, to get the first 10 rows of data from the StormEvents table stored in a certain URI:
Note
The adx() operator isn't supported for custom detections.
Use arg() operator for Azure Resource Graph queries
The arg() operator can be used to query across deployed Azure resources like subscriptions, virtual machines, CPU, storage, and the like.
This feature was previously only available in log analytics in Microsoft Sentinel. In the Microsoft Defender portal, the arg() operator works over Microsoft Sentinel data (that is, Defender XDR tables aren't supported). This allows users to use the operator in advanced hunting without needing to manually open a Microsoft Sentinel window.
Note that queries using the arg() operator return the first 1,000 records only. Read Query data in Azure Resource Graph by using arg() for more details.
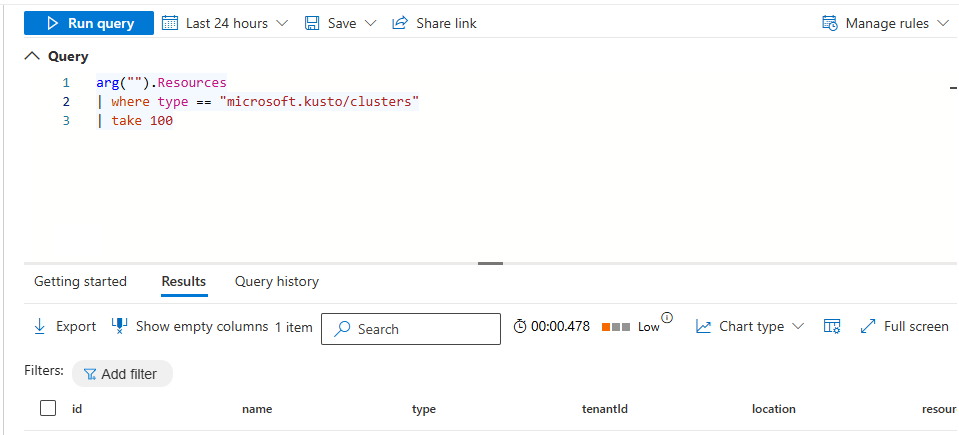
In the query editor, enter arg(""). followed by the Azure Resource Graph table name.
For example:
You can also, for instance, filter a query that searches over Microsoft Sentinel data based on the results of an Azure Resource Graph query:
arg("").Resources
| where type == "microsoft.compute/virtualmachines" and properties.hardwareProfile.vmSize startswith "Standard_D"
| join (
Heartbeat
| where TimeGenerated > ago(1d)
| distinct Computer
)
on $left.name == $right.Computer
Use saved queries
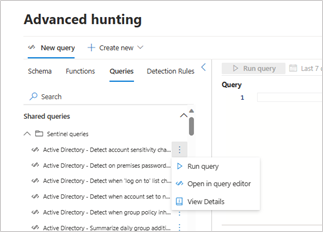
To use a saved query from Microsoft Sentinel, go to the Queries tab and scroll until you find the query that you want. Double-click the query name to load the query in the query editor. For more options, select the vertical ellipses (  ) to the right of the query. From here, you can perform the following actions:
) to the right of the query. From here, you can perform the following actions:
Run query – Loads the query in the query editor and runs it automatically.
Open in query editor – Loads the query in the query editor.
View details – Opens the query details side pane where you can inspect the query, run the query, or open the query in the editor.
For editable queries, more options are available:
- Edit details – Opens the query details side pane with the option to edit the details like description (if applicable) and the query itself; only the folder names (location) of Microsoft Sentinel queries can't be edited.
- Delete – Deletes the query.
- Rename – Allows you to modify the query name.
Create custom analytics and detection rules
To help discover threats and anomalous behaviors in your environment, you can create customized detection rules.
For analytics rules that apply to data ingested through the connected Microsoft Sentinel workspace, select Manage rules > Create analytics rule.
The Analytics rule wizard appears. Fill up the required details as described in Analytics rule wizard—General tab.
You can also create custom detection rules that query data from both Microsoft Sentinel and Defender XDR tables. Select Manage rules > Create custom detection. Read Create and manage custom detection rules for more information.
In custom detection rule creation, you can only query data ingested as analytics logs (that is, not as basic logs or auxiliary logs, see log management plans to check the different tiers) otherwise the rule creation won't proceed.
If your Defender XDR data is ingested into Microsoft Sentinel, you have the option to choose between Create custom detection and Create analytics rule.