How Defender for Cloud Apps helps protect your Google Workspace environment
As a cloud file storage and collaboration tool, Google Workspace enables your users to share their documents across your organization and partners in a streamlined and efficient way. Using Google Workspace may expose your sensitive data not only internally, but also to external collaborators, or even worse make it publicly available via a shared link. Such incidents can be caused by malicious actors, or by unaware employees. Google Workspace also provides a large third-party app eco-system to help boost productivity. Using these apps can expose your organization to the risk of malicious apps or use of apps with excessive permissions.
Connecting Google Workspace to Defender for Cloud Apps gives you improved insights into your users' activities, provides threat detection using machine learning based anomaly detections, information protection detections (such as detecting external information sharing), enables automated remediation controls, and detects threats from enabled third-party apps in your organization.
Main threats
- Compromised accounts and insider threats
- Data leakage
- Insufficient security awareness
- Malicious third-party apps and Google add-ons
- Malware
- Ransomware
- Unmanaged bring your own device (BYOD)
How Defender for Cloud Apps helps to protect your environment
- Detect cloud threats, compromised accounts, and malicious insiders
- Discover, classify, label, and protect regulated and sensitive data stored in the cloud
- Discover and manage OAuth apps that have access to your environment
- Enforce DLP and compliance policies for data stored in the cloud
- Limit exposure of shared data and enforce collaboration policies
- Use the audit trail of activities for forensic investigations
SaaS security posture management
Connect Google Workspace to automatically get security recommendations in Microsoft Secure Score. In Secure Score, select Recommended actions and filter by Product = Google Workspace.
Google Workspace supports security recommendations to Enable MFA enforcement.
For more information, see:
Control Google Workspace with built-in policies and policy templates
You can use the following built-in policy templates to detect and notify you about potential threats:
| Type | Name |
|---|---|
| Built-in anomaly detection policy | Activity from anonymous IP addresses Activity from infrequent country Activity from suspicious IP addresses Impossible travel Activity performed by terminated user (requires Microsoft Entra ID as IdP) Malware detection Multiple failed login attempts Unusual administrative activities |
| Activity policy template | Logon from a risky IP address |
| File policy template | Detect a file shared with an unauthorized domain Detect a file shared with personal email addresses Detect files with PII/PCI/PHI |
For more information about creating policies, see Create a policy.
Automate governance controls
In addition to monitoring for potential threats, you can apply and automate the following Google Workspace governance actions to remediate detected threats:
| Type | Action |
|---|---|
| Data governance | - Apply Microsoft Purview Information Protection sensitivity label - Grant read permission to domain - Make a file/folder in Google Drive private - Reduce public access to file/folder - Remove a collaborator from a file - Remove Microsoft Purview Information Protection sensitivity label - Remove external collaborators on file/folder - Remove file editor's ability to share - Remove public access to file/folder - Require user to reset password to Google - Send DLP violation digest to file owners - Send DLP violation to last file editor - Transfer file ownership - Trash file |
| User governance | - Suspend user - Notify user on alert (via Microsoft Entra ID) - Require user to sign in again (via Microsoft Entra ID) - Suspend user (via Microsoft Entra ID) |
| OAuth app governance | - Revoke OAuth app permission |
For more information about remediating threats from apps, see Governing connected apps.
Protect Google Workspace in real time
Review our best practices for securing and collaborating with external users and blocking and protecting the download of sensitive data to unmanaged or risky devices.
Connect Google Workspace to Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps
This section provides instructions for connecting Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps to your existing Google Workspace account using the connector APIs. This connection gives you visibility into and control over Google Workspace use. For information about how Defender for Cloud Apps protects Google Workspace, see Protect Google Workspace.
Note
File download activities for Google Workspace aren't displayed in Defender for Cloud Apps.
Configure Google Workspace
As a Google Workspace Super Admin, sign in to https://console.cloud.google.com.
Select the project dropdown in the top ribbon and then select New Project to start a new project.
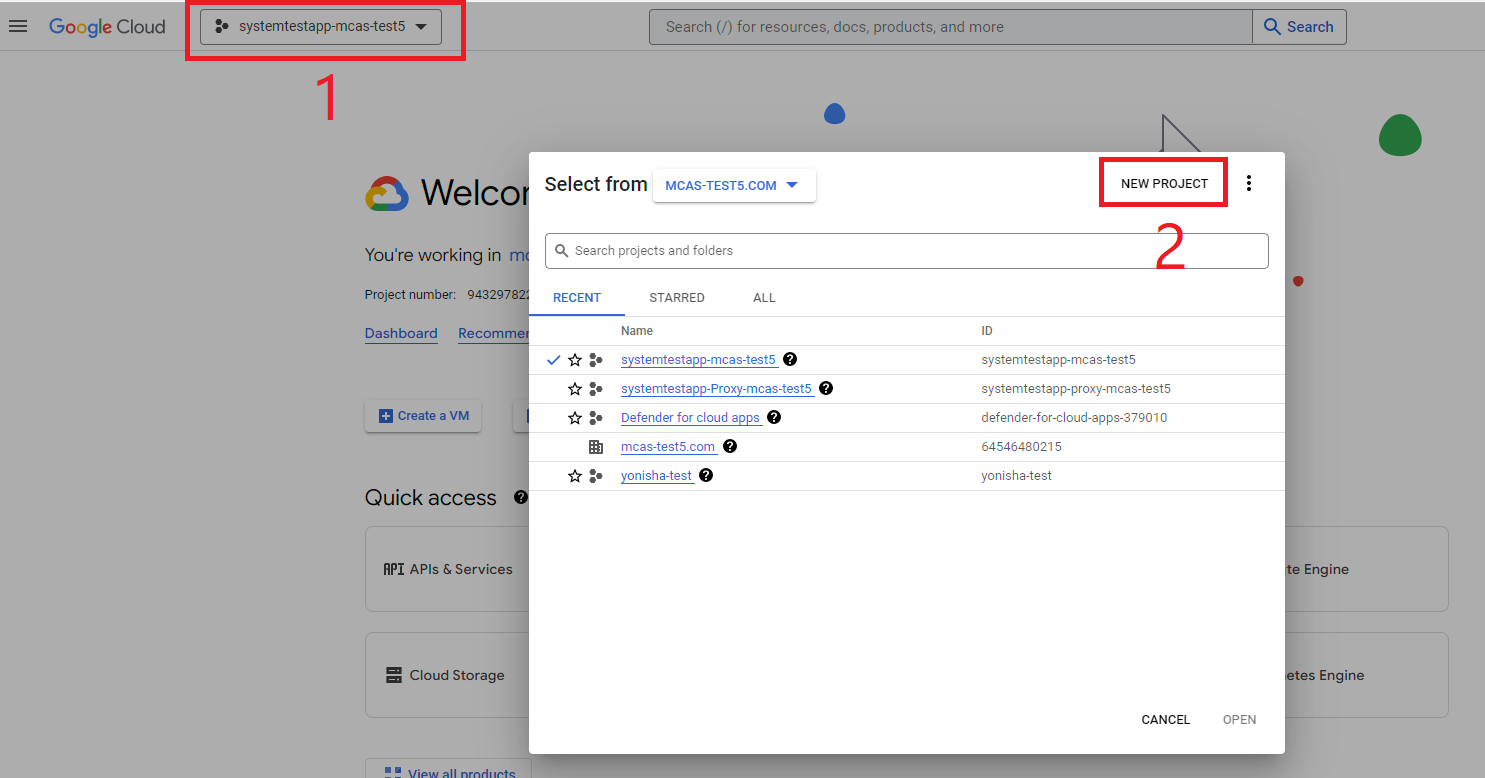
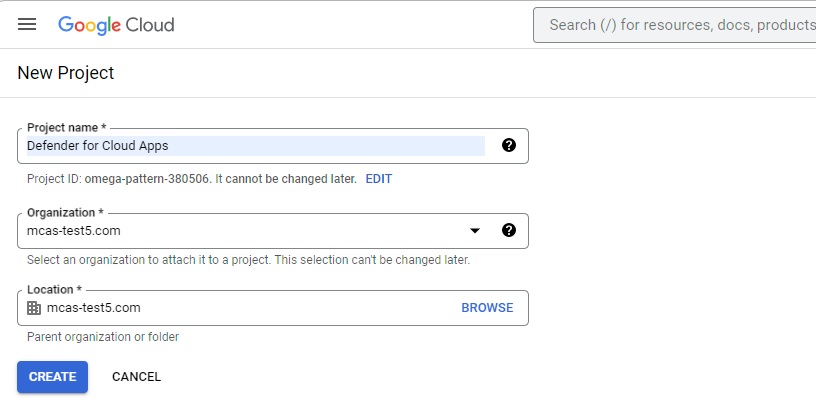
In the New project page, name your project as follows: Defender for Cloud Apps and select Create.
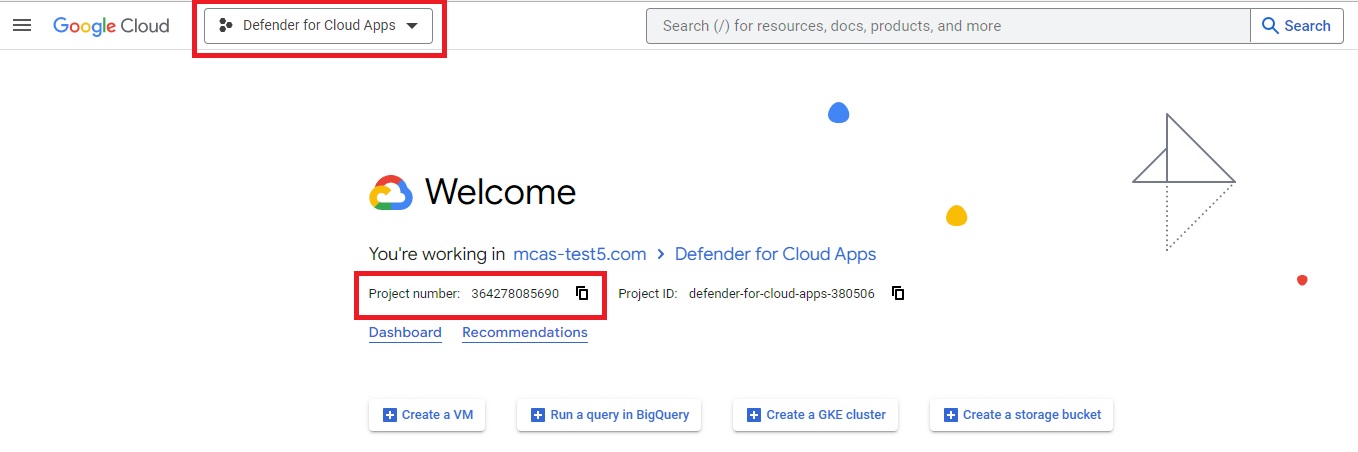
After the project is created, select the created project from the top ribbon. Copy the Project number, you'll need it later.
In the navigation menu, go to APIs & Services > Library. Enable the following APIs (use the search bar if the API isn't listed):
- Admin SDK API
- Google Drive API
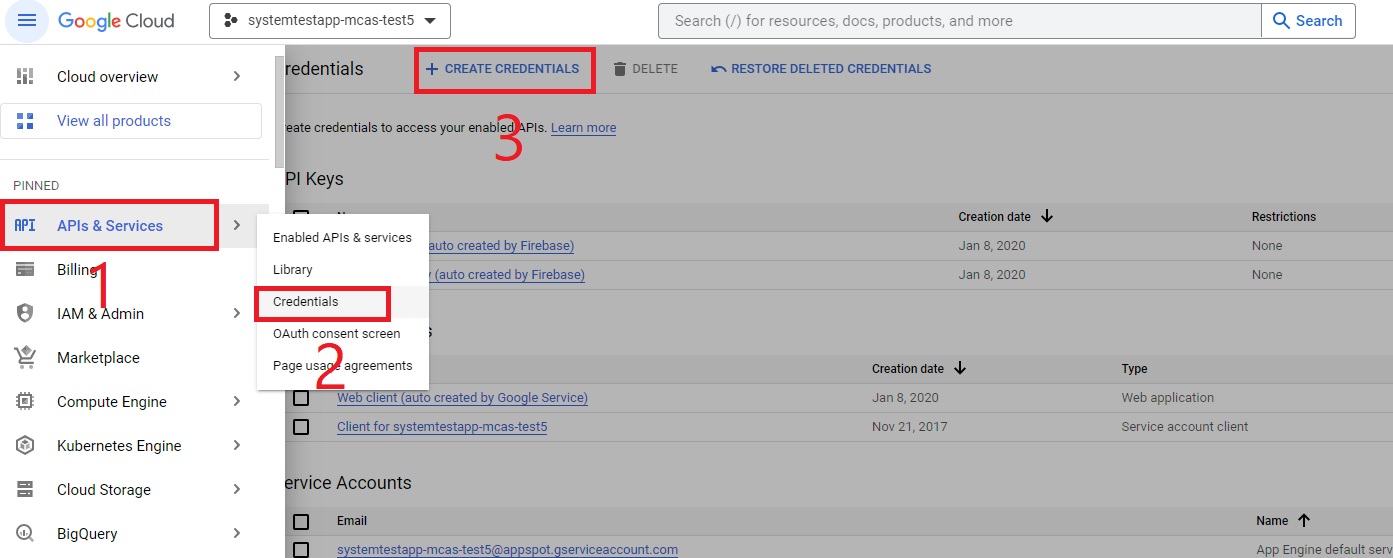
In the navigation menu, go to APIs & Services > Credentials and do the following steps:
Select CREATE CREDENTIALS.
Select Service Account.
Service account details: Provide the name as Defender for Cloud Apps and description as API connector from Defender for Cloud Apps to a Google workspace account.
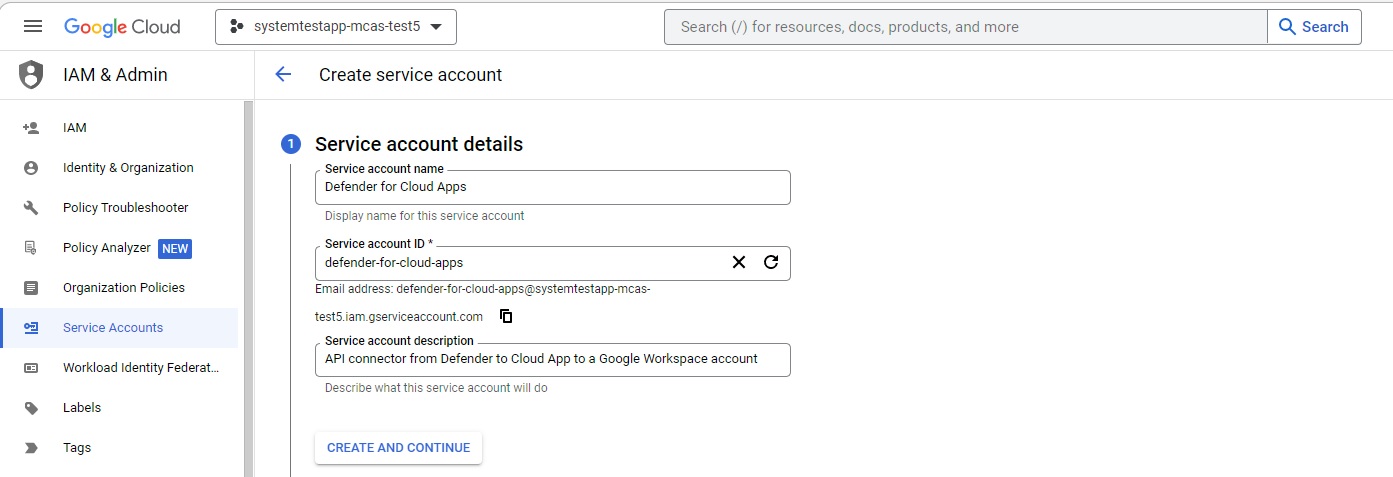
Select CREATE AND CONTINUE.
Under Grant this service account access to project, for Role select Project > Editor, and then select Done.
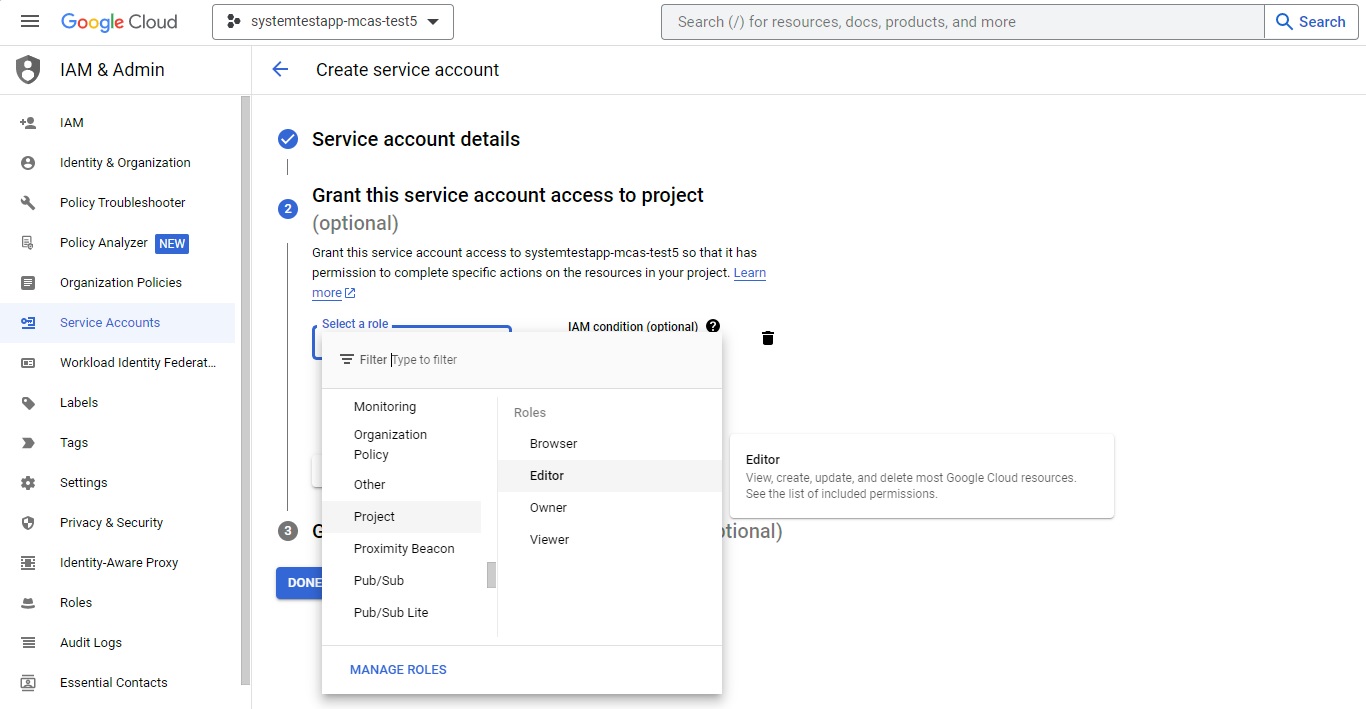
In the navigation menu, return to APIs & Services > Credentials.
Under Service Accounts, locate and edit the service account you created earlier by selecting the pencil icon.
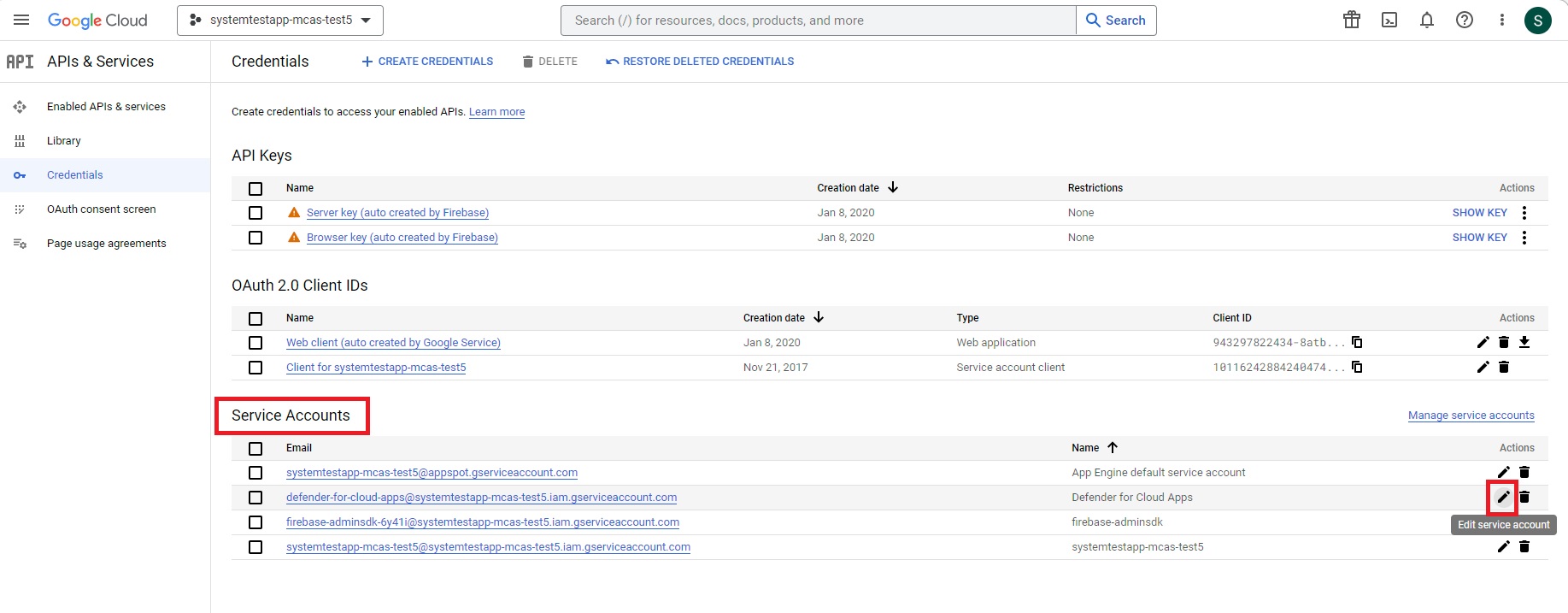
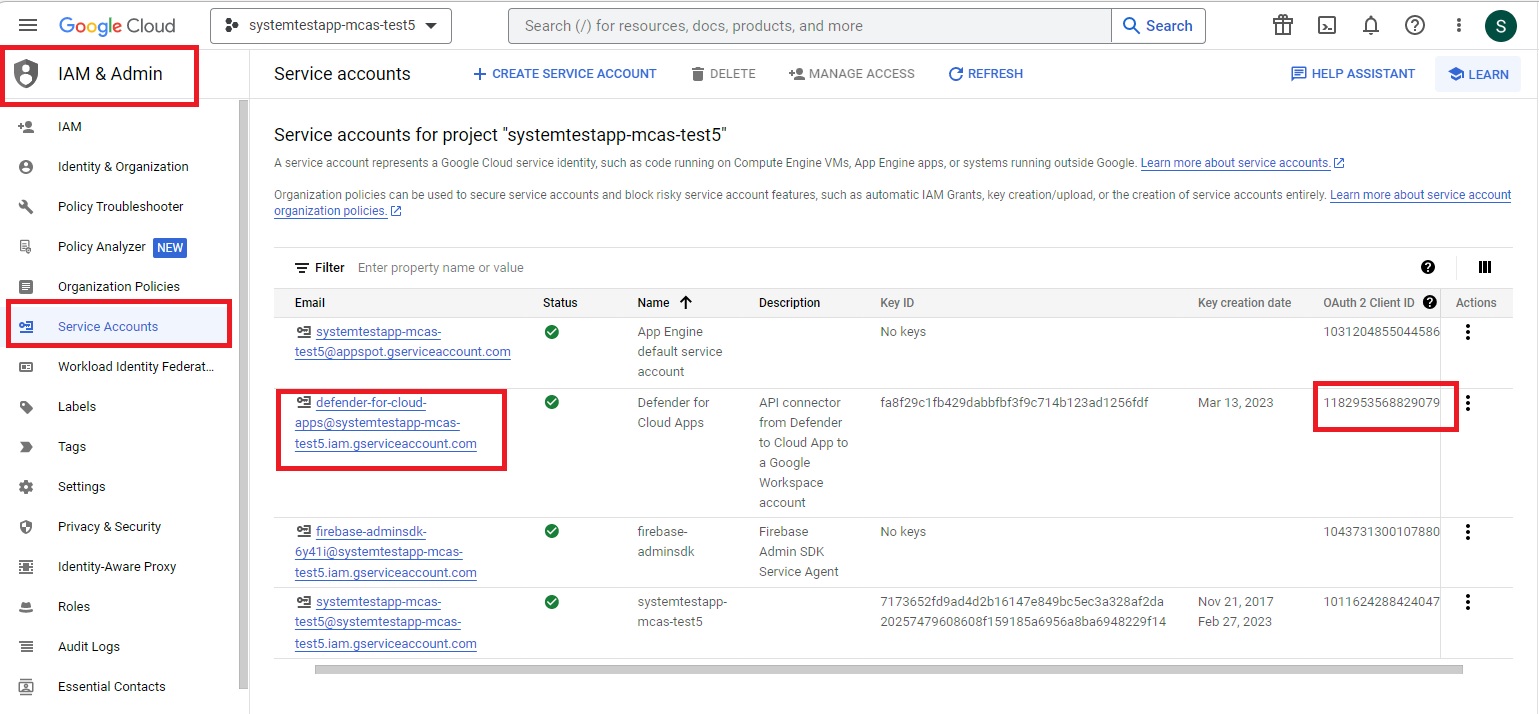
Copy the email address. You'll need it later.
Navigate to KEYS from the top ribbon.
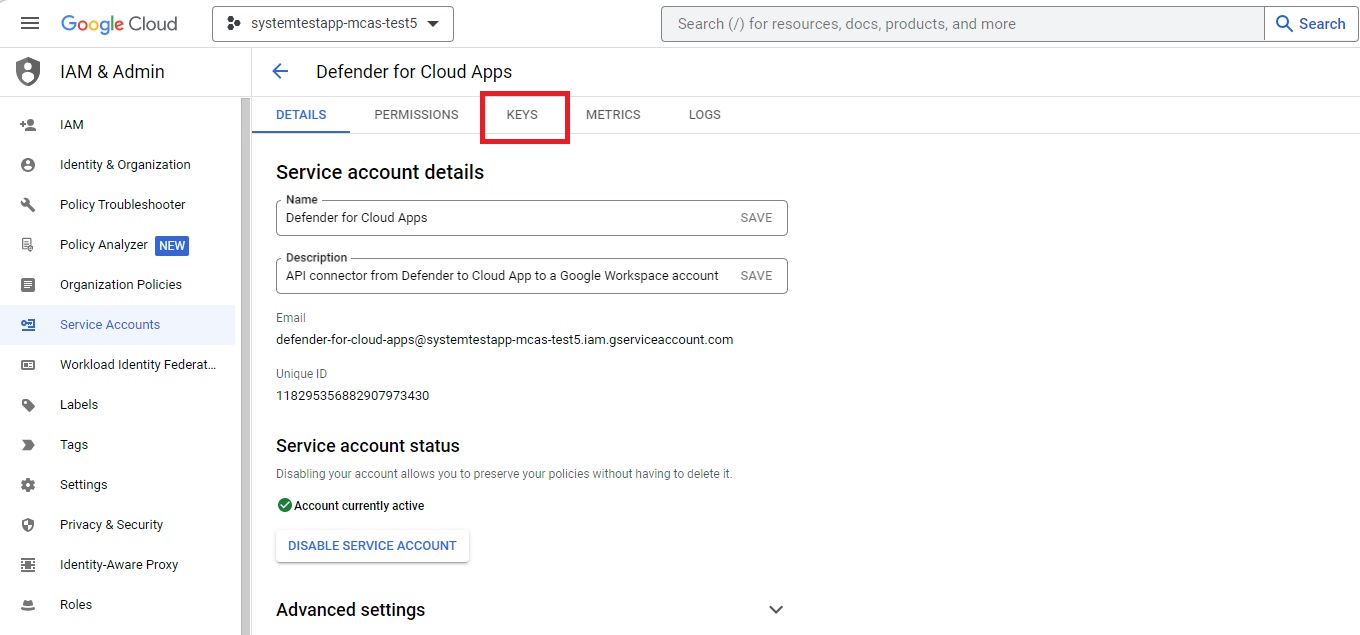
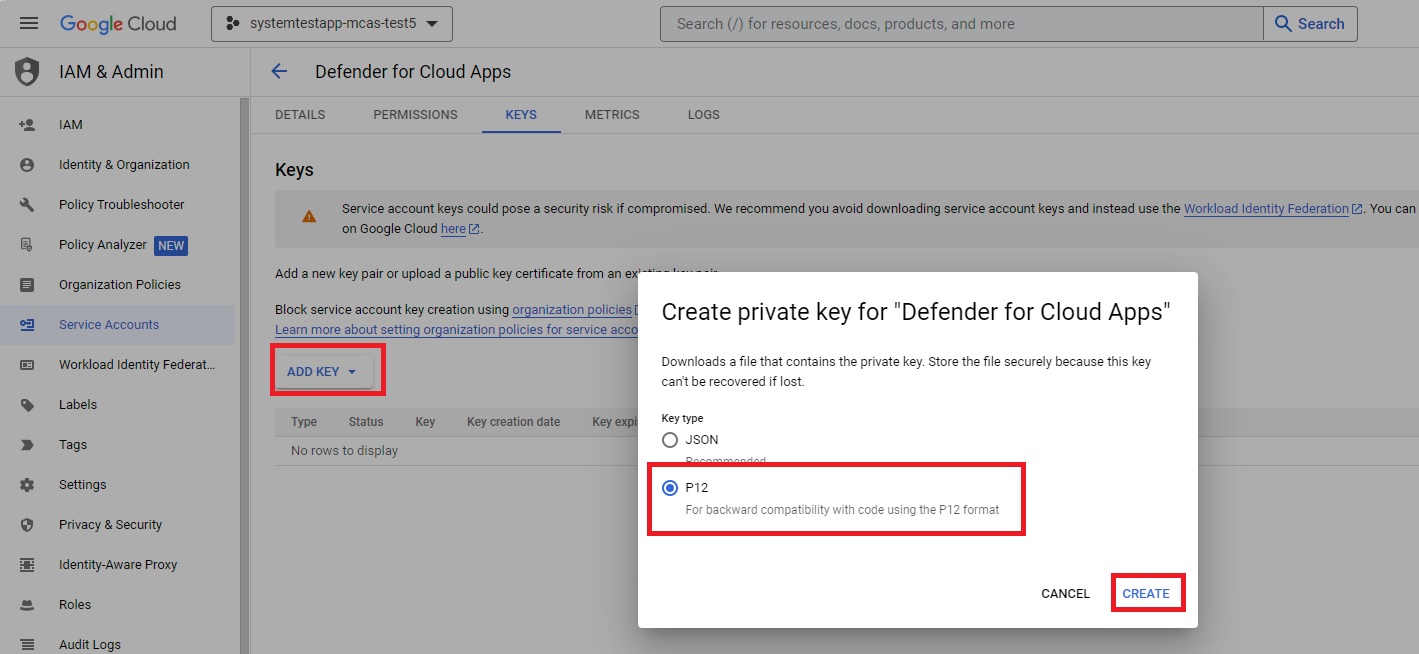
From the ADD KEY menu, select Create new key.
Select P12, and then select CREATE. Save the downloaded file and the password required to use the file.
In the navigation menu, go to IAM & Admin > Service accounts. Copy the Client ID assigned to the service account you have just created - you'll need it later.
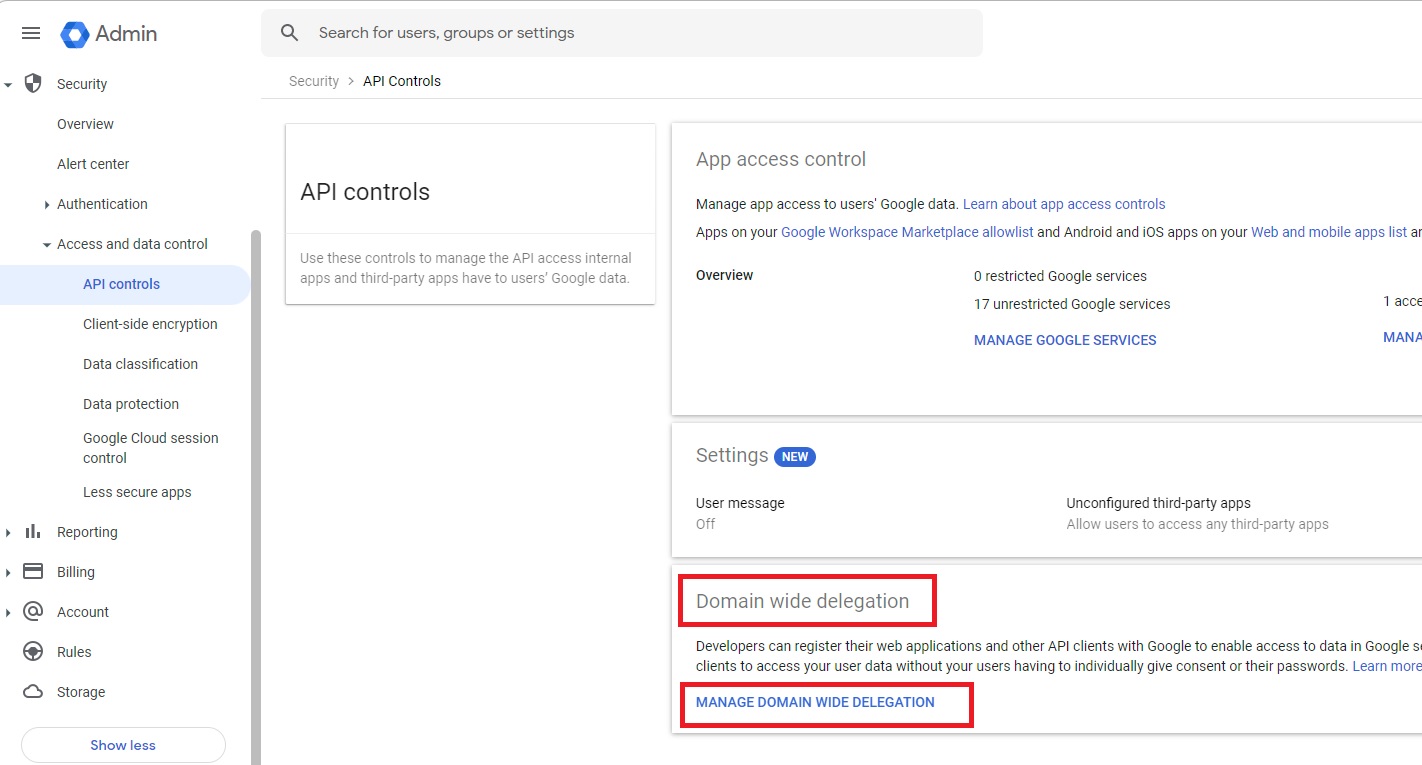
Go to admin.google.com and in the navigation menu, go to Security > Access and data control > API Controls. Then do the following:
Under Domain wide delegation, select MANAGE DOMAIN WIDE DELEGATION.
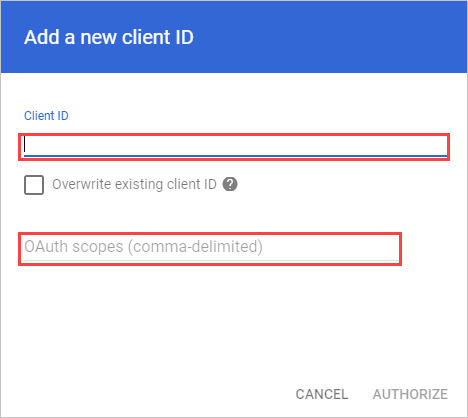
Select Add new.
In the Client ID box, enter the Client ID that you copied earlier.
In the OAuth Scopes box, enter the following list of required scopes (copy the text and paste it in the box):
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/admin.reports.audit.readonly,https://www.googleapis.com/auth/admin.reports.usage.readonly,https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive,https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive.appdata,https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive.apps.readonly,https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive.file,https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive.metadata.readonly,https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive.readonly,https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive.scripts,https://www.googleapis.com/auth/admin.directory.user.readonly,https://www.googleapis.com/auth/admin.directory.user.security,https://www.googleapis.com/auth/admin.directory.user.alias,https://www.googleapis.com/auth/admin.directory.orgunit,https://www.googleapis.com/auth/admin.directory.notifications,https://www.googleapis.com/auth/admin.directory.group.member,https://www.googleapis.com/auth/admin.directory.group,https://www.googleapis.com/auth/admin.directory.device.mobile.action,https://www.googleapis.com/auth/admin.directory.device.mobile,https://www.googleapis.com/auth/admin.directory.user
Select AUTHORIZE.
Configure Defender for Cloud Apps
In the Microsoft Defender Portal, select Settings. Then choose Cloud Apps. Under Connected apps, select App Connectors.
To provide the Google Workspace connection details, under App connectors, do one of the following:
For a Google Workspace organization that already has a connected GCP instance
- In the list of connectors, at the end of row in which the GCP instance appears, select the three dots and then select Connect Google Workspace instance.
For a Google Workspace organization that does not already have a connected GCP instance
- In the Connected apps page, select +Connect an app, and then select Google Workspace.
In the Instance name window, give your connector a name. Then select Next.
In the Add Google key, fill in the following information:
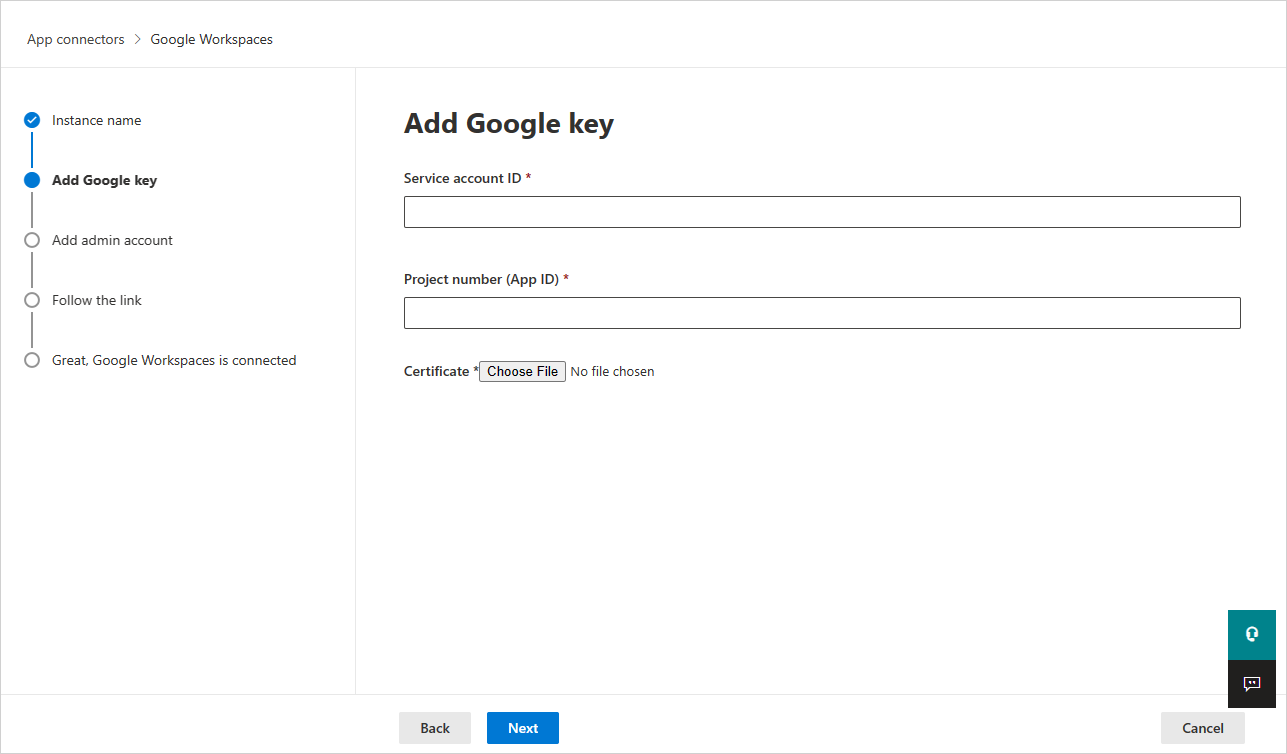
Enter the Service account ID, the Email that you copied earlier.
Enter the Project number (App ID) that you copied earlier.
Upload the P12 Certificate file that you saved earlier.
Enter the email address of your Google Workspace Super Admin.
Deploying with an account that is not a Google Workspace Super Admin will lead to failure in the API test and does not allow Defender for Cloud Apps to correctly function. We request specific scopes so even as Super Admin, Defender for Cloud Apps is still limited.
If you have a Google Workspace Business or Enterprise account, select the check box. For information about which features are available in Defender for Cloud Apps for Google Workspace Business or Enterprise, see Enable instant visibility, protection, and governance actions for your apps.
Select Connect Google Workspaces.
In the Microsoft Defender Portal, select Settings. Then choose Cloud Apps. Under Connected apps, select App Connectors. Make sure the status of the connected App Connector is Connected.
After connecting Google Workspace, you'll receive events for seven days prior to connection.
After connecting Google Workspace, Defender for Cloud Apps performs a full scan. Depending on how many files and users you have, completing the full scan can take a while. To enable near real-time scanning, files on which activity is detected are moved to the beginning of the scan queue. For example, a file that is edited, updated, or shared is scanned right away. This doesn't apply to files that aren't inherently modified. For example, files that are viewed, previewed, printed, or exported are scanned during the regular scan.
SaaS Security Posture Management (SSPM) data (Preview) is shown in the Microsoft Defender Portal on the Secure Score page. For more information, see Security posture management for SaaS apps.
If you have any problems connecting the app, see Troubleshooting App Connectors.
Next steps
If you run into any problems, we're here to help. To get assistance or support for your product issue, please open a support ticket.