Essential Eight patch operating systems
This table outlines the ISM controls related to patch operating systems.
| ISM control Dec 2024 | Maturity Level | Control | Measure |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISM-1694 | 1, 2, 3 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in operating systems of internet-facing servers and internet-facing network devices are applied within two weeks of release when vulnerabilities are assessed as noncritical by vendors and no working exploits exist. | Using Windows Update for Business, and defined update rings, the patches are installed with 2 weeks of release. |
| ISM-1695 | 1, 2 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in operating systems of workstations, non-internet-facing servers and non-internet-facing network devices are applied within one month of release. | IT administrators deploy updates with a deadline configuration of the desired date in Microsoft Configuration Manager |
| ISM-1696 | 3 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in operating systems of workstations, non-internet-facing servers and non-internet-facing network devices are applied within 48 hours of release when vulnerabilities are assessed as critical by vendors or when working exploits exist. | IT administrators deploy updates with a deadline configuration of As soon as Possible in Microsoft Configuration Manager |
| ISM-1701 | 1, 2, 3 | A vulnerability scanner is used at least daily to identify missing patches or updates for vulnerabilities in operating systems of internet-facing servers and internet-facing network devices. | Devices onboarded to Defender for Endpoint. Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management will continuously monitor and detect risk across an organization’s devices. |
| ISM-1702 | 1, 2, 3 | A vulnerability scanner is used at least fortnightly to identify missing patches or updates for vulnerabilities in operating systems of workstations, non-internet-facing servers and non-internet-facing network devices. | IT admin configures the Software Update feature of Configuration Manager to run a scan for missing patches on system at least once every 14 days. |
| ISM-1877 | 1, 2, 3 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in operating systems of internet-facing servers and internet-facing network devices are applied within 48 hours of release when vulnerabilities are assessed as critical by vendors or when working exploits exist. | Using Windows Update for Business expedited patch deployment method, the patches are installed within 48 hours. |
| ISM-1501 | 1, 2, 3 | Operating systems that are no longer supported by vendors are replaced. | Using the defined Rings, WUfB will automatically update devices to the latest feature update. |
| ISM-1879 | 3 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in drivers are applied within 48 hours of release when vulnerabilities are assessed as critical by vendors or when working exploits exist. | Using the defined Rings, WUfB will automatically update devices to the latest feature update. |
| ISM-1900 | 3 | A vulnerability scanner is used at least fortnightly to identify missing patches or updates for vulnerabilities in firmware. | Devices will be onboarded to Defender for Endpoint. Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management will continuously monitor and detect risk across an organization’s devices. |
| ISM-1902 | 3 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in operating systems of workstations, non-internet-facing servers and non-internet-facing network devices are applied within one month of release when vulnerabilities are assessed as noncritical by vendors and no working exploits exist. | IT admin configures the Software Update feature of Configuration Manager to run a scan for missing patches on system at least once every 14 days. |
| ISM-1903 | 3 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in firmware are applied within 48 hours of release when vulnerabilities are assessed as critical by vendors or when working exploits exist. | Intune’s Drivers and Firmware deployment method deploys the latest secure Drivers and Firmware version. |
| ISM-1904 | 3 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in firmware are applied within one month of release when vulnerabilities are assessed as noncritical by vendors and no working exploits exist. | Intune’s Drivers and Firmware deployment method will be used to deploy the latest secure Drivers and Firmware version. |
| ISM-1697 | 3 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in drivers are applied within one month of release when vulnerabilities are assessed as noncritical by vendors and no working exploits exist. | Intune Driver and Firmware deployment method will be used patch the vulnerabilities in drivers and firmware |
| ISM-1703 | 3 | A vulnerability scanner is used at least fortnightly to identify missing patches or updates for vulnerabilities in drivers. | Devices will be onboarded to Defender for Endpoint. Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management will continuously monitor and detect risk across an organization’s devices. |
| ISM-17041 | 1, 2, 3 | Office productivity suites, web browsers and their extensions, email clients, PDF software, Adobe Flash Player, and security products that are no longer supported by vendors are removed. | Intune Application deployment method is used to remove unsupported applications and extensions2. |
| ISM-18071 | 1, 2, 3 | An automated method of asset discovery is used at least fortnightly to support the detection of assets for subsequent vulnerability scanning activities. | Use a scanner to perform asset discovery and maintain asset inventory2. |
| ISM-18081 | 1, 2, 3 | A vulnerability scanner with an up-to-date vulnerability database is used for vulnerability scanning activities. | DVM's vulnerability database is continuously updated as Microsoft and others discover vulnerabilities in software installed on your network2. |
Note
1 These controls cover both Patch Application and Patch OS within Essential 8.
2 For details on how to implement these controls, see Patch Applications Section.
Windows Update for Business
Windows Update for Business (WUfB) enables IT administrators to keep their organization’s Windows devices up to date with the latest security and quality updates and Windows features by directly connecting these endpoints to Windows Update. IT administrators can use the integration between Microsoft Intune and WUfB to configure update settings on devices and configure the deferral of update installation.
Windows Update for Business provides management policies for several types of updates:
- Feature updates: These updates contain not only security and quality revisions but also significant feature additions and changes. Beginning with Windows 10 21H2, feature updates are released annually in the second half of the calendar year. Release information for feature updates is documented here: Windows 10 - release information | Microsoft Docs
- Quality updates: Traditional operating system updates, typically released on the second Tuesday of each month (though these updates can be released at any time). These include security, critical, and driver updates. Quality updates are cumulative.
- Windows Drivers: Device drivers that are applicable to managed devices.
- Microsoft product updates: Updates for other Microsoft products, such as MSI version of Microsoft 365 apps and .NET (Dot Net) Framework. These updates can be enabled or disabled by using Windows Update for Business policy.
Windows Update for Business Rings
WUfB has the concept of Rings. Rings are a collection of WUfB settings and policies targeted to a specific group of devices. Organizations can use as many rings as required, although most organizations have settled on fewer rings than they may have previously used with other patching tools such as Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager. A recommended number of Rings to start with is between 3 to 5 Rings.
Important Windows Update for Business settings and terminology
WUfB introduces some new concepts and terminology that administrators may not be familiar with:
- Detection: Devices periodically check in to the Windows Update service to check if any updates are being offered. This check-in and determination that an update is available for the device is referred to as detection.
- Deferral: Windows Update for Business provides the ability to defer an update from being offered to a device for a specified number of days.
- Deadline: The deadline setting allows administrators to specify the number of days before quality updates are installed on a device. After the specified number of days has elapsed, the updates will be automatically installed. The deadline countdown starts from the time that an update is offered (that is, when an update is detected as specified via the deferral option) to the device.
- Grace period: The grace period setting allows administrators to specify a number of days before a reboot occurs to apply and install updates. After the specified number of days has elapsed, a reboot will occur automatically. The reboot countdown starts from the time an update was successfully installed.
Windows Update for Business settings timeline example
| Deadline Value | Grace Period Value | Forced Update Installation Time | Forced Reboot |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | Immediately after detection | Immediately after installation |
| 2 | 2 | 2 days after detection | 2 days after update installation |
Windows Update for Business Ring configuration
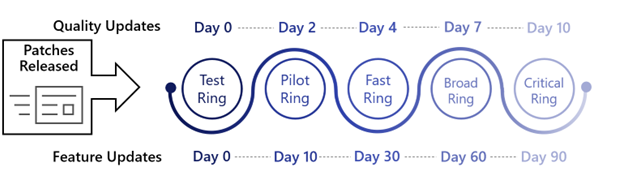
The following is a sample WUfB Ring configuration, with 5 total Rings. For each Ring, the recommended deferral, deadline, and grace period are listed. The complete configuration for each Ring have been provided for ease of reference.
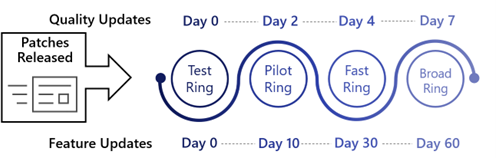
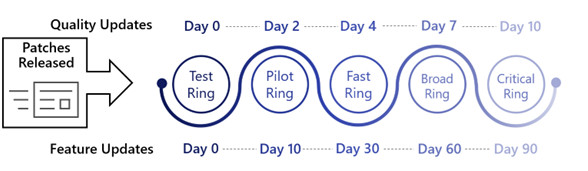
- Ring 0 – Test Devices: Dedicated test devices (critical apps & initial smokescreen)
- Ring 1 – Pilot Devices: IT admins, early adopters (comprised with 1% of total devices)
- Ring 2 – Fast Devices: Random assortment of devices (comprised of 9% of total devices)
- Ring 3 – Broad Devices: Broad deployment (comprised of 90% of total devices)
- Ring 4 – Critical Devices: Executive staff, business critical devices, etc.
Ring 0: Test devices
- Install updates 0 days after release.
Organizations should configure a ‘Ring 0’, comprised of dedicated testing devices.
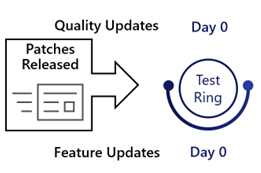
These devices receive updates without any delay. Administrators can use these devices with the latest updates to perform an initial validation of critical applications and functionality still works as expected.
| Quality Update Deferral | Feature Update Deferral | Deadline Value | Grace Period Value | Forced Quality Update Installation Time | Forced Reboot |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Immediately after release and detection | Immediately after forced update installation |
See Windows Update for Business Ring Configuration for the complete configuration for this Ring.
Ring 1: Pilot
- Install updates 2 days after release (1% of devices)
IT staff and selected early adopters comprise Ring 1, typically around 1% of total managed devices.
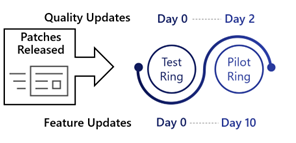
Apart from the initial testing with Ring 0, this Ring provides the first line of testing by users performing their day-to-day work to uncover any issues before an expanded number of devices receive the updates.
| Quality Update Deferral | Feature Update Deferral | Deadline Value | Grace Period Value | Forced Quality Update Installation Time | Forced Reboot |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 10 | 2 | 2 | 4 days after quality update release and detection | 2 days after forced update installation |
See Windows Update for Business Ring Configuration for the complete configuration for this Ring.
Note
Exclude Privileged Access Workstations that would be used to troubleshoot and resolve issues should they occur from this Ring. The Broad Ring would be an appropriate Ring for these devices.
Ring 2: Fast
- Install updates 4 days after release (9% of devices)
A random assortment, comprised of 9% of the organizations endpoints should be added to Ring 2.
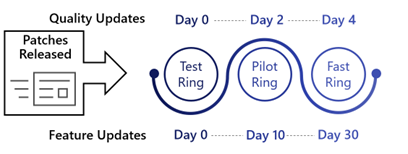
These devices are configured to receive updates 4 days after release, allowing for more testing by an increased number of users before broad deployment to the rest of the organization.
| Quality Update Deferral | Feature Update Deferral | Deadline Value | Grace Period Value | Forced Quality Update Installation Time | Forced Reboot |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 30 | 2 | 2 | 6 days after quality update release and detection | 2 days after forced update installation |
See Windows Update for Business Ring Configuration for the complete configuration for this Ring.
Ring 3: Broad
- Install updates 7 days after release (90% of devices)
All remaining devices should be configured to be part of Ring 3.
By this stage, organizations have the confidence that updates can be broadly installed across their devices. Ring 3 configures updates to be deferred by 7 days from release before being automatically installed.
| Quality Update Deferral | Feature Update Deferral | Deadline Value | Grace Period Value | Forced Quality Update Installation Time | Forced Reboot |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | 60 | 2 | 2 | 9 days after quality update release and detection | 2 days after forced update installation |
See Windows Update for Business Ring Configuration for the complete configuration for this Ring.
Ring 4: Critical systems
- Install updates 14 days after release
Some organizations have a small number of critical devices, for example devices that are used by executive staff.
For these types of devices, organizations may want to further defer the installation of both quality and feature updates to minimize any potential disruption. These devices would be part of Ring 4, specifically for these critical devices.
| Quality Update Deferral | Feature Update Deferral | Grace Period Value | Deadline Value | Update Installation Time | Forced Reboot |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 90 | 2 | 2 | 12 days after quality update release and detection | 2 days after forced update installation |
See Windows Update for Business Ring Configuration in the appendix for the complete configuration for this Ring.
| ISM control Dec 2024 | Maturity Level | Control | Measure |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1694 | 1, 2, 3 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in operating systems of internet-facing servers and internet-facing network devices are applied within two weeks of release when vulnerabilities are assessed as noncritical by vendors and no working exploits exist. | Using Windows Update for Business, and defined update rings, the patches are installed with 2 weeks of release. |
| 1501 | 1, 2, 3 | Operating systems that are no longer supported by vendors are replaced. | Using the defined Rings, WUfB will automatically update devices to the latest feature update. |
Expediting quality updates
Intune provides the capability to expedite quality updates, speeding up the installation of quality updates, such as the most recent patch Tuesday release or an out-of-band security update for a zero-day flaw. To speed up installation, expedite updates uses available services, like Windows Push Notification Service (WNS) and push notification channels, to deliver the message to devices that there's an expedited update to install. This process enables devices to start the download and installation of an expedited update as soon as possible, without having to wait for the device to check in for updates.
Implementation details – expediting quality updates
To expedite quality updates:
- Create a Quality updates for Windows 10 and later profile, under Devices > Windows > Quality updates for Windows 10 and later (Preview)
- Provide a name. It's suggested that the name of the policy aligns to the quality update version being expedited for ease of reference.
- Define the quality updates that Windows Update for Business expedites the installation of if the device Operating System version is less than.
- Define the number of days until a restart of the device is enforced
- Assign the profile to a group containing all applicable Windows devices
Note
If the number of days to wait before a restart is enforced is set to 0, the device will immediately restart upon receiving the update. The user won't receive the option to delay the reboot.
| ISM control Dec 2024 | Maturity Level | Control | Measure |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1877 | 1, 2, 3 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in operating systems of internet-facing servers and internet-facing network devices are applied within 48 hours of release when vulnerabilities are assessed as critical by vendors or when working exploits exist. | Using Windows Update for Business expedited patch deployment method, the patches are installed within 48 hours. |
| 1879 | 3 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in drivers are applied within 48 hours of release when vulnerabilities are assessed as critical by vendors or when working exploits exist. | Using the defined Rings, WUfB automatically updates devices to the latest feature update. |
Note
It's recommended to eventually remove the expediting quality update policy, usually once confirmed that the patch has been successfully deployed to all devices, or it's superseded by the next month’s updates.
Delivery Optimization
Delivery Optimization is a cloud-managed solution that allows clients to download updates from alternate sources (such as other peers on the network) in addition to the traditional internet-based servers. When configured via Intune, Delivery Optimization settings can be configured for Windows devices to reduce internet bandwidth consumption when update binaries are downloaded.
Implementation details – Delivery Optimization policy
- Create a Delivery Optimization policy, under Devices > Windows > Configuration Profile > Create profile > Platform > Windows 10 and later > Profile type templates > Delivery optimization
- Provide a name for the policy
- In the Configuration Settings page, use the values as per the Delivery Optimization Policy Settings in the appendix and create the policy.
- Assign the profile to a group containing all applicable Windows devices.
Intune Drivers and Firmware update management
With Windows Driver Update Management in Microsoft Intune, you gain the ability to oversee, authorize for deployment, and temporarily halt the rollout of driver updates across your managed Windows 10 and Windows 11 devices. Intune, alongside the Windows Update for Business (WUfB) Deployment Service (DS), handles the intricate process of identifying relevant driver updates for devices under a driver updates policy. These updates are categorized by Intune and WUfB-DS, streamlining the process of distinguishing between recommended updates suitable for all devices and optional updates tailored for specific needs. Through Windows driver update policies, you retain full control over the installation of driver updates on your devices.
Here's what you can do:
- Enable Automatic Approvals for Recommended Driver Updates: Policies configured for automatic approval promptly green light and deploy each new recommended driver update version to the devices assigned to the policy. Recommended drivers typically represent the latest update flagged as essential by the driver publisher. Additionally, drivers not designated as the current recommended version are cataloged as other drivers, offering optional updates. Subsequently, when a newer driver update from the OEM is released and identified as the current recommended driver update, Intune automatically adds it to the policy and moves the previously recommended driver to the list of other drivers.
- Configure policy to require manual approval of all updates: This policy ensures that administrators must approve a driver update before it can be deployed. Newer versions of driver updates for devices with this policy are automatically added to the policy but remain inactive until approved.
- Manage which drivers are approved for deployment: You can edit any driver update policy to modify which drivers are approved for deployment. You can pause the deployment of any individual driver update to stop its deployment to new devices, and then later reapprove the paused update to enable Windows Update to resume installing it on applicable devices.
Steps to deploy Drivers and Firmware update via Intune Drivers and Firmware management feature
Step 1: Create a driver update profile and deployment rings
When a driver policy update policy is created, IT administrator can choose between automatic and manual updates.
- Automatic: Automatically approve all recommended drivers and set how long after discovery to start offering them.
- Manual: Manually approve drivers and select the day to start offering the update when you approve them. With this option, no drivers are offered until manually approved.
To create a set of deployment rings, we recommend using the following combination of settings:
- Approval method: Automatically approve all recommended driver updates
- Make updates available after (days)
Step 2: Review available drivers
Once the policy is created, let devices scan for updates for about a day or so. The Drivers to review column includes the count of new recommended driver updates ready to review for manual approval. In an automatic policy, Drivers to review stay at 0 since recommended drivers are automatically approved. This is a great indicator that new drivers have been discovered and are awaiting a decision whether to approve or decline deploying those drivers.
Step 3: Approve drivers
When an IT administrator approves a driver, additionally an approval date in future can be provided. Once drivers are approved, Intune managed windows device will receive them in the next policy sync cycle, which is typically every 8 hours.
| ISM control Dec 2024 | Maturity Level | Control | Measure |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISM-1697 | 3 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in drivers are applied within one month of release when vulnerabilities are assessed as noncritical by vendors and no working exploits exist. | Intune’s Driver and Firmware deployment method will be used to approve and deploy the latest version of the driver that mitigates vulnerabilities |
| ISM-1903 | 3 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in firmware are applied within 48 hours of release when vulnerabilities are assessed as critical by vendors or when working exploits exist. | IT administrator approves the newer version of the firmware in the Intune console when firmware vulnerabilities are assessed as critical by the vendors |
| ISM-1904 | 3 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in firmware are applied within one month of release when vulnerabilities are assessed as noncritical by vendors and no working exploits exist. | Intune’s Drivers and Firmware deployment method deploys the latest secure Drivers and Firmware version. |
Monitoring update installation
Note
Update Compliance has been deprecated from March 2023.
Reporting on compliance using Update Compliance (Log Analytics)
Update Compliance allows for the monitoring of quality and feature updates for Windows 10 or Windows 11 Professional, Education, and Enterprise editions. Update Compliance collates Windows client diagnostic data to report on the status of updates on Windows devices into a Log Analytics workspace. Update Compliance displays information for all devices onboarded onto the service to help determine if they're up to date with the following:
- Security updates: A device is up to date on quality updates whenever it has the latest applicable quality update installed. Quality updates are monthly cumulative updates that are specific to a version of Windows client.
- Feature updates: A device is up to date on feature updates whenever it has the latest applicable feature update installed. Update Compliance considers the Servicing Channel when determining update applicability.
For more information about the prerequisites for provisioning a Log Analytics workspace for Update Compliance, see Get started with Update Compliance - Windows Deployment.
Onboarding devices to Update Compliance
- Once the Update Compliance solution has been created, retrieve your Commercial ID by navigating to the Solutions tab for your Log Analytics workspace, and then select the WaaSUpdateInsights solution. A CommercialID is a globally unique identifier assigned to a specific Log Analytics workspace.
- Configure the policy to match the Update Compliance Policy
- From the console, change the value of CommercialID to your unique CommercialID (collected during step 1)
- Assign the profile to a group containing all applicable Windows devices.
Using Update Compliance reports
Consolidated diagnostics data is presented in various reporting sections readily available in Update Compliance. Data collected is stored for 28 days within Update Compliance.
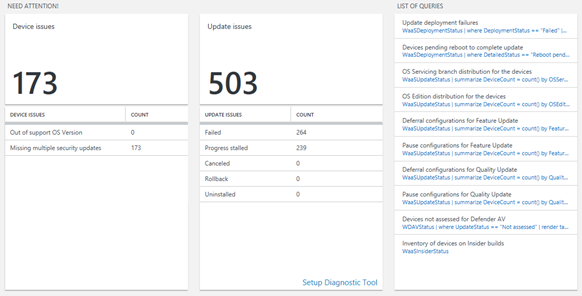
Need attention compliance report section
This section provides a breakdown of all Windows client devices and update issues detected by Update Compliance. The summary tile for this section counts the number of devices that have issues, while the blades within the section breakdown the issues encountered, such as devices with unsupported operating systems versions and missing security updates. Devices surfaced in these reports require remediation by an administrator. There's also a predefined list of queries that provide values but don't fit within any other main section, such as devices that have pending reboots, configurations paused and more.
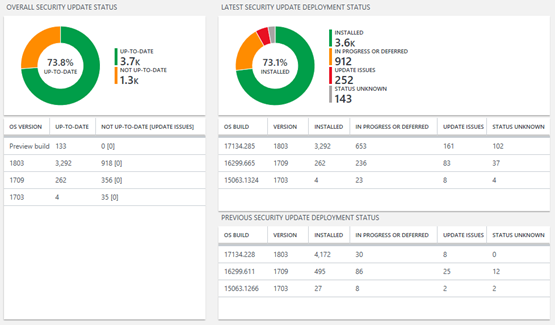
Security update status compliance report section
This section lists the percentage of devices that are on the latest security update released for the version of Windows the device is running. Selecting this section provides blades that summarize the overall status of security updates across all devices and a summary of their deployment progress towards the latest two security updates.
Feature update status compliance report section
This section lists the percentage of devices that are on the latest feature update that is applicable to a given device. Selecting this section provides blades that summarize the overall feature update status across all devices and a summary of deployment status for different versions of Windows client in your environment.
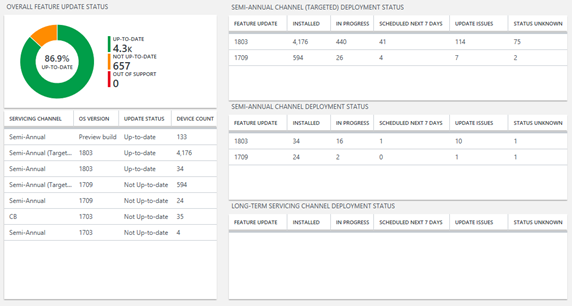
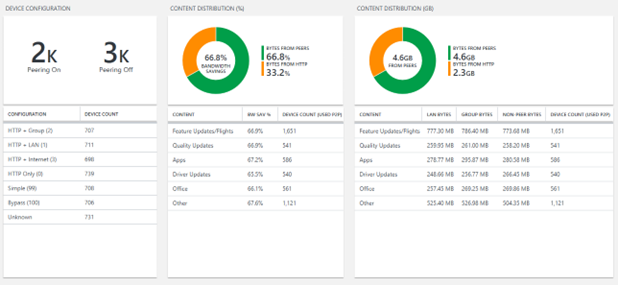
Delivery Optimization status compliance report section
This section summarizes bandwidth savings incurred by utilizing Delivery Optimization in your environment. It provides a breakdown of Delivery Optimization configuration across devices and summarizes bandwidth savings and utilization across multiple content types.
Windows Autopatch
One of the most expensive aspects of the software update management process is to make sure devices (physical and virtual) are always healthy to receive and report software updates for each software update release cycle. Having a way of measuring, quickly detecting and remediating when something goes wrong with on-going change management processes is important; it helps mitigate high Helpdesk ticket volumes, reduces cost, and improves overall update management results.
Windows Autopatch is a cloud service that automates patching for Windows, Microsoft 365 Apps for Enterprise, Microsoft Edge, Microsoft Teams, Surface Driver/Firmware, Published Drivers/ Firmware marked as Mandatory in Windows Update store, Windows 365 and Azure Virtual Desktop (AVD) for your organization. Windows Autopatch provides an extra layer for your organization to mitigate issues when deploying Windows Updates. Windows Autopatch deployment rings are segregated at the device level, meaning, during the Windows Autopatch device registration process, we assign devices to one of the deployment rings: Test, First, Fast, or Broad.
Windows Autopatch is included with Windows 10/11 Enterprise E3 or higher. There are additional prerequisites for using Autopatch including some network configurations which should be considered part of the rollout.
Autopatch enrollment steps
Step 1: Readiness assessment
The Readiness assessment tool checks the settings in Microsoft Intune and Microsoft Entra ID to ensure it works with Windows Autopatch as part of enrolling your tenant.
Important
Microsoft recommends that you use roles with the fewest permissions. Minimizing the number of users with the Global Administrator role helps improve security for your organization.
To enable the Readiness assessment:
- As a Global Administrator, go to Intune
- In the left pane, select Tenant administration and then navigate to Windows Autopatch > Tenant enrollment.
The Readiness assessment tool checks Intune settings to confirm deployment rings for Windows 10 or later and minimum administrator requirements and unlicensed administrators. It also checks your Microsoft Entra settings including co-management and licenses.
The Readiness assessment tool provides a report and advises of any issues that must resolved and what steps are needed to be performed to get to a ready state. Once issues have been resolved, you can move to the next step.
Step 2: Verify admin contacts
The purpose of this step is to confirm your organization has admins for each area of focus, such that the Windows Autopatch Service Engineering Team can contact your organization's admin regarding your support request in future and expands on the minimum admin set during the enrollment process.
| Area of focus | Description |
|---|---|
| Devices | Device registration |
| Device health | |
| Updates | Windows quality updates |
| Microsoft 365 Apps for enterprise updates | |
| Microsoft Edge updates | |
| Microsoft Teams updates |
Complete the following steps to add admin contacts:
- Sign into Intune.
- Under Tenant administration in the Windows Autopatch section, select Admin contacts.
- Select Add.
- Enter the contact details including name, email, phone number and preferred language. For a support ticket, the ticket's primary contact's preferred language determines the language used for email communications.
- Select an Area of focus and enter details of the contact's knowledge and authority in the specified area of focus.
- Select Save to add the contact.
- Repeat for each area of focus.
Note
An admin may have multiple focus areas, especially in smaller organizations.
Step 3: Device registration
The Windows Autopatch device registration process is transparent for end-users.
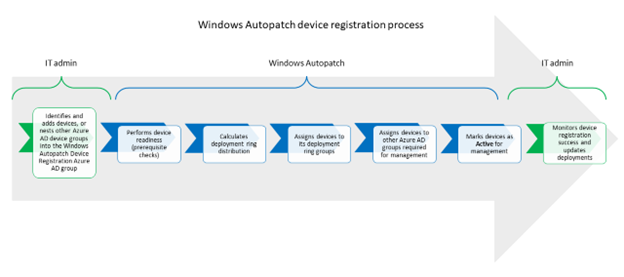
Windows Autopatch must register your existing devices into its service to manage update deployments on your behalf. To perform device registration:
- IT admin reviews Windows Autopatch device registration prerequisites prior to register devices with Windows Autopatch
- IT admin identifies devices to be managed by Windows Autopatch and adds them into the Windows Autopatch Device Registration Microsoft Entra group
- Windows Autopatch then:
- Performs device readiness prior registration (prerequisite checks)
- Calculates the deployment ring distribution
- Assigns devices to a deployment ring, based on the previous calculation
- Assigns devices to other Microsoft Entra groups required for management
- Marks devices as active for management so it can apply its update deployment policies
- IT admin then monitors the device registration trends and the update deployment reports The detailed device registration work flow can be found here.
Windows Autopatch device types
Any device (either physical or virtual) that contains a Microsoft Entra device ID, can be added into the Windows Autopatch Device registration Microsoft Entra group. This can be through either direct membership or by being part of another Microsoft Entra group (either dynamic or assigned) that's nested to this group, so it can be registered with Windows Autopatch. The only exception is Windows 365 Cloud PCs, as these virtual devices must be registered with Windows Autopatch from the Windows 365 provisioning policy.
Autopatch for Windows 365
Windows 365 Enterprise gives IT admins the option to register devices with the Windows Autopatch service as part of the Windows 365 provisioning policy creation. This option provides a seamless experience for admins and users to ensure your Cloud PCs are always up to date. When IT admins decide to manage their Windows 365 Cloud PCs with Windows Autopatch, the Windows 365 provisioning policy creation process calls Windows Autopatch device registration APIs to register devices on behalf of the IT admin. To register a new Windows 365 Cloud PC devices with Windows Autopatch from the Windows 365 Provisioning Policy:
- Go to Intune.
- In the left pane, select Devices.
- Navigate to Provisioning > Windows 365.
- Select Provisioning policies > Create policy.
- Provide a policy name and select Join Type.
- Select Next.
- Choose the desired image and select Next.
- Under the Microsoft managed services section, select Windows Autopatch. Then, select Next.
- Assign your policy accordingly and select Next.
- Select Create.
Now your newly provisioned Windows 365 Enterprise Cloud PCs will automatically be enrolled and managed by Windows Autopatch.
Windows Autopatch on Azure Virtual Desktop
Windows Autopatch is available for Azure Virtual Desktop. Enterprise admins can provision their Azure Virtual Desktop workloads to be managed by Windows Autopatch using the existing device registration process as per physical machines. Windows Autopatch provides the same scope of service with virtual machines as it does with physical devices. However, Windows Autopatch defers any Azure Virtual Desktop specific support to Azure support, unless otherwise specified.
Autopatch dashboard and reporting
Autopatch provides a summary dashboard and various reports of current status and historical (longitudinal) reporting (up to 90 days) of all devices enrolled into Autopatch, which can be exported into a CSV file if needed. To view the current update status for all your enrolled devices:
- Sign into the Intune.
- Navigate to Reports > Windows Autopatch > Windows Quality Updates.
The All Devices Report contains:
| Information | Description |
|---|---|
| Device name | The name of the device. |
| Microsoft Entra device ID | The current Microsoft Entra ID recorded device ID for the device. |
| Serial number | The current Intune recorded serial number for the device. |
| Deployment ring | The currently assigned Windows Autopatch deployment ring for the device. |
| Update status | The current update status for the device |
| Update sub status | The current update sub status for the device |
| OS version | The current version of Windows installed on the device. |
| OS revision | The current revision of Windows installed on the device. |
| Intune last check-in time | The last time the device checked in to Intune. |
| ISM control Dec 2024 | Maturity level | Control | Measure |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1694 | 1, 2, 3 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in operating systems of internet-facing servers and internet-facing network devices are applied within two weeks of release when vulnerabilities are assessed as noncritical by vendors and no working exploits exist. | For devices enrolled with Windows Autopatch, updates are installed within 2 weeks. |
| 1877 | 1, 2, 3 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in operating systems of internet-facing servers and internet-facing network devices are applied within 48 hours of release when vulnerabilities are assessed as critical by vendors or when working exploits exist. | Autopatch groups give the organization the flexibility to bring in deadlines to within 48 hours if necessary. |
| 1879 | 3 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in drivers are applied within 48 hours of release when vulnerabilities are assessed as critical by vendors or when working exploits exist. | Autopatch groups give the organization the flexibility to bring in deadlines to within 48 hours if necessary. |
Using Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management to identify vulnerabilities
Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management (DVM) delivers asset visibility, intelligent assessments, and built-in remediation tools for Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, iOS, and network devices.
As a prerequisite, endpoints need to be onboarded to Microsoft Defender for Endpoint. There are other additional prerequisites for using DVM. Once onboarded, DVM is able to assess if vulnerabilities are applicable to individual devices and provide recommended actions.
Implementation details – onboarding endpoints into Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
- Create a new Windows Configuration Profile with a type of Template > Microsoft Defender for Endpoint (desktop devices running Windows 10 or later).
- Set Expedite telemetry reporting frequency to Enable.
- Assign the profile to a group containing all applicable Windows devices.
Discovery of vulnerabilities Using Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management
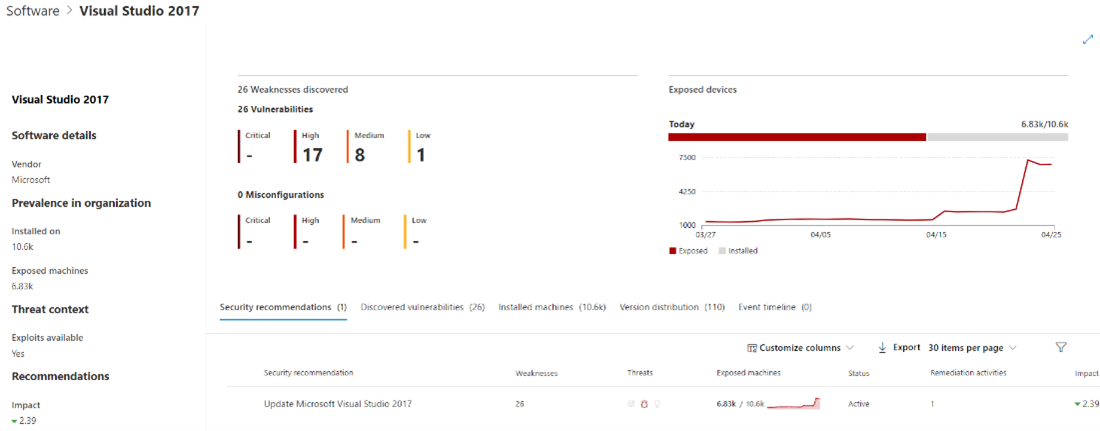
Once devices have been onboarded to Defender for Endpoint, DVM can determine if any devices are potentially exposed to vulnerabilities and provide security recommendations for each identified weakness.
In the Microsoft Security Portal under Vulnerability Management > Inventories, software products identified across endpoints onboarded to Defender for Endpoint are shown, including the vendor name, weaknesses found, threats associated with them and exposed devices.
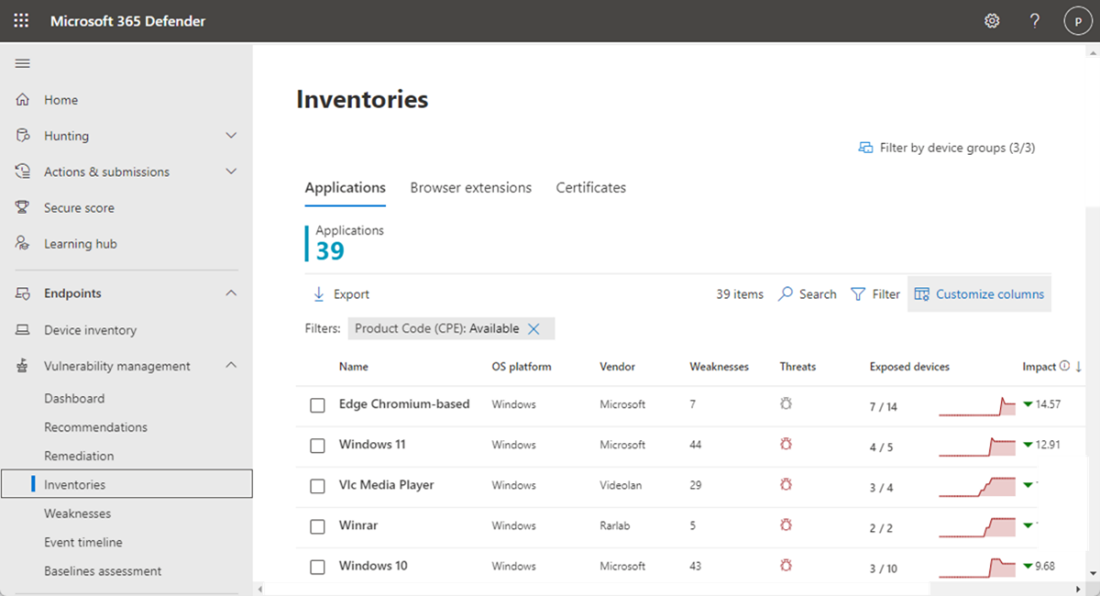
You can also look at software inventories on specific devices by navigating to the Device Inventory page. Select the name of a device to open the device page (like Computer1), then select the Software inventory tab to see a list of all the known software present on the device. Select a specific software entry to open the flyout with more information.
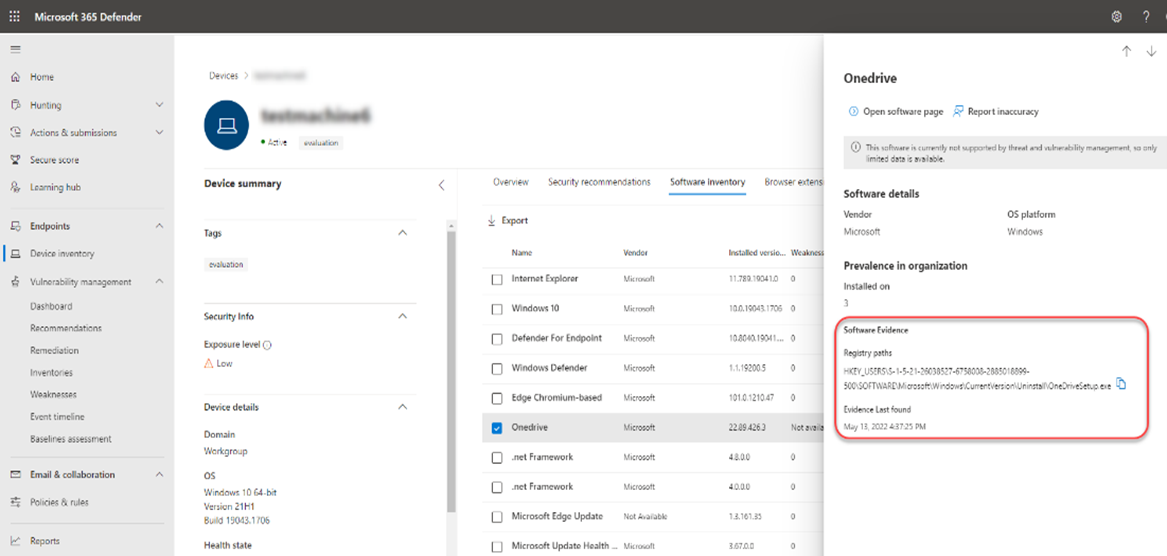
Opening the specific software page provides more details about the application as shown in following screenshot. Details displayed include:
- Corresponding security recommendations for the weaknesses and vulnerabilities identified.
- Named CVEs of discovered vulnerabilities.
- Devices that have the software installed (along with device name, domain, OS, and more).
- Software version list (including number of devices the version is installed on, the number of discovered vulnerabilities, and the names of the installed devices).
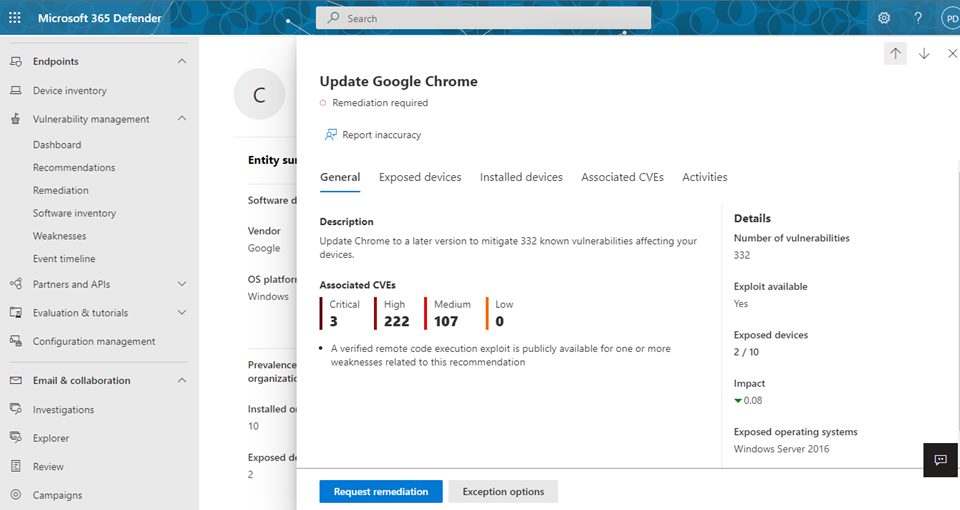
Remediating vulnerabilities Using Microsoft Intune
The DVM capabilities are designed to bridge the gap between Security and IT administrators through the remediation request workflow. The DVM remediation actions can use native integrations to generate remediation tasks in Intune. Additionally, the DVM API can be used to orchestrate remediation processes and actions with third party tools where required. The following steps describe the remediation workflow using DVM and Intune:
To use this capability, enable the Microsoft Intune connection.
- In the Microsoft Defender portal.
- Navigate to Settings > Endpoints > General > Advanced features.
- Scroll down and look for the Microsoft Intune connection.
- By default, the toggle is turned off. Turn the Microsoft Intune connection toggle to On.
Note
Enabling the connection to Microsoft Intune is required to create a corresponding Intune security task when creating a remediation request in DVM. The option to create an Intune security task does not appear if the connection is not enabled.
- Go to the Vulnerability management navigation menu in the Microsoft Defender portal and select Recommendations.
- Select a security recommendation you would like to request remediation for, and then select Remediation options.
- Fill out the form, including what you are requesting remediation for, applicable device groups, priority, due date, and optional notes.
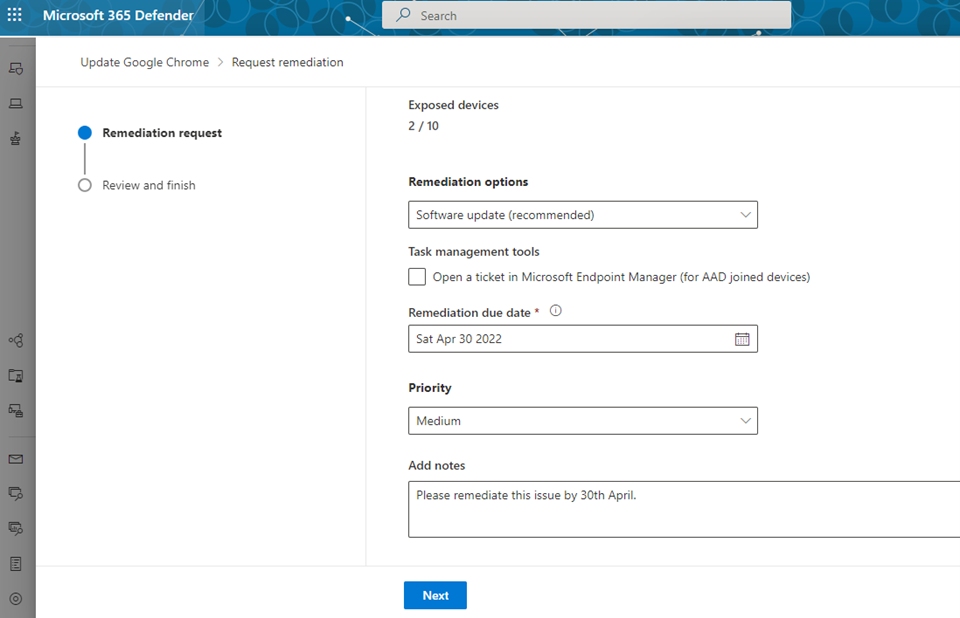
Submitting a remediation request creates a remediation activity item within DVM, which can be used for monitoring any remediation progress. When an administrator submits a remediation request from the Security recommendations page, a security task is created that can be tracked on the Remediation page, and a remediation ticket is created in Microsoft Intune. This won't trigger remediation or apply any changes to devices.
The following image shows a security task created in Intune:
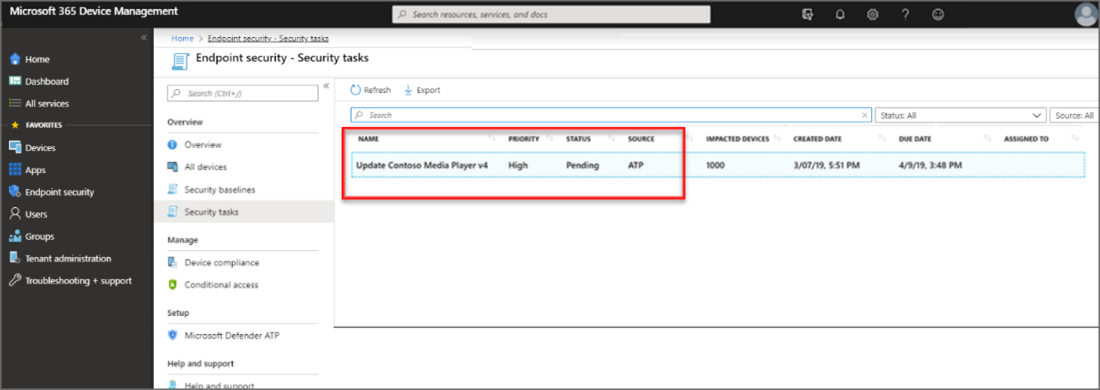
- The Intune administrator selects the security task to view details about the task. The admin then selects Accept, which updates the status in both Intune, and in Defender for Endpoint to Accepted.
The Intune administrator then remediates the task based on the guidance provided. The guidance varies depending on the type of remediation that's needed. When available, remediation guidance includes links that open relevant panes for configurations in Intune.
Additional information on DVM can be found in Patch Applications Section.
| ISM control Dec 2024 | Maturity Level | Control | Measure |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1701 | 1, 2, 3 | A vulnerability scanner is used at least daily to identify missing patches or updates for vulnerabilities in operating systems of internet-facing servers and internet-facing network devices. | Devices will be onboarded to Defender for Endpoint. Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management will continuously monitor and detect risk across an organization’s devices. |
| 1703 | 3 | A vulnerability scanner is used at least fortnightly to identify missing patches or updates for vulnerabilities in drivers. | Devices will be onboarded to Defender for Endpoint. Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management will continuously monitor and detect risk across an organization’s devices. |
| 1900 | 3 | A vulnerability scanner is used at least fortnightly to identify missing patches or updates for vulnerabilities in firmware. | Devices will be onboarded to Defender for Endpoint. Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management will continuously monitor and detect risk across an organization’s devices. |
Compliance based on the device’s operating system version
Compliance policies in Intune provide the capability to determine if a device is compliant or noncompliant based on whether a device can meet one or more configured requirements. This compliance state of the device is assessed when accessing corporate resources that are protected by Conditional Access to either allow or deny access to the resource.
Intune can determine if a device is either compliant or noncompliant based on the current Operating System version of the device. Using the device compliance grant control in Conditional Access, users will only be able to access corporate resources on devices that meet or exceed the minimum Operating System version.
Implementation details: Windows Update Compliance policy
- Create a Windows Compliance Policy, under Devices > Windows > Compliance policies > Create Policy > Platform > Windows 10 and Later.
- Provide a name for the policy.
- Select Device Properties, enter the minimum Operating System version to be considered compliant in minimum OS version.
- Assign the profile to a group containing all applicable Windows devices.
A typical compliance policy that assesses devices based on their operating system value has been provided.
Note
The value supplied for the minimum OS version for both Windows 11 and Windows 10 will need to be incremented over time.
| ISM control Dec 2024 | Maturity Level | Control | Measure |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1407 | 3 | The latest release, or the previous release, of operating systems are used. | Users using devices that don't meet the OS Version defined in the assigned Compliance Policy will be unable to access corporate resource, when used in combination with Conditional Access. |
Patching non-internet-facing systems
Microsoft suggests using cloud services such as Microsoft Intune and Azure Update Manager to maintain system’s OS version and patching the vulnerabilities.
However, for systems and servers that are offline, Microsoft advises using Microsoft Configuration Manager’s Patch management capabilities. See Microsoft Configuration Manager for more details.
| ISM control Dec 2024 | Maturity Level | Control | Measure |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISM-1695 | 1, 2 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in operating systems of workstations, non-internet-facing servers and non-internet-facing network devices are applied within one month of release. | IT administrators deploy updates with a deadline configuration of the desired date in Microsoft Configuration Manager |
| ISM-1696 | 3 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in operating systems of workstations, non-internet-facing servers and non-internet-facing network devices are applied within 48 hours of release when vulnerabilities are assessed as critical by vendors or when working exploits exist. | IT administrators deploy updates with a deadline configuration of As soon as Possible in Microsoft Configuration Manager |
| ISM-1702 | 1, 2, 3 | A vulnerability scanner is used at least fortnightly to identify missing patches or updates for vulnerabilities in operating systems of workstations, non-internet-facing servers and non-internet-facing network devices. | IT admin configures the Software Update feature of Configuration Manager to run a scan for missing patches on system at least once every 14 days. |
| ISM-1902 | 3 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in operating systems of workstations, non-internet-facing servers and non-internet-facing network devices are applied within one month of release when vulnerabilities are assessed as noncritical by vendors and no working exploits exist. | IT administrators deploy updates with a deadline configuration of the desired date in Microsoft Configuration Manager. |