SSL Certificate Validation for Java Applications
Note
Bing Maps for Enterprise service retirement
Bing Maps for Enterprise is deprecated and will be retired. Free (Basic) account customers can continue to use Bing Maps for Enterprise services until June 30th, 2025. Enterprise account customers can continue to use Bing Maps for Enterprise services until June 30th, 2028. To avoid service disruptions, all implementations using Bing Maps for Enterprise REST APIs and SDKs will need to be updated to use Azure Maps by the retirement date that applies to your Bing Maps for Enterprise account type.
Azure Maps is Microsoft's next-generation maps and geospatial services for developers. Azure Maps has many of the same features as Bing Maps for Enterprise, and more. To get started with Azure Maps, create a free Azure subscription and an Azure Maps account. For more information about azure Maps, see Azure Maps Documentation. For migration guidance, see Bing Maps Migration Overview.
Bing Maps APIs support both HTTP and HTTPS requests that use Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocols. The SSL and TLS endpoints are secured by certificates. For example, when you query a data source directly from your browser by using the Bing Spatial Data Services (SDS) as in the following example, you can view the certificate chain by clicking the “lock” icon.
https://spatial.virtualearth.net/REST/v1/data/
f22876ec257b474b82fe2ffcb8393150/
NavteqNA/
NavteqPOIs
?spatialFilter=nearby(40.83274904439099,-74.3163299560546935,5)
&$filter=EntityTypeID%20eq%20'6000'
&$select=EntityID,DisplayName,Latitude,Longitude,__Distance&
$top=3
&key=INSERT_YOUR_BING_MAPS_KEY
The following image shows an example of a certificate chain.
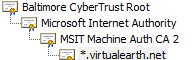
Java applications that access the Bing Maps APIs using SSL must implement their own certificate validation checks. The level of validation can vary per application, and often includes validation of the root certificate against a trusted root list. The validation performed by an application is equivalent to the validation that your browser uses to verify an SSL certificate before showing the “lock” icon.
For Java applications, private keys and the associated X.509 certificate chains that authenticate the corresponding public keys are found in the “keystore”. The “keystore” also manages certificates from trusted entities. After you install the Java Runtime Environment (JRE) or the Java Development Kit (JDK), you will find the “keystore” in the /lib/security directory of your JRE. By default, this subdirectory contains a file named cacerts that contains certificates for many Root Certificate Authorities (Root CAs).
Java provides a “keytool” in order to manage your “keystore”. To view a list of currently installed certificates, open a command prompt and run the following command from the bin directory of the JRE.
keytool -list -keystore ..\lib\security\cacerts
If you access a Bing Maps API from a Java application via SSL and you do not have the certificate for the Root CA in your “keystore” you will see an error message similar to this:
Exception in thread "main" com.sun.jersey.api.client.ClientHandlerException: javax.net.ssl.SSLHandshakeException: sun.security.validator.ValidatorException: PKIX path building failed: sun.security.provider.certpath.SunCertPathBuilderException: unable to find valid certification path to requested target…
Configuring Root Certificates
The following steps show how to install the SSL certificates required to access Bing Maps APIs.
Baltimore CyberTrust Root
To configure the Baltimore CyberTrust Root:
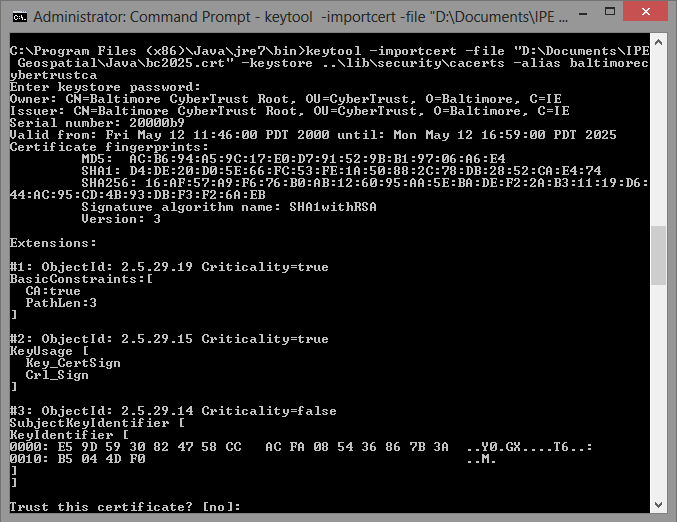
Download the Baltimore CyberTrust Root cert and save it to a location on your computer. Note the location as you will need it for the install command below.
Open a command prompt and run the following “keytool” command from the
bindirectory of the JRE. This starts the certificate installation. You must insert the directory path to the downloaded certificate from step 1 before running the command. If you are running the Windows operating system, you will need to run the command prompt as an administrator.keytool -importcert -file "InsertCertificateDownloadLocation\bc2025.crt" -keystore ..\lib\security\cacerts -alias baltimorecybertrustcaWhen you run the command, the information in the following screenshot appears. To verify the install, type yes.