Remote work using Azure VPN Gateway VPN connections
This article describes the options that are available to organizations to set up remote access for their users or to supplement their existing solutions with additional capacity. The Azure VPN Gateway point-to-site VPN solution is cloud-based and can be provisioned quickly to cater for the increased demand of users to work from home. It can scale up easily and turned off just as easily and quickly when the increased capacity isn't needed anymore.
About point-to-site VPN
A point-to-site (P2S) VPN gateway connection lets you create a secure connection to your virtual network from an individual client computer. A P2S connection is established by starting it from the client computer. This solution is useful for telecommuters who want to connect to Azure VNets or on-premises data centers from a remote location, such as from home or a conference. For more information about Azure point-to-site VPN, see About VPN Gateway point-to-site VPN and the VPN Gateway FAQ.
The following table shows the client operating systems and the authentication options that are available to them. It would be helpful to select the authentication method based on the client OS that is already in use. For example, select OpenVPN with Certificate-based authentication if you have a mixture of client operating systems that need to connect. Also, note that point-to-site VPN is only supported on route-based VPN gateways.
| Authentication method | Tunnel type | Client OS | VPN client |
|---|---|---|---|
| Certificate | |||
| IKEv2, SSTP | Windows | Native VPN client | |
| IKEv2 | macOS | Native VPN client | |
| IKEv2 | Linux | strongSwan | |
| OpenVPN | Windows | Azure VPN client OpenVPN client version 2.x OpenVPN client version 3.x |
|
| OpenVPN | macOS | OpenVPN client | |
| OpenVPN | iOS | OpenVPN client | |
| OpenVPN | Linux | Azure VPN Client OpenVPN client |
|
| Microsoft Entra ID | |||
| OpenVPN | Windows | Azure VPN client | |
| OpenVPN | macOS | Azure VPN Client | |
| OpenVPN | Linux | Azure VPN Client |
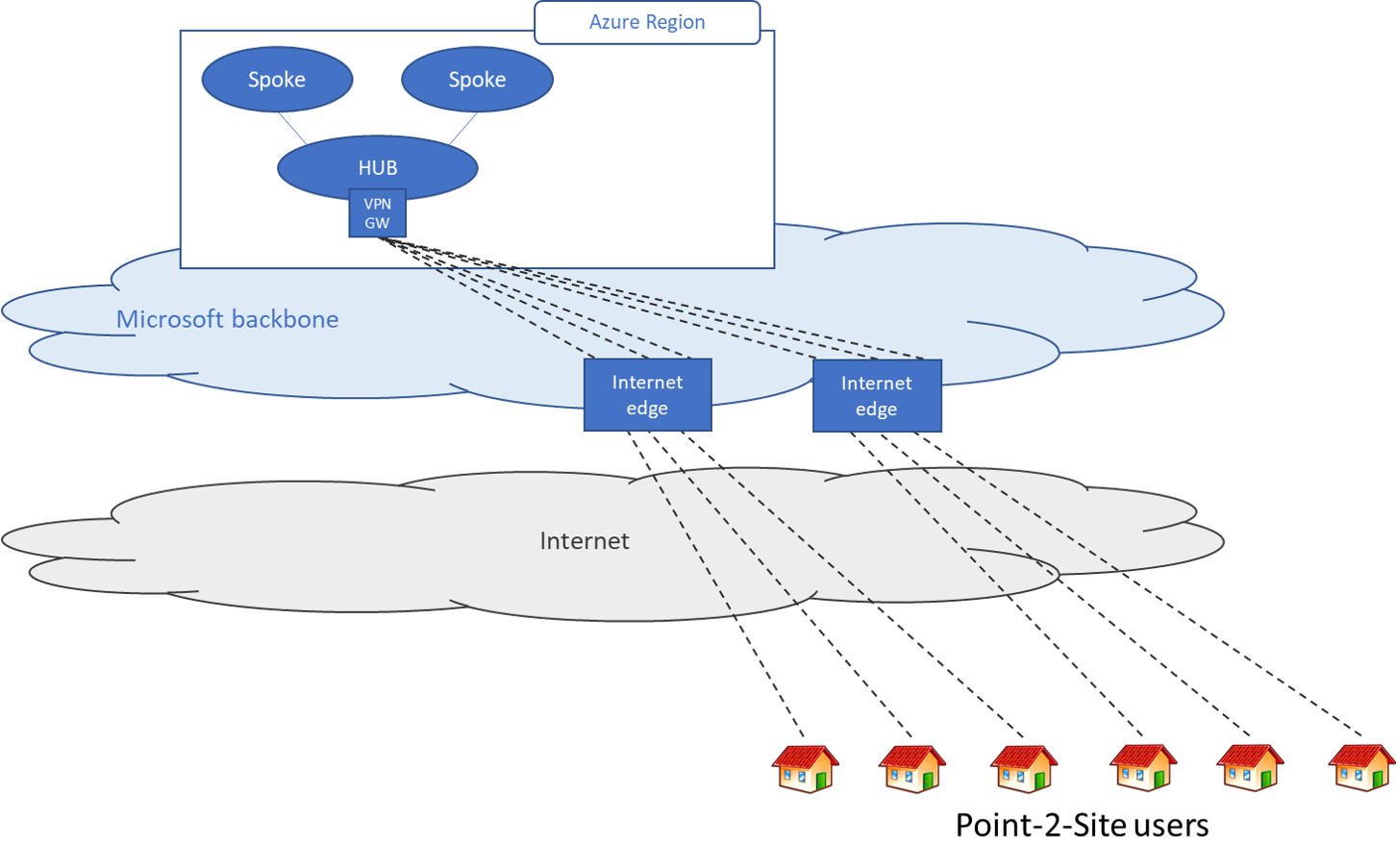
Scenario 1 - Users need access to resources in Azure only
In this scenario, the remote users only need to access to resources that are in Azure.
At a high level, the following steps are needed to enable users to connect to Azure resources securely:
Create a virtual network gateway (if one doesn't exist).
Configure point-to-site VPN on the gateway.
- For certificate authentication, see Configure point-to-site certificate authentication.
- For Microsoft Entra ID authentication, see Configure point-to-site Microsoft Entra ID authentication
- For troubleshooting point-to-site connections, see Troubleshooting: Azure point-to-site connection problems.
Download and distribute the VPN client configuration.
Distribute the certificates (if certificate authentication is selected) to the clients.
Connect to Azure VPN.
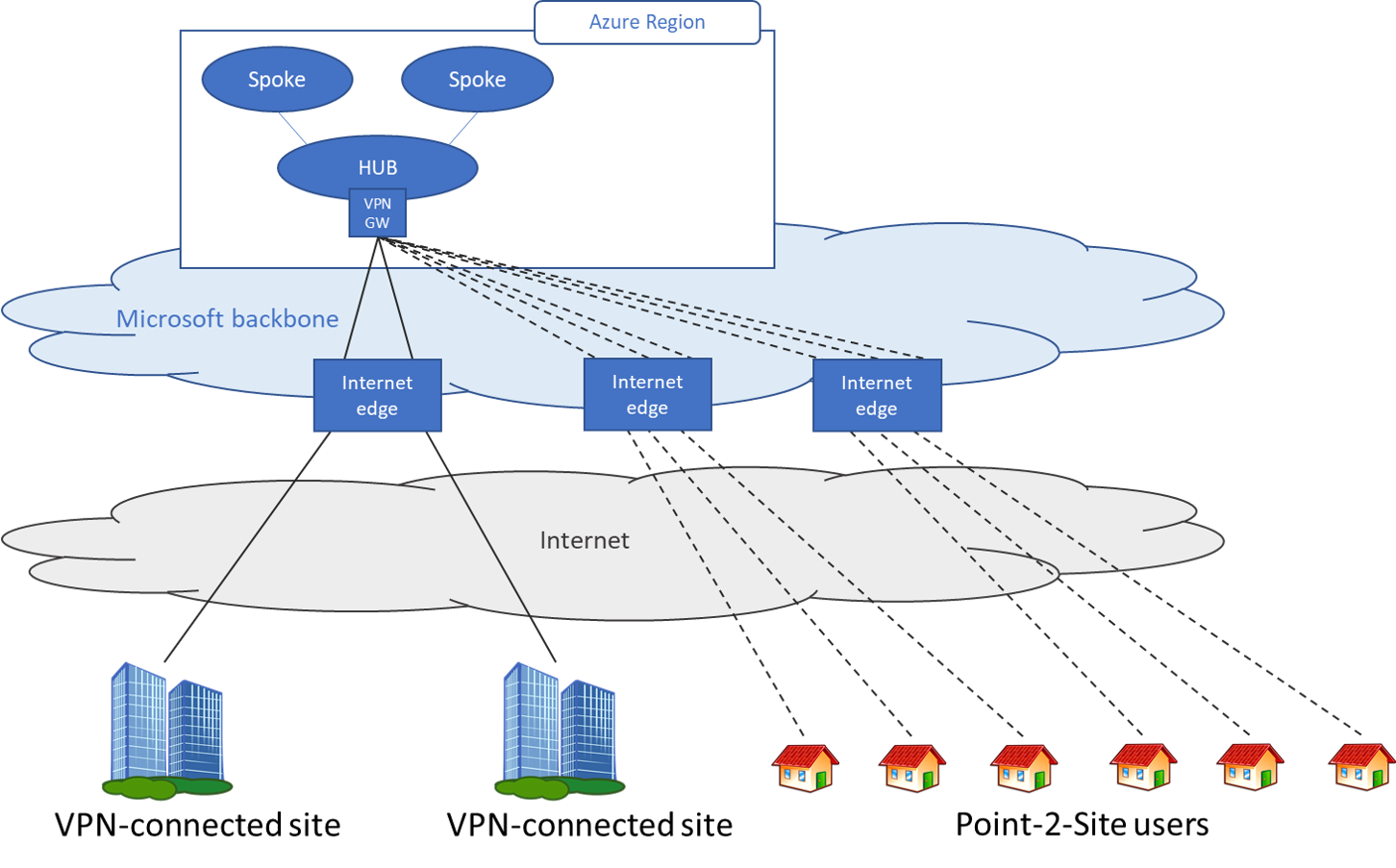
Scenario 2 - Users need access to resources in Azure and/or on-premises resources
In this scenario, the remote users need to access to resources that are in Azure and in the on premises data center(s).
At a high level, the following steps are needed to enable users to connect to Azure resources securely:
- Create a virtual network gateway (if one doesn't exist).
- Configure point-to-site VPN on the gateway (see Scenario 1).
- Configure a site-to-site tunnel on the Azure virtual network gateway with BGP enabled.
- Configure the on-premises device to connect to Azure virtual network gateway.
- Download the point-to-site profile from the Azure portal and distribute to clients
To learn how to set up a site-to-site VPN tunnel, see Create a site-to-site VPN connection.
Next Steps
- Configure a P2S connection - Microsoft Entra ID authentication
- Configure a P2S connection - Certificate authentication
- Configure a P2S connection - RADIUS authentication
- About VPN Gateway point-to-site VPN
- About point-to-site VPN routing
"OpenVPN" is a trademark of OpenVPN Inc.