Create a site-to-site VPN connection - Azure CLI
This article shows you how to use the Azure CLI to create a site-to-site (S2S) VPN gateway connection from your on-premises network to a virtual network (VNet).
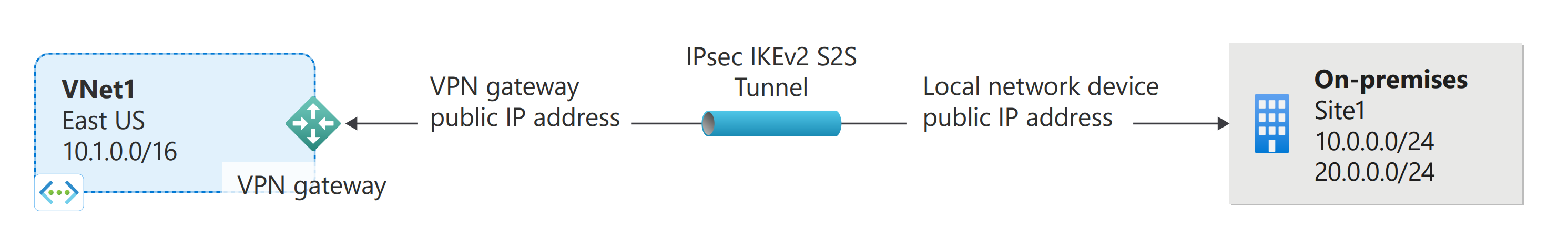
A site-to-site VPN gateway connection is used to connect your on-premises network to an Azure virtual network over an IPsec/IKE (IKEv1 or IKEv2) VPN tunnel. This type of connection requires a VPN device located on-premises that has an externally facing public IP address assigned to it. The steps in this article create a connection between the VPN gateway and the on-premises VPN device using a shared key. For more information about VPN gateways, see About VPN gateway.
Before you begin
Verify that your environment meets the following criteria before beginning configuration:
Verify that you have a functioning route-based VPN gateway. To create a VPN gateway, see Create a VPN gateway.
If you're unfamiliar with the IP address ranges located in your on-premises network configuration, you need to coordinate with someone who can provide those details for you. When you create this configuration, you must specify the IP address range prefixes that Azure routes to your on-premises location. None of the subnets of your on-premises network can overlap with the virtual network subnets that you want to connect to.
VPN devices:
- Make sure you have a compatible VPN device and someone who can configure it. For more information about compatible VPN devices and device configuration, see About VPN devices.
- Determine if your VPN device supports active-active mode gateways. This article creates an active-active mode VPN gateway, which is recommended for highly available connectivity. Active-active mode specifies that both gateway VM instances are active. This mode requires two public IP addresses, one for each gateway VM instance. You configure your VPN device to connect to the IP address for each gateway VM instance.
If your VPN device doesn't support this mode, don't enable this mode for your gateway. For more information, see Design highly available connectivity for cross-premises and VNet-to-VNet connections and About active-active mode VPN gateways.
This article requires version 2.0 or later of the Azure CLI.
Use the Bash environment in Azure Cloud Shell. For more information, see Quickstart for Bash in Azure Cloud Shell.
If you prefer to run CLI reference commands locally, install the Azure CLI. If you're running on Windows or macOS, consider running Azure CLI in a Docker container. For more information, see How to run the Azure CLI in a Docker container.
If you're using a local installation, sign in to the Azure CLI by using the az login command. To finish the authentication process, follow the steps displayed in your terminal. For other sign-in options, see Sign in with the Azure CLI.
When you're prompted, install the Azure CLI extension on first use. For more information about extensions, see Use extensions with the Azure CLI.
Run az version to find the version and dependent libraries that are installed. To upgrade to the latest version, run az upgrade.
Create the local network gateway
The local network gateway typically refers to your on-premises location. You give the site a name by which Azure can refer to it, then specify the IP address of the on-premises VPN device to which you'll create a connection. You also specify the IP address prefixes that will be routed through the VPN gateway to the VPN device. The address prefixes you specify are the prefixes located on your on-premises network. If your on-premises network changes, you can easily update the prefixes.
Use the following values:
- The --gateway-ip-address is the IP address of your on-premises VPN device.
- The --local-address-prefixes are your on-premises address spaces.
Use the az network local-gateway create command to add a local network gateway. The following example shows a local network gateway with multiple address prefixes. Replace the values with your own.
az network local-gateway create --gateway-ip-address [IP address of your on-premises VPN device] --name Site1 --resource-group TestRG1 --local-address-prefixes 10.3.0.0/16 10.0.0.0/24
Configure your VPN device
Site-to-site connections to an on-premises network require a VPN device. In this step, you configure your VPN device. When you configure your VPN device, you need the following values:
Shared key: This shared key is the same one that you specify when you create your site-to-site VPN connection. In our examples, we use a simple shared key. We recommend that you generate a more complex key to use.
Public IP addresses of your virtual network gateway instances: Obtain the IP address for each VM instance. If your gateway is in active-active mode, you'll have an IP address for each gateway VM instance. Be sure to configure your device with both IP addresses, one for each active gateway VM. Active-standby mode gateways have only one IP address.
To find the public IP address of your virtual network gateway, use the az network public-ip list command. For easy reading, the output is formatted to display the list of public IPs in table format. In the example, VNet1GWpip1 is the name of the public IP address resource.
az network public-ip list --resource-group TestRG1 --output table
Depending on the VPN device that you have, you might be able to download a VPN device configuration script. For more information, see Download VPN device configuration scripts.
The following links provide more configuration information:
For information about compatible VPN devices, see About VPN devices.
Before you configure your VPN device, check for any known device compatibility issues.
For links to device configuration settings, see Validated VPN devices. We provide the device configuration links on a best-effort basis, but it's always best to check with your device manufacturer for the latest configuration information.
The list shows the versions that we tested. If the OS version for your VPN device isn't on the list, it still might be compatible. Check with your device manufacturer.
For basic information about VPN device configuration, see Overview of partner VPN device configurations.
For information about editing device configuration samples, see Editing samples.
For cryptographic requirements, see About cryptographic requirements and Azure VPN gateways.
For information about parameters that you need to complete your configuration, see Default IPsec/IKE parameters. The information includes IKE version, Diffie-Hellman (DH) group, authentication method, encryption and hashing algorithms, security association (SA) lifetime, perfect forward secrecy (PFS), and Dead Peer Detection (DPD).
For IPsec/IKE policy configuration steps, see Configure custom IPsec/IKE connection policies for S2S VPN and VNet-to-VNet.
To connect multiple policy-based VPN devices, see Connect a VPN gateway to multiple on-premises policy-based VPN devices.
Create the VPN connection
Create a site-to-site VPN connection between your virtual network gateway and your on-premises VPN device. If you're using an active-active mode gateway (recommended), each gateway VM instance has a separate IP address. To properly configure highly available connectivity, you must establish a tunnel between each VM instance and your VPN device. Both tunnels are part of the same connection.
Create the connection using the az network vpn-connection create command. The shared key must match the value you used for your VPN device configuration.
az network vpn-connection create --name VNet1toSite1 --resource-group TestRG1 --vnet-gateway1 VNet1GW -l eastus --shared-key abc123 --local-gateway2 Site1
After a short while, the connection will be established.
Verify the VPN connection
You can verify that your connection succeeded by using the az network vpn-connection show command. In the example, '--name' refers to the name of the connection that you want to test. When the connection is in the process of being established, its connection status shows 'Connecting'. Once the connection is established, the status changes to 'Connected'. Modify the following example with the values for your environment.
az network vpn-connection show --name <connection-name> --resource-group <resource-group-name>
If you want to use another method to verify your connection, see Verify a VPN Gateway connection.
Common tasks
This section contains common commands that are helpful when working with site-to-site configurations. For the full list of CLI networking commands, see Azure CLI - Networking.
To view local network gateways
To view a list of the local network gateways, use the az network local-gateway list command.
az network local-gateway list --resource-group TestRG1
To modify local network gateway IP address prefixes - no gateway connection
If you want to add or remove IP address prefixes and your gateway doesn't have a connection yet, you can update the prefixes using az network local-gateway create. To overwrite the current settings, use the existing name of your local network gateway. If you use a different name, you create a new local network gateway, instead of overwriting the existing one. You can also use this command to update the gateway IP address for the VPN device.
Each time you make a change, the entire list of prefixes must be specified, not just the prefixes that you want to change. Specify only the prefixes that you want to keep. In this case, 10.0.0.0/24 and 10.3.0.0/16
az network local-gateway create --gateway-ip-address 203.0.113.34 --name Site2 -g TestRG1 --local-address-prefixes 10.0.0.0/24 10.3.0.0/16
To modify local network gateway IP address prefixes - existing gateway connection
If you have a gateway connection and want to add or remove IP address prefixes, you can update the prefixes using az network local-gateway update. This results in some downtime for your VPN connection.
Each time you make a change, the entire list of prefixes must be specified, not just the prefixes that you want to change. In this example, 10.0.0.0/24 and 10.3.0.0/16 are already present. We add the prefixes 10.5.0.0/16 and 10.6.0.0/16 and specify all 4 of the prefixes when updating.
az network local-gateway update --local-address-prefixes 10.0.0.0/24 10.3.0.0/16 10.5.0.0/16 10.6.0.0/16 --name VNet1toSite2 -g TestRG1
To modify the local network gateway 'gatewayIpAddress'
If you change the public IP address for your VPN device, you need to modify the local network gateway with the updated IP address. When modifying the gateway, be sure to specify the existing name of your local network gateway. If you use a different name, you create a new local network gateway, instead of overwriting the existing gateway information.
To modify the gateway IP address, replace the values 'Site2' and 'TestRG1' with your own using the az network local-gateway update command.
az network local-gateway update --gateway-ip-address 203.0.113.170 --name Site2 --resource-group TestRG1
Verify that the IP address is correct in the output:
"gatewayIpAddress": "203.0.113.170",
To verify the shared key values
Verify that the shared key value is the same value that you used for your VPN device configuration. If it isn't, either run the connection again using the value from the device, or update the device with the value from the return. The values must match. To view the shared key, use the az network vpn-connection-list.
az network vpn-connection shared-key show --connection-name VNet1toSite2 --resource-group TestRG1
To view the VPN gateway Public IP address
To find the public IP address of your virtual network gateway, use the az network public-ip list command. For easy reading, the output for this example is formatted to display the list of public IPs in table format.
az network public-ip list --resource-group TestRG1 --output table
Next steps
- For information about BGP, see the BGP overview and How to configure BGP.
- For information about forced tunneling, see About forced tunneling.
- For information about highly available active-active connections, see Highly Available cross-premises and VNet-to-VNet connectivity.
- For a list of networking Azure CLI commands, see Azure CLI.
- For information about creating a site-to-site VPN connection using Azure Resource Manager template, see Create a site-to-site VPN connection.
- For information about creating a VNet-to-VNet VPN connection using Azure Resource Manager template, see Deploy HBase geo replication.