Rolling upgrades with MaxSurge on Virtual Machine Scale Sets
Rolling upgrades with MaxSurge can help improve service uptime during upgrade events. With MaxSurge enabled, new instances are created in batches using the latest scale model. When the new instances are fully created and healthy, the scale set then deletes instances in batches matching the old scale set model. The process continues until all instances are brought up-to-date.
Note
To configure MaxSurge upgrades, register the following feature flag:
Register-AzProviderFeature -FeatureName MaxSurgeRollingUpgrade -ProviderNamespace Microsoft.Compute
To update the image reference version during an upgrade, register the following feature flag:
Register-AzProviderFeature -FeatureName ImageReferenceUpgradeForVmoVMs -ProviderNamespace Microsoft.Compute
Concepts
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Rolling upgrade batch size % | Specifies how many of the total instances of your scale set you want to be upgraded at one time. Example: A batch size of 20% when you have 10 instances in your scale set results in upgrade batches with two instances each. |
| Pause time between batches (sec) | Specifies how long you want your scale set to wait between finishing an upgrade batch and starting a new one. Example: A pause time of 10 seconds means that once a batch is successfully completed, the scale set will wait 10 seconds before moving onto the next batch. |
| Max unhealthy instance % | Specifies the total number of instances allowed to be marked as unhealthy before and during the rolling upgrade. Example: A max unhealthy instance % of 20 means if you have a scale set of 10 instances and more than two instances in the entire scale set report back as unhealthy, the rolling upgrade stops. |
| Max unhealthy upgrade % | Specifies the total number of instances allowed to be marked as unhealthy after being upgraded. Example: A max unhealthy upgrade % of 20 means if you have a scale set of 10 instances and more than two instances in the entire scale set report back as unhealthy after being upgraded, the rolling upgrade is canceled. |
| Prioritize unhealthy instances | Tells the scale set to upgrade instances reporting as unhealthy before upgrading instances reporting as healthy. Example: If some instances in your scale are failed or unhealthy when a rolling upgrade begins, the scale set updates those instances first. |
| Enable cross-zone upgrade | Allows the scale set to ignore Availability Zone boundaries when determining batches. This essentially lets the rolling upgrade treat your scale set as a regional deployment instead of a zonal deployment. |
Considerations
- Automatic OS image upgrades and automatic extension upgrades automatically inherit the rolling upgrade policy and use it to perform upgrades. For Virtual Machine Scale Sets using Uniform Orchestration, when MaxSurge set to
true, automatic OS image upgrades and automatic extension upgrades will also be applied using the MaxSurge upgrade method. For Virtual Machine Scale Sets with Flexible Orchestration, enabling automatic OS image upgrades and MaxSurge together is not yet supported. - When using rolling upgrades with MaxSurge, new virtual machines are created using the latest scale set model to replace virtual machines using the old scale set model. These newly created virtual machines counts towards your overall core quota. Additionally, these new virtual machines have new IP addresses and are placed into an existing subnet. You also need to have enough IP address quota and subnet space available to deploy these newly created virtual machines.
- During the MaxSurge rolling upgrade processes, Azure performs a quota check before each new batch. If that quota check fails, the upgrade will default to a non-MaxSurge upgrade and be upgraded in place.
- When using rolling upgrades with MaxSurge on Virtual Machine Scale Sets with Uniform Orchestration, the new virtual machine that is created with the updated model to replace the virtual machine with the older model may be placed into a different update domain than the previous virtual machine.
- If attaching a virtual machine to a Virtual Machine Scale Set, the attached virtual machine should also have an application health extension. If an attached virtual machine does not have a health extension configured and reporting application health, the rolling upgrade may be impacted.
MaxSurge vs in place upgrades
MaxSurge upgrades
Rolling upgrades with MaxSurge creates new instances with the latest scale set model to replace instances running with the old model. By creating new instances, you can ensure that your scale set capacity doesn't drop below the set instance count during the duration of the upgrade process.
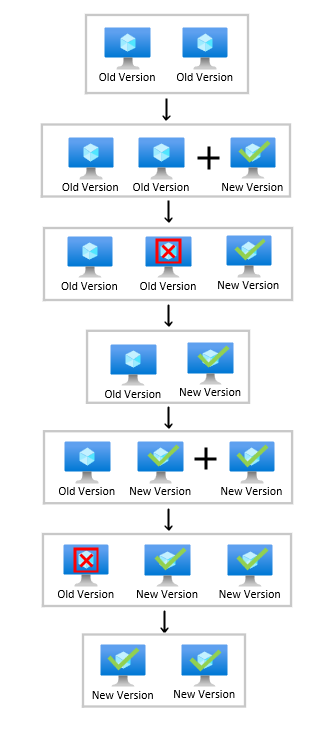
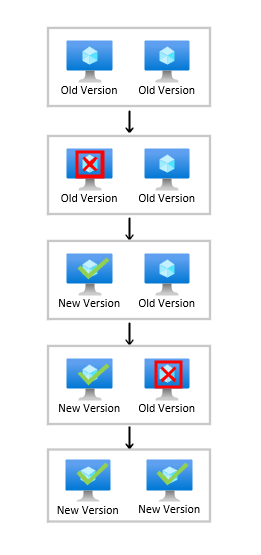
In place upgrades
Rolling upgrades with MaxSurge disabled performs upgrades in place. Depending on the type of upgrade, the virtual machines may not be available for traffic during the upgrade process. This may reduce your scale set capacity during the upgrade process but doesn't consume any extra quota.
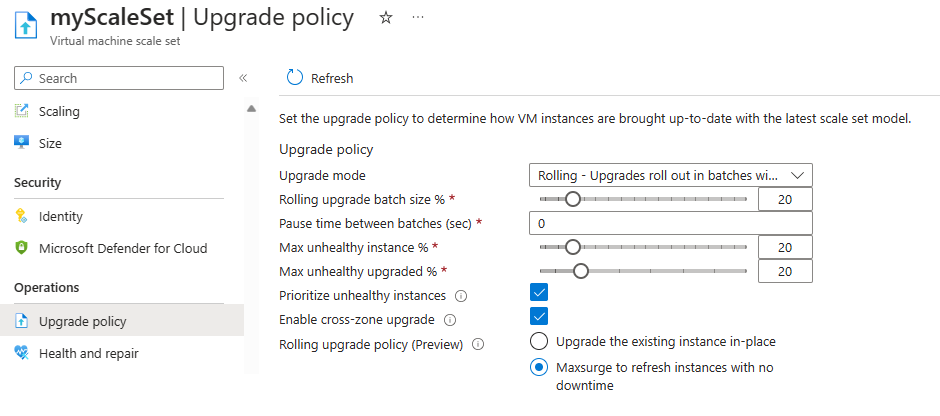
Configure rolling upgrades with MaxSurge
Enabling or disabling MaxSurge can be done during or after scale set provisioning. When using a rolling upgrade policy, the scale set must also use an application health extension or a health probe. It's suggested to create the scale set with a manual upgrade policy and update the policy to rolling after successfully confirming the application health is being properly reported.
Select the Virtual Machine Scale Set you want to change the upgrade policy for. In the menu under Settings, select Upgrade Policy and from the drop-down menu, select Rolling - Upgrades roll out in batches with optional pause.
Next steps
To learn more about upgrades for Virtual Machine Scale Sets, see configure rolling upgrade policy.