Quickstart: Create a Traffic Manager profile for a highly available web application using Azure CLI
This quickstart describes how to create a Traffic Manager profile that delivers high availability for your web application.
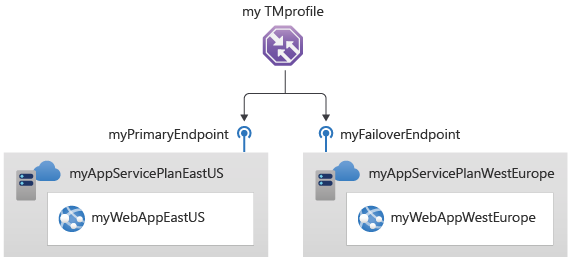
In this quickstart, you'll create two instances of a web application. Each of them is running in a different Azure region. You'll create a Traffic Manager profile based on endpoint priority. The profile directs user traffic to the primary site running the web application. Traffic Manager continuously monitors the web application. If the primary site is unavailable, it provides automatic failover to the backup site.
If you don't have an Azure subscription, create an Azure free account before you begin.
Prerequisites
Use the Bash environment in Azure Cloud Shell. For more information, see Quickstart for Bash in Azure Cloud Shell.
If you prefer to run CLI reference commands locally, install the Azure CLI. If you're running on Windows or macOS, consider running Azure CLI in a Docker container. For more information, see How to run the Azure CLI in a Docker container.
If you're using a local installation, sign in to the Azure CLI by using the az login command. To finish the authentication process, follow the steps displayed in your terminal. For other sign-in options, see Sign in with the Azure CLI.
When you're prompted, install the Azure CLI extension on first use. For more information about extensions, see Use extensions with the Azure CLI.
Run az version to find the version and dependent libraries that are installed. To upgrade to the latest version, run az upgrade.
- This article requires version 2.0.28 or later of the Azure CLI. If using Azure Cloud Shell, the latest version is already installed.
Create a resource group
Create a resource group with az group create. An Azure resource group is a logical container into which Azure resources are deployed and managed.
The following example creates a resource group named myResourceGroup in the eastus location:
az group create \
--name myResourceGroup \
--location eastus
Create a Traffic Manager profile
Create a Traffic Manager profile using az network traffic-manager profile create that directs user traffic based on endpoint priority.
mytrafficmanagerprofile='mytrafficmanagerprofile'$RANDOM
az network traffic-manager profile create \
--name $mytrafficmanagerprofile \
--resource-group myResourceGroup \
--routing-method Priority \
--path '/' \
--protocol "HTTP" \
--unique-dns-name $mytrafficmanagerprofile \
--ttl 30 \
--port 80
Create web apps
For this quickstart, you'll need two instances of a web application deployed in two different Azure regions (East US and West Europe). Each will serve as primary and failover endpoints for Traffic Manager.
Create web app service plans
Create web app service plans using az appservice plan create for the two instances of the web application that you will deploy in two different Azure regions.
az appservice plan create \
--name myAppServicePlanEastUS \
--resource-group myResourceGroup \
--location eastus \
--sku S1
az appservice plan create \
--name myAppServicePlanWestEurope \
--resource-group myResourceGroup \
--location westeurope \
--sku S1
Create a web app in the app service plan
Create two instances the web application using az webapp create in the App Service plans in the East US and West Europe Azure regions.
mywebappeastus='myWebAppEastUS'$RANDOM
myWebAppWestEurope='myWebAppWestEurope'$RANDOM
az webapp create \
--name $mywebappeastus \
--plan myAppServicePlanEastUS \
--resource-group myResourceGroup
az webapp create \
--name $myWebAppWestEurope \
--plan myAppServicePlanWestEurope \
--resource-group myResourceGroup
Add Traffic Manager endpoints
Add the two Web Apps as Traffic Manager endpoints using az network traffic-manager endpoint create to the Traffic Manager profile as follows:
- Determine the Web App ID and add the Web App located in the East US Azure region as the primary endpoint to route all the user traffic.
- Determine the Web App ID and add the Web App located in the West Europe Azure region as the failover endpoint.
When the primary endpoint is unavailable, traffic automatically routes to the failover endpoint.
East US endpoint
App1ResourceId=$(az webapp show --name $mywebappeastus --resource-group myResourceGroup --query id --output tsv)
az network traffic-manager endpoint create \
--name $mywebappeastus \
--resource-group myResourceGroup \
--profile-name $mytrafficmanagerprofile \
--type azureEndpoints \
--target-resource-id $App1ResourceId \
--priority 1 \
--endpoint-status Enabled
West Europe endpoint
App2ResourceId=$(az webapp show --name $myWebAppWestEurope --resource-group myResourceGroup --query id --output tsv)
az network traffic-manager endpoint create \
--name $myWebAppWestEurope \
--resource-group myResourceGroup \
--profile-name $mytrafficmanagerprofile \
--type azureEndpoints \
--target-resource-id $App2ResourceId \
--priority 2 \
--endpoint-status Enabled
Test your Traffic Manager profile
In this section, you'll check the domain name of your Traffic Manager profile. You'll also configure the primary endpoint to be unavailable. Finally, you get to see that the web app is still available. It's because Traffic Manager sends the traffic to the failover endpoint.
In the following example, replace <app1name_eastus> and <app2name_westeurope> with the App Names created for each region in the previous section. Then replace <profile_name> with the profile name used in the previous section.
Determine the DNS name
Determine the DNS name of the Traffic Manager profile using az network traffic-manager profile show.
az network traffic-manager profile show \
--name $mytrafficmanagerprofile \
--resource-group myResourceGroup \
--query dnsConfig.fqdn
Copy the RelativeDnsName value. The DNS name of your Traffic Manager profile is http://<relativednsname>.trafficmanager.net.
View Traffic Manager in action
In a web browser, enter the DNS name of your Traffic Manager profile (http://<relativednsname>.trafficmanager.net) to view your Web App's default website.
Note
In this quickstart scenario, all requests route to the primary endpoint. It is set to Priority 1.
To view Traffic Manager failover in action, disable your primary site using az network traffic-manager endpoint update.
az network traffic-manager endpoint update \ --name $mywebappeastus \ --resource-group myResourceGroup \ --profile-name $mytrafficmanagerprofile \ --type azureEndpoints \ --endpoint-status DisabledCopy the DNS name of your Traffic Manager profile (http://<relativednsname>.trafficmanager.net) to view the website in a new web browser session.
Verify that the web app is still available.
Clean up resources
When you're done, delete the resource groups, web applications, and all related resources using az group delete.
az group delete \
--resource-group myResourceGroup
Next steps
In this quickstart, you created a Traffic Manager profile that provides high availability for your web application. To learn more about routing traffic, continue to the Traffic Manager tutorials.