Beyond Teradata migration, implement a modern data warehouse in Microsoft Azure
This article is part seven of a seven-part series that provides guidance on how to migrate from Teradata to Azure Synapse Analytics. The focus of this article is best practices for implementing modern data warehouses.
Beyond data warehouse migration to Azure
A key reason to migrate your existing data warehouse to Azure Synapse Analytics is to utilize a globally secure, scalable, low-cost, cloud-native, pay-as-you-use analytical database. With Azure Synapse, you can integrate your migrated data warehouse with the complete Microsoft Azure analytical ecosystem to take advantage of other Microsoft technologies and modernize your migrated data warehouse. Those technologies include:
Azure Data Lake Storage for cost effective data ingestion, staging, cleansing, and transformation. Data Lake Storage can free up the data warehouse capacity occupied by fast-growing staging tables.
Azure Data Factory for collaborative IT and self-service data integration with connectors to cloud and on-premises data sources and streaming data.
Common Data Model to share consistent trusted data across multiple technologies, including:
- Azure Synapse
- Azure Synapse Spark
- Azure HDInsight
- Power BI
- Adobe Customer Experience Platform
- Azure IoT
- Microsoft ISV partners
Microsoft data science technologies, including:
- Azure Machine Learning studio
- Azure Machine Learning
- Azure Synapse Spark (Spark as a service)
- Jupyter Notebooks
- RStudio
- ML.NET
- .NET for Apache Spark, which lets data scientists use Azure Synapse data to train machine learning models at scale.
Azure HDInsight to process large amounts of data, and to join big data with Azure Synapse data by creating a logical data warehouse using PolyBase.
Azure Event Hubs, Azure Stream Analytics, and Apache Kafka to integrate live streaming data from Azure Synapse.
The growth of big data has led to an acute demand for machine learning to enable custom-built, trained machine learning models for use in Azure Synapse. Machine learning models enable in-database analytics to run at scale in batch, on an event-driven basis and on-demand. The ability to take advantage of in-database analytics in Azure Synapse from multiple BI tools and applications also guarantees consistent predictions and recommendations.
In addition, you can integrate Azure Synapse with Microsoft partner tools on Azure to shorten time to value.
Let's take a closer look at how you can take advantage of technologies in the Microsoft analytical ecosystem to modernize your data warehouse after you've migrated to Azure Synapse.
Offload data staging and ETL processing to Data Lake Storage and Data Factory
Digital transformation has created a key challenge for enterprises by generating a torrent of new data for capture and analysis. A good example is transaction data created by opening online transactional processing (OLTP) systems to service access from mobile devices. Much of this data finds its way into data warehouses, and OLTP systems are the main source. With customers now driving the transaction rate rather than employees, the volume of data in data warehouse staging tables has been growing rapidly.
With the rapid influx of data into the enterprise, along with new sources of data like Internet of Things (IoT), companies must find ways to scale up data integration ETL processing. One method is to offload ingestion, data cleansing, transformation, and integration to a data lake and process data at scale there, as part of a data warehouse modernization program.
Once you've migrated your data warehouse to Azure Synapse, Microsoft can modernize your ETL processing by ingesting and staging data in Data Lake Storage. You can then clean, transform, and integrate your data at scale using Data Factory before loading it into Azure Synapse in parallel using PolyBase.
For ELT strategies, consider offloading ELT processing to Data Lake Storage to easily scale as your data volume or frequency grows.
Microsoft Azure Data Factory
Azure Data Factory is a pay-as-you-use, hybrid data integration service for highly scalable ETL and ELT processing. Data Factory provides a web-based UI to build data integration pipelines with no code. With Data Factory, you can:
Build scalable data integration pipelines code-free.
Easily acquire data at scale.
Pay only for what you use.
Connect to on-premises, cloud, and SaaS-based data sources.
Ingest, move, clean, transform, integrate, and analyze cloud and on-premises data at scale.
Seamlessly author, monitor, and manage pipelines that span data stores both on-premises and in the cloud.
Enable pay-as-you-go scale-out in alignment with customer growth.
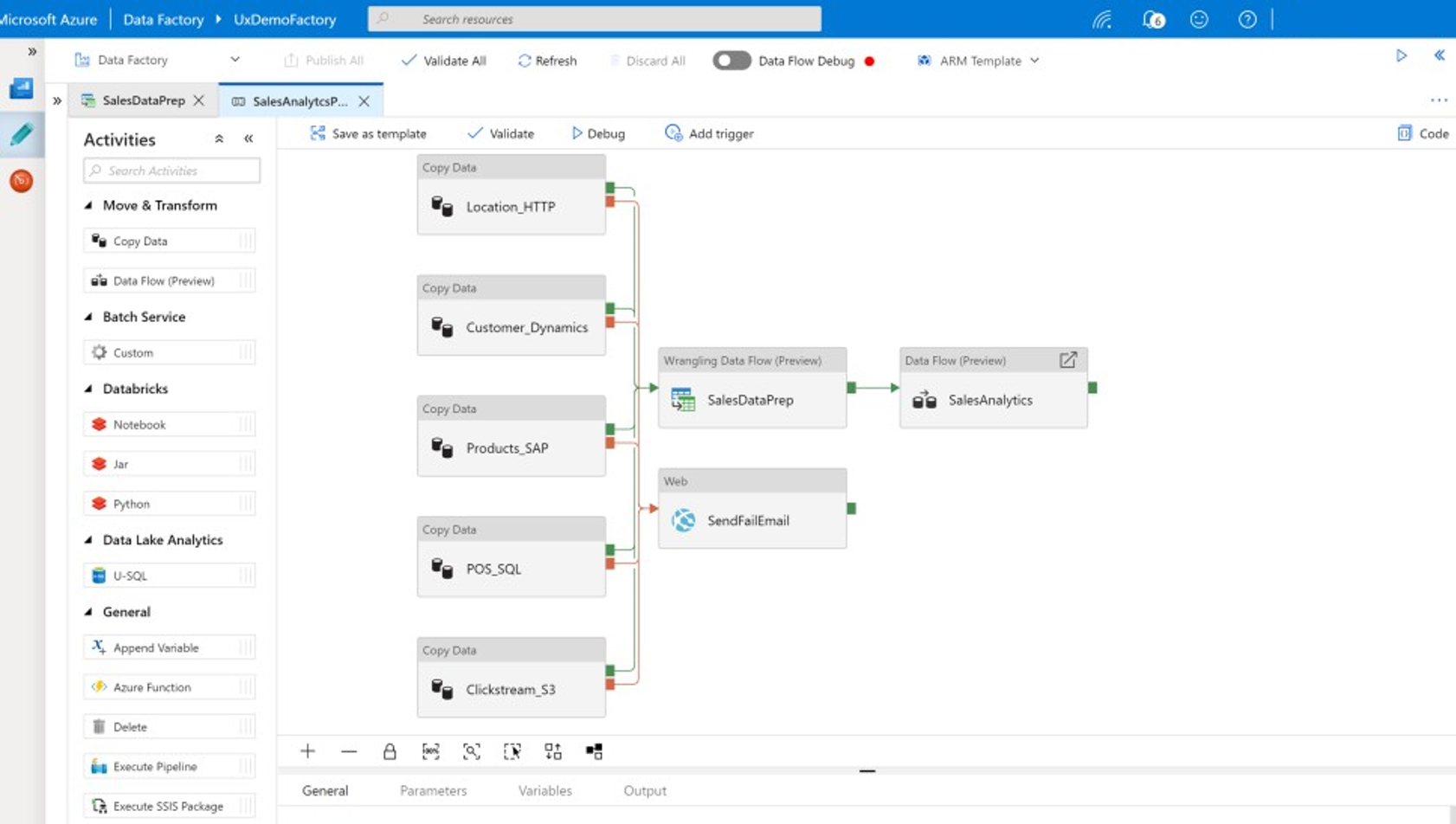
You can use these features without writing any code, or you can add custom code to Data Factory pipelines. The following screenshot shows an example Data Factory pipeline.
Tip
Data Factory lets you build scalable data integration pipelines without code.
Implement Data Factory pipeline development from any of several places, including:
Microsoft Azure portal.
Microsoft Azure PowerShell.
Programmatically from .NET and Python using a multi-language SDK.
Azure Resource Manager (ARM) templates.
REST APIs.
Tip
Data Factory can connect to on-premises, cloud, and SaaS data.
Developers and data scientists who prefer to write code can easily author Data Factory pipelines in Java, Python, and .NET using the software development kits (SDKs) available for those programming languages. Data Factory pipelines can be hybrid data pipelines because they can connect, ingest, clean, transform, and analyze data in on-premises data centers, Microsoft Azure, other clouds, and SaaS offerings.
After you develop Data Factory pipelines to integrate and analyze data, you can deploy those pipelines globally and schedule them to run in batch, invoke them on demand as a service, or run them in real-time on an event-driven basis. A Data Factory pipeline can also run on one or more execution engines and monitor execution to ensure performance and to track errors.
Tip
In Azure Data Factory, pipelines control the integration and analysis of data. Data Factory is enterprise-class data integration software aimed at IT professionals and has data wrangling capability for business users.
Use cases
Data Factory supports multiple use cases, such as:
Prepare, integrate, and enrich data from cloud and on-premises data sources to populate your migrated data warehouse and data marts on Microsoft Azure Synapse.
Prepare, integrate, and enrich data from cloud and on-premises data sources to produce training data for use in machine learning model development and in retraining analytical models.
Orchestrate data preparation and analytics to create predictive and prescriptive analytical pipelines for processing and analyzing data in batch, such as sentiment analytics. Either act on the results of the analysis or populate your data warehouse with the results.
Prepare, integrate, and enrich data for data-driven business applications running on the Azure cloud on top of operational data stores such as Azure Cosmos DB.
Tip
Build training data sets in data science to develop machine learning models.
Data sources
Data Factory lets you use connectors from both cloud and on-premises data sources. Agent software, known as a self-hosted integration runtime, securely accesses on-premises data sources and supports secure, scalable data transfer.
Transform data using Azure Data Factory
Within a Data Factory pipeline, you can ingest, clean, transform, integrate, and analyze any type of data from these sources. Data can be structured, semi-structured like JSON or Avro, or unstructured.
Without writing any code, professional ETL developers can use Data Factory mapping data flows to filter, split, join several types, lookup, pivot, unpivot, sort, union, and aggregate data. In addition, Data Factory supports surrogate keys, multiple write processing options like insert, upsert, update, table recreation, and table truncation, and several types of target data stores—also known as sinks. ETL developers can also create aggregations, including time-series aggregations that require a window to be placed on data columns.
Tip
Professional ETL developers can use Data Factory mapping data flows to clean, transform, and integrate data without the need to write code.
You can run mapping data flows that transform data as activities in a Data Factory pipeline, and if necessary, you can include multiple mapping data flows in a single pipeline. In this way, you can manage the complexity by breaking up challenging data transformation and integration tasks into smaller mapping dataflows that can be combined. And, you can add custom code when needed. In addition to this functionality, Data Factory mapping data flows include the ability to:
Define expressions to clean and transform data, compute aggregations, and enrich data. For example, these expressions can perform feature engineering on a date field to break it into multiple fields to create training data during machine learning model development. You can construct expressions from a rich set of functions that include mathematical, temporal, split, merge, string concatenation, conditions, pattern match, replace, and many other functions.
Automatically handle schema drift so that data transformation pipelines can avoid being impacted by schema changes in data sources. This ability is especially important for streaming IoT data, where schema changes can happen without notice if devices are upgraded or when readings are missed by gateway devices collecting IoT data.
Partition data to enable transformations to run in parallel at scale.
Inspect streaming data to view the metadata of a stream you're transforming.
Tip
Data Factory supports the ability to automatically detect and manage schema changes in inbound data, such as in streaming data.
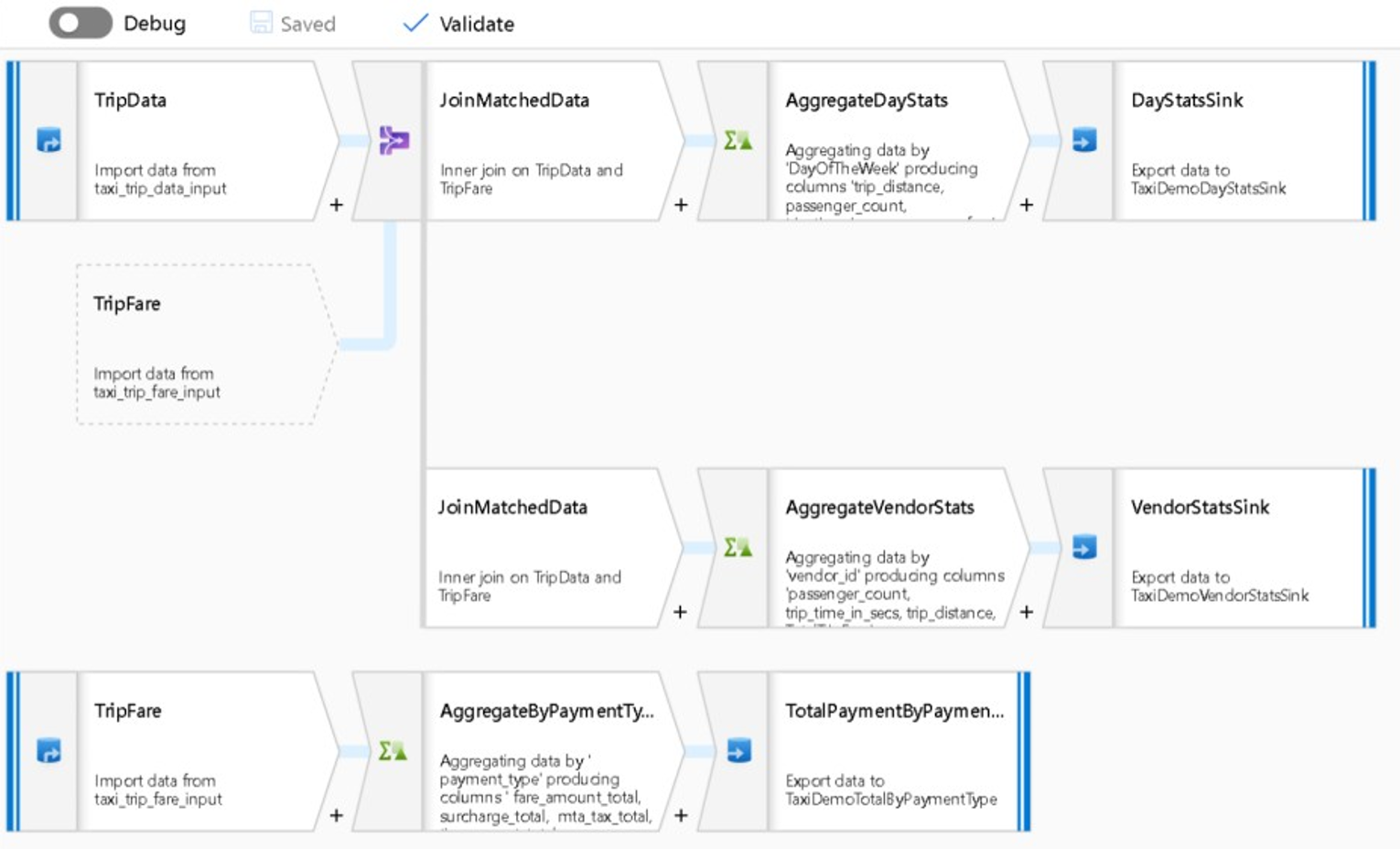
The following screenshot shows an example Data Factory mapping data flow.
Data engineers can profile data quality and view the results of individual data transforms by enabling debug capability during development.
Tip
Data Factory can also partition data to enable ETL processing to run at scale.
If necessary, you can extend Data Factory transformational and analytical functionality by adding a linked service that contains your code into a pipeline. For example, an Azure Synapse Spark pool notebook might contain Python code that uses a trained model to score the data integrated by a mapping data flow.
You can store integrated data and any results from analytics within a Data Factory pipeline in one or more data stores, such as Data Lake Storage, Azure Synapse, or Hive tables in HDInsight. You can also invoke other activities to act on insights produced by a Data Factory analytical pipeline.
Tip
Data Factory pipelines are extensible because Data Factory lets you write your own code and run it as part of a pipeline.
Utilize Spark to scale data integration
At run time, Data Factory internally uses Azure Synapse Spark pools, which are Microsoft's Spark as a service offering, to clean and integrate data in the Azure cloud. You can clean, integrate, and analyze high-volume, high-velocity data, such as click-stream data, at scale. Microsoft's intention is to also run Data Factory pipelines on other Spark distributions. In addition to running ETL jobs on Spark, Data Factory can invoke Pig scripts and Hive queries to access and transform data stored in HDInsight.
Link self-service data prep and Data Factory ETL processing using wrangling data flows
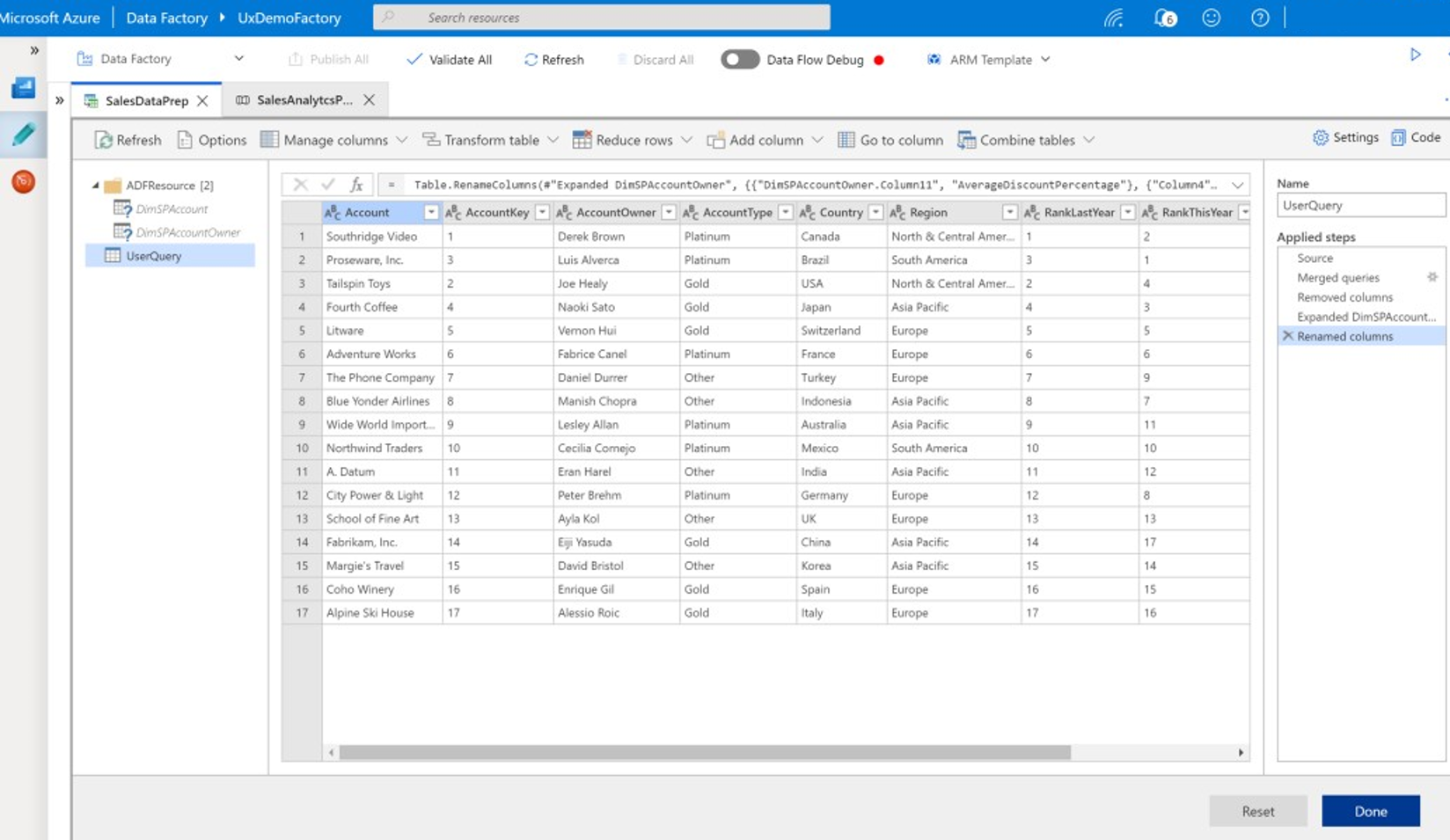
Data wrangling lets business users, also known as citizen data integrators and data engineers, make use of the platform to visually discover, explore, and prepare data at scale without writing code. This Data Factory capability is easy to use and is similar to Microsoft Excel Power Query or Microsoft Power BI dataflows, where self-service business users use a spreadsheet-style UI with drop-down transforms to prepare and integrate data. The following screenshot shows an example Data Factory wrangling data flow.
Unlike Excel and Power BI, Data Factory wrangling data flows use Power Query to generate M code and then translate it into a massively parallel in-memory Spark job for cloud-scale execution. The combination of mapping data flows and wrangling data flows in Data Factory lets professional ETL developers and business users collaborate to prepare, integrate, and analyze data for a common business purpose. The preceding Data Factory mapping data flows diagram shows how both Data Factory and Azure Synapse Spark pool notebooks can be combined in the same Data Factory pipeline. The combination of mapping and wrangling data flows in Data Factory helps IT and business users stay aware of what data flows each has created, and supports data flow reuse to minimize reinvention and maximize productivity and consistency.
Tip
Data Factory supports both wrangling data flows and mapping data flows, so business users and IT users can integrate data collaboratively on a common platform.
Link data and analytics in analytical pipelines
In addition to cleaning and transforming data, Data Factory can combine data integration and analytics in the same pipeline. You can use Data Factory to create both data integration and analytical pipelines, the latter being an extension of the former. You can drop an analytical model into a pipeline to create an analytical pipeline that generates clean, integrated data for predictions or recommendations. Then, you can act on the predictions or recommendations immediately, or store them in your data warehouse to provide new insights and recommendations that can be viewed in BI tools.
To batch score your data, you can develop an analytical model that you invoke as a service within a Data Factory pipeline. You can develop analytical models code-free with Azure Machine Learning studio, or with the Azure Machine Learning SDK using Azure Synapse Spark pool notebooks or R in RStudio. When you run Spark machine learning pipelines on Azure Synapse Spark pool notebooks, analysis happens at scale.
You can store integrated data and any Data Factory analytical pipeline results in one or more data stores, such as Data Lake Storage, Azure Synapse, or Hive tables in HDInsight. You can also invoke other activities to act on insights produced by a Data Factory analytical pipeline.
Use a lake database to share consistent trusted data
A key objective of any data integration setup is the ability to integrate data once and reuse it everywhere, not just in a data warehouse. For example, you might want to use integrated data in data science. Reuse avoids reinvention and ensures consistent, commonly understood data that everyone can trust.
Common Data Model describes core data entities that can be shared and reused across the enterprise. To achieve reuse, Common Data Model establishes a set of common data names and definitions that describe logical data entities. Examples of common data names include Customer, Account, Product, Supplier, Orders, Payments, and Returns. IT and business professionals can use data integration software to create and store common data assets to maximize their reuse and drive consistency everywhere.
Azure Synapse provides industry-specific database templates to help standardize data in the lake. Lake database templates provide schemas for predefined business areas, enabling data to be loaded into a lake database in a structured way. The power comes when you use data integration software to create lake database common data assets, resulting in self-describing trusted data that can be consumed by applications and analytical systems. You can create common data assets in Data Lake Storage by using Data Factory.
Tip
Data Lake Storage is shared storage that underpins Microsoft Azure Synapse, Azure Machine Learning, Azure Synapse Spark, and HDInsight.
Power BI, Azure Synapse Spark, Azure Synapse, and Azure Machine Learning can consume common data assets. The following diagram shows how a lake database can be used in Azure Synapse.
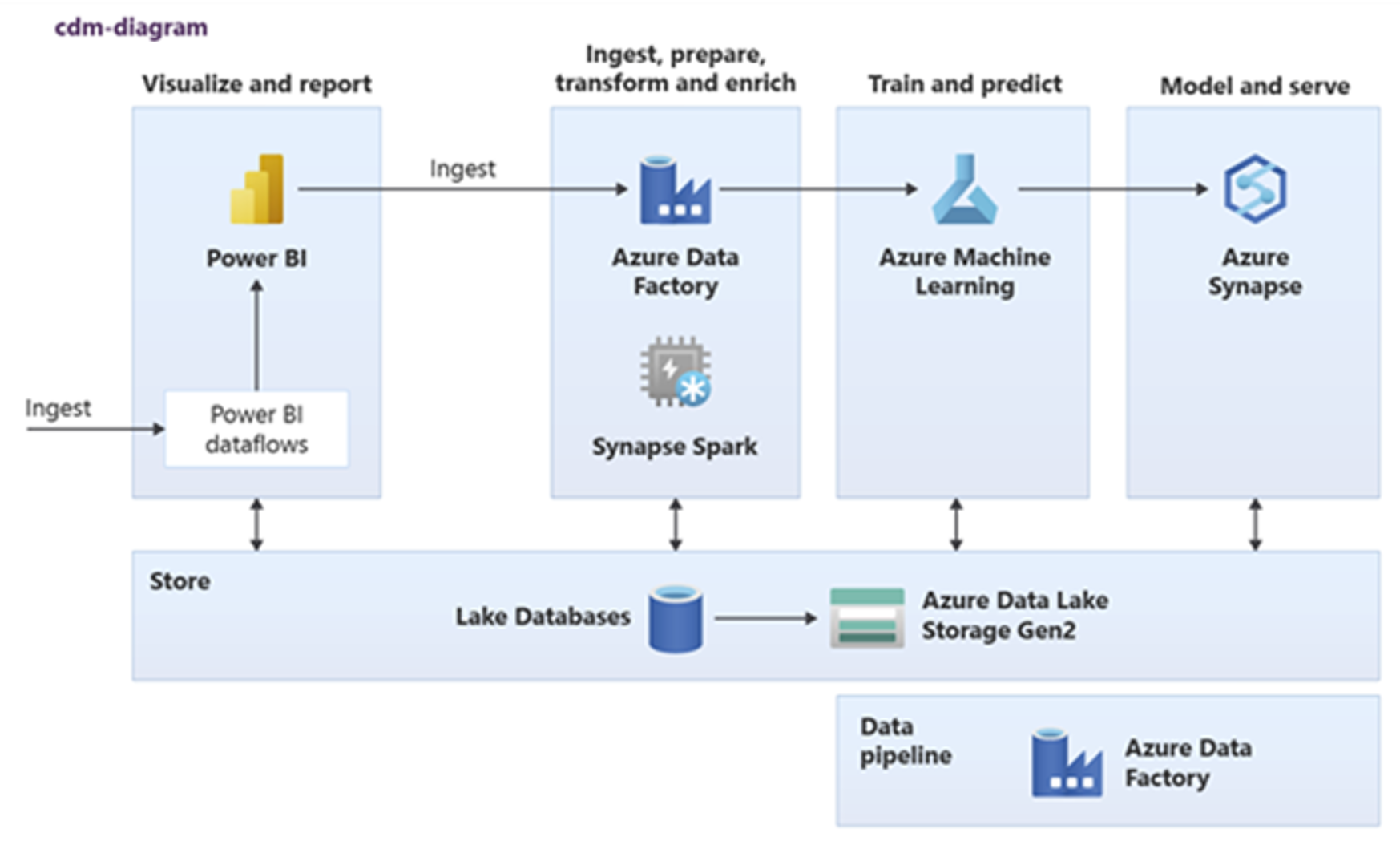
Tip
Integrate data to create lake database logical entities in shared storage to maximize the reuse of common data assets.
Integration with Microsoft data science technologies on Azure
Another key objective when modernizing a data warehouse is to produce insights for competitive advantage. You can produce insights by integrating your migrated data warehouse with Microsoft and third-party data science technologies in Azure. The following sections describe machine learning and data science technologies offered by Microsoft to see how they can be used with Azure Synapse in a modern data warehouse environment.
Microsoft technologies for data science on Azure
Microsoft offers a range of technologies that support advance analysis. With these technologies, you can build predictive analytical models using machine learning or analyze unstructured data using deep learning. The technologies include:
Azure Machine Learning studio
Azure Machine Learning
Azure Synapse Spark pool notebooks
ML.NET (API, CLI, or ML.NET Model Builder for Visual Studio)
.NET for Apache Spark
Data scientists can use RStudio (R) and Jupyter Notebooks (Python) to develop analytical models, or they can use frameworks such as Keras or TensorFlow.
Tip
Develop machine learning models using a no/low-code approach or by using programming languages like Python, R, and .NET.
Azure Machine Learning studio
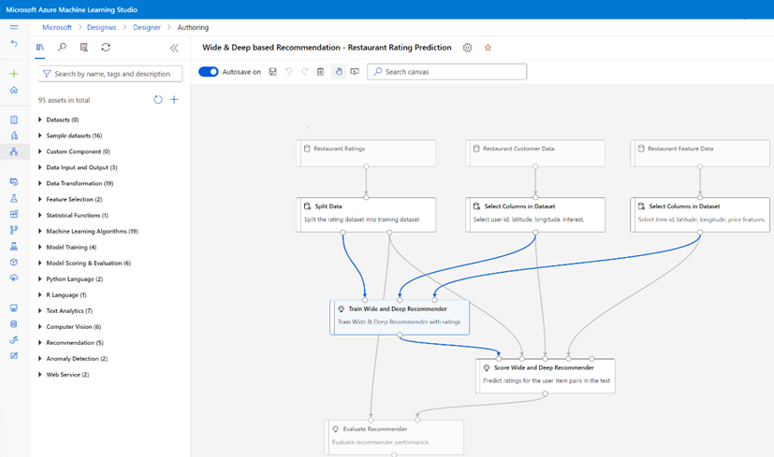
Azure Machine Learning studio is a fully managed cloud service that lets you build, deploy, and share predictive analytics using a drag-and-drop, web-based UI. The following screenshot shows the Azure Machine Learning studio UI.
Azure Machine Learning
Azure Machine Learning provides an SDK and services for Python that supports can help you quickly prepare data and also train and deploy machine learning models. You can use Azure Machine Learning in Azure notebooks using Jupyter Notebook, with open-source frameworks, such as PyTorch, TensorFlow, scikit-learn, or Spark MLlib—the machine learning library for Spark.
Tip
Azure Machine Learning provides an SDK for developing machine learning models using several open-source frameworks.
You can also use Azure Machine Learning to build machine learning pipelines that manage end-to-end workflow, programmatically scale in the cloud, and deploy models both to the cloud and the edge. Azure Machine Learning contains workspaces, which are logical spaces that you can programmatically or manually create in the Azure portal. These workspaces keep compute targets, experiments, data stores, trained machine learning models, Docker images, and deployed services all in one place to enable teams to work together. You can use Azure Machine Learning in Visual Studio with the Visual Studio for AI extension.
Tip
Organize and manage related data stores, experiments, trained models, Docker images, and deployed services in workspaces.
Azure Synapse Spark pool notebooks
An Azure Synapse Spark pool notebook is an Azure-optimized Apache Spark service. With Azure Synapse Spark pool notebooks:
Data engineers can build and run scalable data preparation jobs using Data Factory.
Data scientists can build and run machine learning models at scale using notebooks written in languages such as Scala, R, Python, Java, and SQL to visualize results.
Tip
Azure Synapse Spark is a dynamically scalable Spark as a service offering from Microsoft, Spark offers scalable execution of data preparation, model development, and deployed model execution.
Jobs running in Azure Synapse Spark pool notebooks can retrieve, process, and analyze data at scale from Azure Blob Storage, Data Lake Storage, Azure Synapse, HDInsight, and streaming data services such as Apache Kafka.
Tip
Azure Synapse Spark can access data in a range of Microsoft analytical ecosystem data stores on Azure.
Azure Synapse Spark pool notebooks support autoscaling and auto-termination to reduce total cost of ownership (TCO). Data scientists can use the MLflow open-source framework to manage the machine learning lifecycle.
ML.NET
ML.NET is an open-source, cross-platform machine learning framework for Windows, Linux, macOS. Microsoft created ML.NET so that .NET developers can use existing tools, such as ML.NET Model Builder for Visual Studio, to develop custom machine learning models and integrate them into their .NET applications.
Tip
Microsoft has extended its machine learning capability to .NET developers.
.NET for Apache Spark
.NET for Apache Spark extends Spark support beyond R, Scala, Python, and Java to .NET and aims to make Spark accessible to .NET developers across all Spark APIs. While .NET for Apache Spark is currently only available on Apache Spark in HDInsight, Microsoft intends to make .NET for Apache Spark available on Azure Synapse Spark pool notebooks.
Use Azure Synapse Analytics with your data warehouse
To combine machine learning models with Azure Synapse, you can:
Use machine learning models in batch or in real-time on streaming data to produce new insights, and add those insights to what you already know in Azure Synapse.
Use the data in Azure Synapse to develop and train new predictive models for deployment elsewhere, such as in other applications.
Deploy machine learning models, including models trained elsewhere, in Azure Synapse to analyze data in your data warehouse and drive new business value.
Tip
Train, test, evaluate, and run machine learning models at scale on Azure Synapse Spark pool notebooks by using data in Azure Synapse.
Data scientists can use RStudio, Jupyter Notebooks, and Azure Synapse Spark pool notebooks together with Azure Machine Learning to develop machine learning models that run at scale on Azure Synapse Spark pool notebooks using data in Azure Synapse. For example, data scientists could create an unsupervised model to segment customers to drive different marketing campaigns. Use supervised machine learning to train a model to predict a specific outcome, such as to predict a customer's propensity to churn, or to recommend the next best offer for a customer to try to increase their value. The following diagram shows how Azure Synapse can be used for Azure Machine Learning.
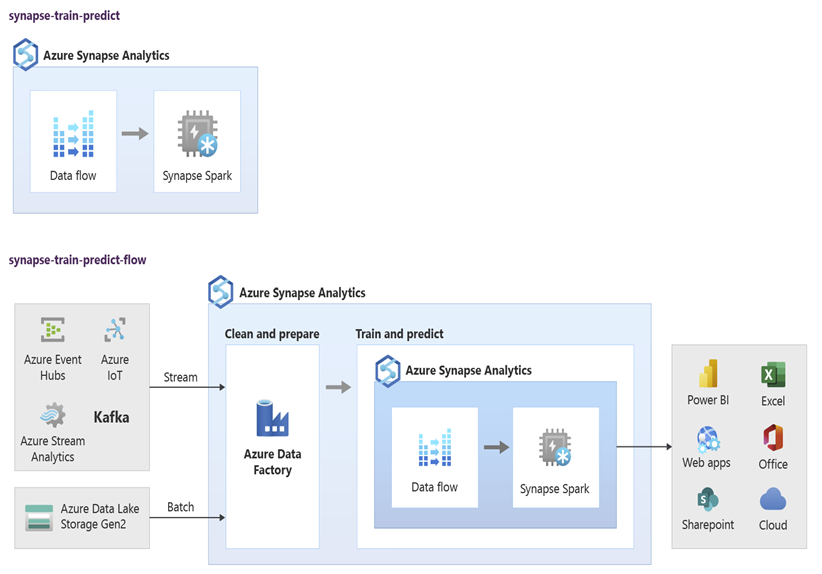
In another scenario, you can ingest social network or review website data into Data Lake Storage, then prepare and analyze the data at scale on an Azure Synapse Spark pool notebook using natural language processing to score customer sentiment about your products or brand. You can then add those scores to your data warehouse. By using big data analytics to understand the effect of negative sentiment on product sales, you add to what you already know in your data warehouse.
Tip
Produce new insights using machine learning on Azure in batch or in real-time and add to what you know in your data warehouse.
Integrate live streaming data into Azure Synapse Analytics
When analyzing data in a modern data warehouse, you must be able to analyze streaming data in real-time and join it with historical data in your data warehouse. An example is combining IoT data with product or asset data.
Tip
Integrate your data warehouse with streaming data from IoT devices or clickstreams.
Once you've successfully migrated your data warehouse to Azure Synapse, you can introduce live streaming data integration as part of a data warehouse modernization exercise by taking advantage of the extra functionality in Azure Synapse. To do so, ingest streaming data via Event Hubs, other technologies like Apache Kafka, or potentially your existing ETL tool if it supports the streaming data sources. Store the data in Data Lake Storage. Then, create an external table in Azure Synapse using PolyBase and point it at the data being streamed into Data Lake Storage so that your data warehouse now contains new tables that provide access to the real-time streaming data. Query the external table as if the data was in the data warehouse by using standard T-SQL from any BI tool that has access to Azure Synapse. You can also join the streaming data to other tables with historical data to create views that join live streaming data to historical data to make it easier for business users to access the data.
Tip
Ingest streaming data into Data Lake Storage from Event Hubs or Apache Kafka, and access the data from Azure Synapse using PolyBase external tables.
In the following diagram, a real-time data warehouse on Azure Synapse is integrated with streaming data in Data Lake Storage.
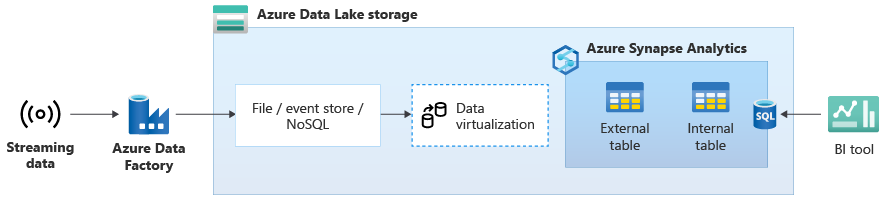
Create a logical data warehouse using PolyBase
With PolyBase, you can create a logical data warehouse to simplify user access to multiple analytical data stores. Many companies have adopted "workload optimized" analytical data stores over the last several years in addition to their data warehouses. The analytical platforms on Azure include:
Data Lake Storage with Azure Synapse Spark pool notebook (Spark as a service), for big data analytics.
HDInsight (Hadoop as a service), also for big data analytics.
NoSQL Graph databases for graph analysis, which could be done in Azure Cosmos DB.
Event Hubs and Stream Analytics, for real-time analysis of data in motion.
You might have non-Microsoft equivalents of these platforms, or a master data management (MDM) system that needs to be accessed for consistent trusted data on customers, suppliers, products, assets, and more.
Tip
PolyBase simplifies access to multiple underlying analytical data stores on Azure for ease of access by business users.
Those analytical platforms emerged because of the explosion of new data sources inside and outside the enterprise and the demand by business users to capture and analyze the new data. The new data sources include:
Machine generated data, such as IoT sensor data and clickstream data.
Human generated data, such as social network data, review web site data, customer inbound email, images, and video.
Other external data, such as open government data and weather data.
This new data goes beyond the structured transaction data and main data sources that typically feed data warehouses and often includes:
- Semi-structured data like JSON, XML, or Avro.
- Unstructured data like text, voice, image, or video, which is more complex to process and analyze.
- High volume data, high velocity data, or both.
As a result, new more complex kinds of analysis have emerged, such as natural language processing, graph analysis, deep learning, streaming analytics, or complex analysis of large volumes of structured data. These kinds of analysis typically don't happen in a data warehouse, so it's not surprising to see different analytical platforms for different types of analytical workloads, as shown in the following diagram.
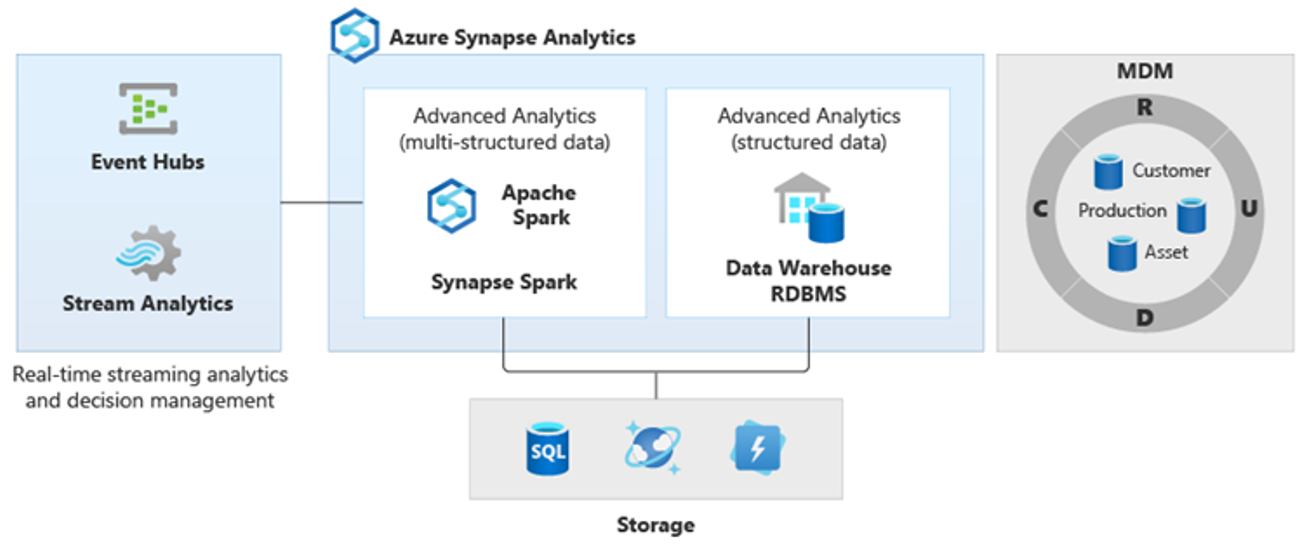
Tip
The ability to make data in multiple analytical data stores look like it's all in one system and join it to Azure Synapse is known as a logical data warehouse architecture.
Because these platforms produce new insights, it's normal to see a requirement to combine the new insights with what you already know in Azure Synapse, which is what PolyBase makes possible.
By using PolyBase data virtualization inside Azure Synapse, you can implement a logical data warehouse where data in Azure Synapse is joined to data in other Azure and on-premises analytical data stores like HDInsight, Azure Cosmos DB, or streaming data flowing into Data Lake Storage from Stream Analytics or Event Hubs. This approach lowers the complexity for users, who access external tables in Azure Synapse and don't need to know that the data they're accessing is stored in multiple underlying analytical systems. The following diagram shows a complex data warehouse structure accessed through comparatively simpler yet still powerful UI methods.
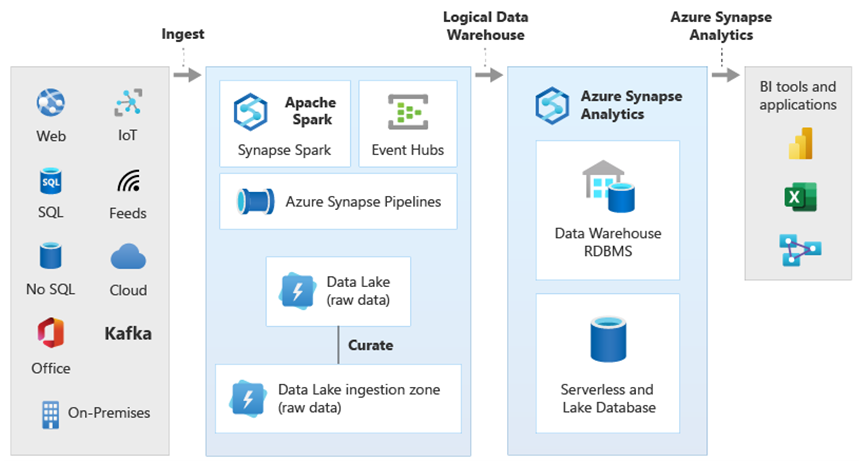
The diagram shows how other technologies in the Microsoft analytical ecosystem can be combined with the capability of the logical data warehouse architecture in Azure Synapse. For example, you can ingest data into Data Lake Storage and curate the data using Data Factory to create trusted data products that represent Microsoft lake database logical data entities. This trusted, commonly understood data can then be consumed and reused in different analytical environments such as Azure Synapse, Azure Synapse Spark pool notebooks, or Azure Cosmos DB. All insights produced in these environments are accessible via a logical data warehouse data virtualization layer made possible by PolyBase.
Tip
A logical data warehouse architecture simplifies business user access to data and adds new value to what you already know in your data warehouse.
Conclusions
After you migrate your data warehouse to Azure Synapse, you can take advantage of other technologies in the Microsoft analytical ecosystem. By doing so, you not only modernize your data warehouse, but bring insights produced in other Azure analytical data stores into an integrated analytical architecture.
You can broaden your ETL processing to ingest data of any type into Data Lake Storage, and then prepare and integrate the data at scale using Data Factory to produce trusted, commonly understood data assets. Those assets can be consumed by your data warehouse and accessed by data scientists and other applications. You can build real-time and batch oriented analytical pipelines and create machine learning models to run in batch, in real-time on streaming data, and on-demand as a service.
You can use PolyBase or COPY INTO to go beyond your data warehouse to simplify access to insights from multiple underlying analytical platforms on Azure. To do so, create holistic integrated views in a logical data warehouse that support access to streaming, big data, and traditional data warehouse insights from BI tools and applications.
By migrating your data warehouse to Azure Synapse, you can take advantage of the rich Microsoft analytical ecosystem running on Azure to drive new value in your business.
Next steps
To learn about migrating to a dedicated SQL pool, see Migrate a data warehouse to a dedicated SQL pool in Azure Synapse Analytics.