Reprotect from Azure to Azure VMware Solution private cloud
After failover of Azure VMware Solution VMs to Azure, the first step in failing back to your Azure VMware Solution private cloud is to reprotect the Azure VMs that were created during failover. This article describes how to do this.
Before you begin
- Follow the steps in this article to prepare for reprotection and failback, including setting up a process server in Azure, and an Azure VMware Solution private cloud master target server, and configuring a site-to-site VPN, or ExpressRoute private peering, for failback.
- Make sure that the Azure VMware Solution private cloud configuration server is running and connected to Azure. During failback, the VM must exist in the configuration server database. Otherwise, failback is unsuccessful.
- Delete any snapshots on the Azure VMware Solution private cloud master target server. Reprotection won't work if there are snapshots. The snapshots on the VM are automatically merged during a reprotect job.
- If you're reprotecting VMs gathered into a replication group for multi-VM consistency, make sure they all have the same operating system (Windows or Linux) and make sure that the master target server you deploy has the same type of operating system. All VMs in a replication group must use the same master target server.
- Open the required ports for failback.
- Ensure that the vCenter Server is connected before failback. Otherwise, disconnecting disks and attaching them back to the virtual machine fails.
- If a vCenter Server manages the VMs to which you'll fail back, make sure that you have the required permissions. If you perform a read-only user vCenter Server discovery and protect virtual machines, protection succeeds, and failover works. However, during reprotection, failover is unsuccessful because the datastores can't be discovered, and aren't listed during reprotection. To resolve this problem, you can update the vCenter Server credentials with an appropriate account/permissions, and then retry the job.
- If you used a template to create your virtual machines, ensure that each VM has its own UUID for the disks. If the Azure VMware Solution VM UUID clashes with the UUID of the master target server because both were created from the same template, reprotection fails. Deploy from a different template.
- If you're failing back to an alternate vCenter Server, make sure that the new vCenter Server and the master target server are discovered. Typically if they're not the datastores aren't accessible, or aren't visible in Reprotect.
- Verify the following scenarios in which you can't fail back:
- If you're using either the ESXi 5.5 free edition or the vSphere 6 Hypervisor free edition. Upgrade to a different version.
- If you have a Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1 physical server.
- VMware vSphere VMs can't fail back to Hyper-V.
- VMs that have been migrated.
- A VM that's been moved to another resource group.
- A replica Azure VM that's been deleted.
- A replica Azure VM that isn't protected.
- Review the types of failback you can use - original location recovery and alternate location recovery.
Enable reprotection
Enable replication. You can reprotect specific VMs, or a recovery plan:
- If you reprotect a recovery plan, you must provide the values for every protected machine.
- If VMs belong to a replication group for multi-VM consistency, they can only be reprotected using a recovery plan. VMs in a replication group must use the same master target server
Note
The amount of data sent from Azure to erstwhile source during reprotect, can be anything between 0 bytes and sum of disk size for all protected machines, and can't be calculated.
Before you start
- After a VM boots in Azure after failover, it takes some time for the agent to register back to the configuration server (up to 15 minutes). During this time, you won't be able to reprotect and an error message indicates that the agent isn't installed. If this happens, wait for a few minutes, and then reprotect.
- If you want to fail back the Azure VM to an existing Azure VMware Solution VM, mount the VM datastores with read/write access on the master target server's ESXi host.
- If you want to fail back to an alternate location, for example if the Azure VMware Solution VM doesn't exist, select the retention drive and datastore that are configured for the master target server. When you fail back to the Azure VMware Solution private cloud, the virtual machines in the failback protection plan use the same datastore as the master target server. A new VM is then created in vCenter.
Enable reprotection as follows:
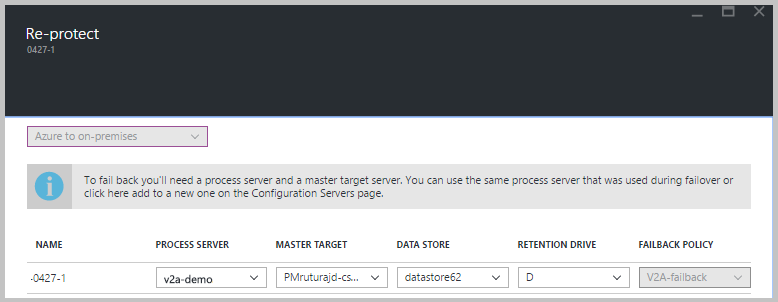
Select Vault > Replicated items. Right-click the virtual machine that failed over, and then select Re-Protect. Or, from the command buttons, select the machine, and then select Re-Protect.
Verify that the Azure to On-premises direction of protection is selected.
In Master Target Server and Process Server, select the on-premises master target server and the process server.
For Datastore, select the datastore to which you want to recover the disks in Azure VMware Solution. This option is used when the Azure VMware Solution VM is deleted, and you need to create new disks. This option is ignored if the disks already exist. You still need to specify a value.
Select the retention drive.
The failback policy is automatically selected.
Select OK to begin reprotection.
A job begins to replicate the Azure VM to the Azure VMware Solution private cloud. You can track the progress on the Jobs tab.
- When the reprotection succeeds, the VM enters a protected state.
- The Azure VMware Solution VM is turned off during reprotection. This helps ensure data consistency during replication.
- Don't turn on the Azure VMware Solution VM after reprotection finishes.
Next steps
- If you encounter any issues, review the troubleshooting article.
- After the Azure VMs are protected, you can run a failback. Failback shuts down the Azure VM and boots the Azure VMware Solution VM. Expect some downtime for the application, and choose a failback time accordingly.