Set up a network for Azure Monitor for SAP solutions
In this how-to guide, you learn how to configure an Azure virtual network so that you can deploy Azure Monitor for SAP solutions. You learn how to:
- Create a new subnet for use with Azure Functions.
- Set up outbound internet access to the SAP environment that you want to monitor.
Create a new subnet
Azure Functions is the data collection engine for Azure Monitor for SAP solutions. You must create a new subnet to host Azure Functions.
Create a new subnet with an IPv4/25 block or larger because you need at least 100 IP addresses for monitoring resources. After you successfully create a subnet, verify the following steps to ensure connectivity between the Azure Monitor for SAP solutions subnet and your SAP environment subnet:
- If both the subnets are in different virtual networks, do a virtual network peering between the virtual networks.
- If the subnets are associated with user-defined routes, make sure the routes are configured to allow traffic between the subnets.
- If the SAP environment subnets have network security group (NSG) rules, make sure the rules are configured to allow inbound traffic from the Azure Monitor for SAP solutions subnet.
- If you have a firewall in your SAP environment, make sure the firewall is configured to allow inbound traffic from the Azure Monitor for SAP solutions subnet.
For more information, see how to integrate your app with an Azure virtual network.
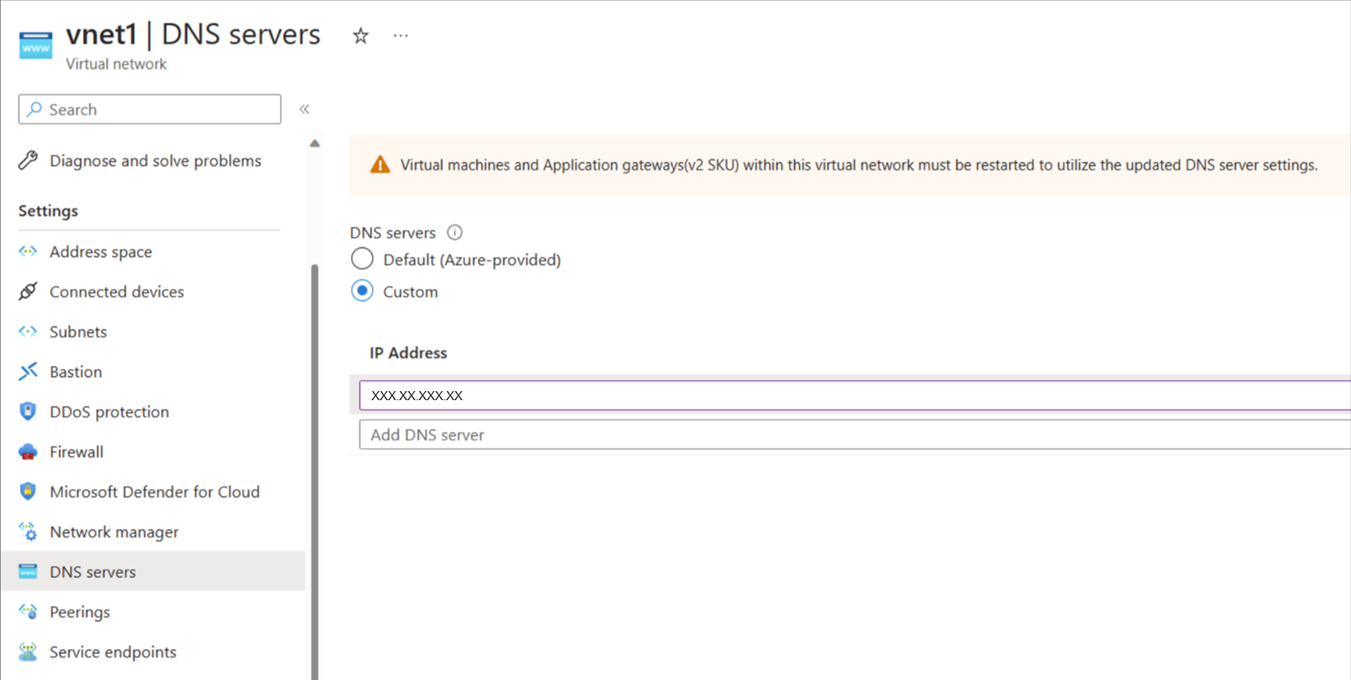
Use Custom DNS for your virtual network
This section only applies if you're using Custom DNS for your virtual network. Add the IP address 168.63.129.16, which points to Azure DNS Server. This arrangement resolves the storage account and other resource URLs that are required for proper functioning of Azure Monitor for SAP solutions.
Configure outbound internet access
In many use cases, you might choose to restrict or block outbound internet access to your SAP network environment. However, Azure Monitor for SAP solutions requires network connectivity between the subnet that you configured and the systems that you want to monitor. Before you deploy an Azure Monitor for SAP solutions resource, you must configure outbound internet access or the deployment fails.
There are multiple methods to address restricted or blocked outbound internet access. Choose the method that works best for your use case:
Use Route All
Route All is a standard feature of virtual network integration in Azure Functions, which is deployed as part of Azure Monitor for SAP solutions. Enabling or disabling this setting only affects traffic from Azure Functions. This setting doesn't affect any other incoming or outgoing traffic within your virtual network.
You can configure the Route All setting when you create an Azure Monitor for SAP solutions resource through the Azure portal. If your SAP environment doesn't allow outbound internet access, disable Route All. If your SAP environment allows outbound internet access, keep the default setting to enable Route All.
You can only use this option before you deploy an Azure Monitor for SAP solutions resource. It's not possible to change the Route All setting after you create the Azure Monitor for SAP solutions resource.
Allow inbound traffic
If you have NSG or User-Defined Route rules that block inbound traffic to your SAP environment, you must modify the rules to allow the inbound traffic. Also, depending on the types of providers you're trying to add, you must unblock a few ports, as shown in the following table.
| Provider type | Port number |
|---|---|
| Prometheus OS | 9100 |
| Prometheus HA Cluster on RHEL | 44322 |
| Prometheus HA Cluster on SUSE | 9100 |
| SQL Server | 1433 (can be different if you aren't using the default port) |
| DB2 Server | 25000 (can be different if you aren't using the default port) |
| SAP HANA DB | 3<instance number>13, 3<instance number>15 |
| SAP NetWeaver | 5<instance number>13, 5<instance number>15 |
Use service tags
If you use NSGs, you can create Azure Monitor for SAP solutions-related virtual network service tags to allow appropriate traffic flow for your deployment. A service tag represents a group of IP address prefixes from a specific Azure service.
You can use this option after you deploy an Azure Monitor for SAP solutions resource.
Find the subnet associated with your Azure Monitor for SAP solutions managed resource group:
- Sign in to the Azure portal.
- Search for or select the Azure Monitor for SAP solutions service.
- On the Overview page for Azure Monitor for SAP solutions, select your Azure Monitor for SAP solutions resource.
- On the managed resource group's page, select the Azure Functions app.
- On the app's page, select the Networking tab. Then select VNET Integration.
- Review and note the subnet details. You need the subnet's IP address to create rules in the next step.
Select the subnet's name to find the associated NSG. Note the NSG's information.
Set new NSG rules for outbound network traffic:
- Go to the NSG resource in the Azure portal.
- On the NSG menu, under Settings, select Outbound security rules.
- Select Add to add the following new rules:
Priority Name Port Protocol Source Destination Action 450 allow_monitor 443 TCP Azure Functions subnet Azure Monitor Allow 501 allow_keyVault 443 TCP Azure Functions subnet Azure Key Vault Allow 550 allow_storage 443 TCP Azure Functions subnet Storage Allow 600 allow_azure_controlplane 443 Any Azure Functions subnet Azure Resource Manager Allow 650 allow_ams_to_source_system Any Any Azure Functions subnet Virtual network or comma-separated IP addresses of the source system Allow 660 deny_internet Any Any Any Internet Deny
The Azure Monitor for SAP solution's subnet IP address refers to the IP of the subnet associated with your Azure Monitor for SAP solutions resource. To find the subnet, go to the Azure Monitor for SAP solutions resource in the Azure portal. On the Overview page, review the vNet/subnet value.
For the rules that you create, allow_vnet must have a lower priority than deny_internet. All other rules also need to have a lower priority than allow_vnet. The remaining order of these other rules is interchangeable.