Quickstart: Use GitHub Actions to connect to Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server
APPLIES TO:  Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server
Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server
Get started with GitHub Actions by using a workflow to deploy database updates to Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server.
Prerequisites
You need:
- An Azure account with an active subscription. Create an account for free.
- A GitHub repository with sample data (
data.sql). If you don't have a GitHub account, sign up for free. - An Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server instance.
- Create an instance of Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server.
Workflow file overview
A GitHub Actions workflow is defined by a YAML (.yml) file in the /.github/workflows/ path in your repository. This definition contains the various steps and parameters that make up the workflow.
The file has two sections:
| Section | Tasks |
|---|---|
| Authentication | 1. Generate deployment credentials. |
| Deploy | 1. Deploy the database. |
Generate deployment credentials
To use Azure Login action with OIDC, you need to configure a federated identity credential on a Microsoft Entra application or a user-assigned managed identity.
Option 1: Microsoft Entra application
- Create a Microsoft Entra application with a service principal by Azure portal, Azure CLI, or Azure PowerShell.
- Copy the values for Client ID, Subscription ID, and Directory (tenant) ID to use later in your GitHub Actions workflow.
- Assign an appropriate role to your service principal by Azure portal, Azure CLI, or Azure PowerShell.
- Configure a federated identity credential on a Microsoft Entra application to trust tokens issued by GitHub Actions to your GitHub repository.
Option 2: User-assigned managed identity
- Create a user-assigned managed identity.
- Copy the values for Client ID, Subscription ID, and Directory (tenant) ID to use later in your GitHub Actions workflow.
- Assign an appropriate role to your user-assigned managed identity.
- Configure a federated identity credential on a user-assigned managed identity to trust tokens issued by GitHub Actions to your GitHub repository.
Copy the Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server connection string
In the Azure portal, go to your Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server instance and from the resource menu, under Settings, select Connect. In that page, use the Database name combo box to select the name of the database you want to connect to. Expand the Connect from your app section, and copy ADO.NET connection string, and replace the placeholder value {your_password} with your actual password. The connection string looks similar to this.
Server={servername.postgres.database.azure.com};Database={your_database};Port=5432;User Id={adminusername};Password={your_password};Ssl Mode=Require;
You use the connection string as a GitHub secret.
Configure the GitHub secrets
You need to provide your application's Client ID, Directory (tenant) ID, and Subscription ID to the login action. These values can either be provided directly in the workflow or can be stored in GitHub secrets and referenced in your workflow. Saving the values as GitHub secrets is the more secure option.
In GitHub, go to your repository.
Select Security > Secrets and variables > Actions.

Select New repository secret.
Note
To enhance workflow security in public repositories, use environment secrets instead of repository secrets. If the environment requires approval, a job cannot access environment secrets until one of the required reviewers approves it.
Create secrets for
AZURE_CLIENT_ID,AZURE_TENANT_ID, andAZURE_SUBSCRIPTION_ID. Copy these values from your Microsoft Entra application or user-assigned managed identity for your GitHub secrets:GitHub secret Microsoft Entra application or user-assigned managed identity AZURE_CLIENT_ID Client ID AZURE_SUBSCRIPTION_ID Subscription ID AZURE_TENANT_ID Directory (tenant) ID Note
For security reasons, we recommend using GitHub Secrets rather than passing values directly to the workflow.
Add your workflow
Go to Actions for your GitHub repository.
Select Set up your workflow yourself.
Delete everything after the
on:section of your workflow file. For example, your remaining workflow may look like this.name: CI on: push: branches: [ main ] pull_request: branches: [ main ]Rename your workflow
PostgreSQL for GitHub Actionsand add the checkout and sign in actions. These actions check out your site code and authenticate with Azure using the GitHub secret(s) you created earlier.name: PostgreSQL for GitHub Actions on: push: branches: [ main ] pull_request: branches: [ main ] jobs: build: runs-on: ubuntu-latest steps: - uses: actions/checkout@v1 - uses: azure/login@v2 with: client-id: ${{ secrets.AZURE_CLIENT_ID }} tenant-id: ${{ secrets.AZURE_TENANT_ID }} subscription-id: ${{ secrets.AZURE_SUBSCRIPTION_ID }}Use the Azure PostgreSQL Deploy action to connect to your Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server instance. Replace
POSTGRESQL_SERVER_NAMEwith the name of your server. You should have an Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server data file nameddata.sqlat the root level of your repository.- uses: azure/postgresql@v1 with: connection-string: ${{ secrets.AZURE_POSTGRESQL_CONNECTION_STRING }} server-name: POSTGRESQL_SERVER_NAME plsql-file: './data.sql'Complete your workflow by adding an action to sign out of Azure. Here's the completed workflow. The file appears in the
.github/workflowsfolder of your repository.name: PostgreSQL for GitHub Actions on: push: branches: [ main ] pull_request: branches: [ main ] jobs: build: runs-on: ubuntu-latest steps: - uses: actions/checkout@v1 - uses: azure/login@v2 with: client-id: ${{ secrets.AZURE_CLIENT_ID }} tenant-id: ${{ secrets.AZURE_TENANT_ID }} subscription-id: ${{ secrets.AZURE_SUBSCRIPTION_ID }} - uses: azure/postgresql@v1 with: server-name: POSTGRESQL_SERVER_NAME connection-string: ${{ secrets.AZURE_POSTGRESQL_CONNECTION_STRING }} plsql-file: './data.sql' # Azure logout - name: logout run: | az logout
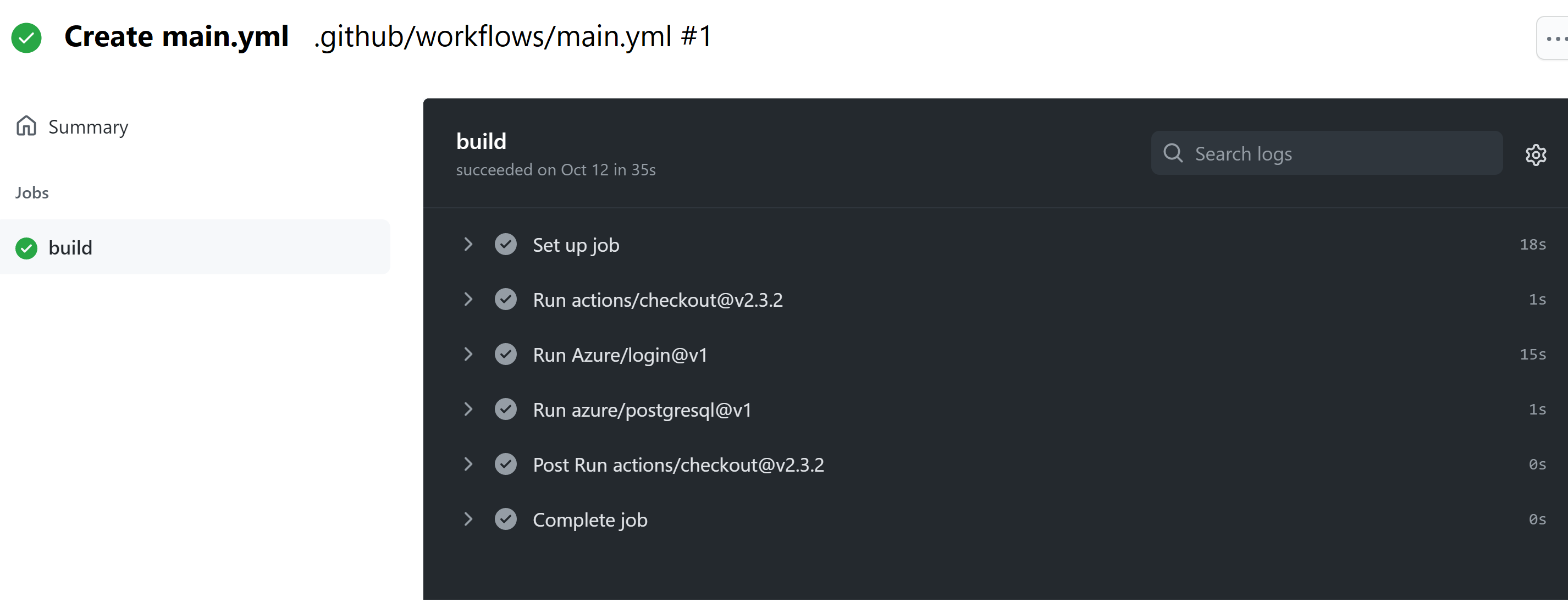
Review your deployment
Go to Actions for your GitHub repository.
Open the first result to see detailed logs of your workflow's run.
Clean up resources
When your Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server database and repository are no longer needed, clean up the resources you deployed by deleting the resource group and your GitHub repository.